Create 3D visualization of variant
Clicking a link provided in the 'Link to 3D Protein Structure' column will show a menu with three options:
- 'Download and Show Structure' will open a 3D view visualizing the consequences of the variant on a protein structure (figure 32.28).
- 'Download and Show All Variants ( x ) on Structure' will open a 3D view visualizing the consequences of x variants on the same protein structure (figure 32.29).
Note 1: Only variants shown in the table will be included in the view (e.g. variants filtered out will be ignored).
Note 2: It is not always possible to visualize variants on the same gene together on the same structure, since many structures in the PDB only cover parts of the whole protein.
Note 3: Even though variants may be possible to visualize together, it does not necessarily mean they occur together on the same protein. For example, in diploid cells, heterozygous variants may not.
- "Help" gives access to this documentation.
|
If you have problems viewing 3D structures, please check your system matches the requirements for 3D viewers. See System requirements. |
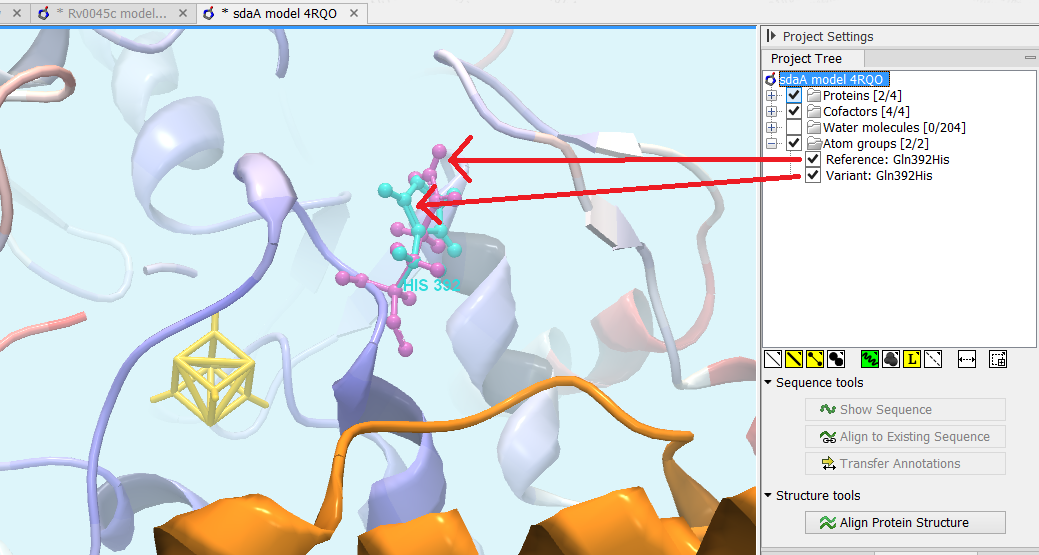
Figure 32.29: Generated 3D view of variant. The reference amino acid is seen in purple and the variant in cyan on top of each other. Only the backbone of protein structures are visualized by default. The modeled protein structure is colored to indicate local model uncertainty - red for flexible and uncertain parts of the structure model and blue for very well defined and accurate parts of the structure model. Other molecules from the PDB file are colored orange or yellow.
The "Download and Show.... " options will do the following:
- Download and import the PDB file containing the protein structure for the variant (found by the 'Link Variants to 3D Protein Structure' tool, see The variant table output).
- Generate biomolecule involving the modeled chain, if the information is available in the PDB file (see Infobox below).
- Create an alignment between the reference protein sequence for the gene impacted by the variant (the query sequence) and the sequence from the protein structure (the template structure).
- Create a model structure for the reference by mapping it onto the template structure based on the sequence alignment (see How a model structure is created).
- Create a model structure with variant(s) by mapping the protein sequence with the variant consequences onto the reference structure model (see How a model structure is created).
- Open a 3D view (a Molecule Project) with the variant structure model shown in backbone representation. The model is colored by temperature (see figure 32.29), to indicate local model uncertainty (see Protein coloring to visualize local structural uncertainties). The consequence(s) of the variant(s) are high-lighted by showing involved amino acids in ball n' sticks representation with the reference colored purple and the variant cyan. Other molecules from the PDB file are shown in orange or yellow coloring (figure 32.29).
From the Project Tree in the Side Panel of the Molecule Project, the category 'Atom groups' contains two entries for each variant shown on the structure - one entry for the reference and one for the variant (figure 32.29). The atom groups contain the visualization of the variant consequence on structure. For variants resulting in amino acid replacements, the affected amino acid is visualized. For variants resulting in amino acid insertions or deletions, the amino acids on each side of the deletion/insertion are visualized.
The template structure is also available from the Proteins category in the Project Tree, but hidden in the initial view. The initial view settings are saved on the Molecule Project as "Initial visualization", and can always be reapplied from the View Settings menu (![]() ) found in the bottom right corner of the Molecule Project (see Side Panel view settings).
) found in the bottom right corner of the Molecule Project (see Side Panel view settings).
Tip: Double-click an entry in the Project Tree to zoom the 3D view to the atoms.
You can save the 3D view (Molecule Project) in the Navigation Area for later inspection and analysis. Read more about how to customize visualization of molecules in Customizing the visualization.
|
Protein structures imported from a PDB file show the tertiary structure of proteins, but not necessarily the biologically relevant form (the quaternary structure). Oftentimes, several copies of a protein chain need to arrange in a multi-subunit complex to form a functioning biomolecule. In some PDB files several copies of a biomolecule are present and in others only one chain from a multi-subunit complex is present. In many cases, PDB files have information about how the molecule structures in the file can form biomolecules. In CLC Genomics Workbench variants are therefore shown in a protein structure context representing a functioning biomolecule, if this information is available in the selected template PDB file. |
