K-mer Based Tree Construction
K-mer Based Tree Construction is a distance-based method that can create trees based on unaligned sequences. K-mers are used to compute distance matrices for distance-based phylogenetic reconstruction methods such as Neighbor Joining and UPGMA. This method is less precise than Create Tree, but is also less resource-intensive and does not require an alignment to be created first. This makes it suitable for creating trees based on larger numbers of long sequences. It is especially useful for whole genome phylogenetic reconstruction for closely related genomes, e.g., genomes with small differences relative to one anotherand few or no structural variations.
To launch K-mer Based Tree Construction, go to:
Tools | Classical Sequence Analysis (![]() ) | Alignments and Trees (
) | Alignments and Trees (![]() ) | K-mer Based Tree Construction (
) | K-mer Based Tree Construction (![]() )
)
This tool accepts individual sequences and sequence lists as input.
In the Tree Construction launch wizard step, select the construction method to use, the k-mer length, and a distance measure (figure 25.1):
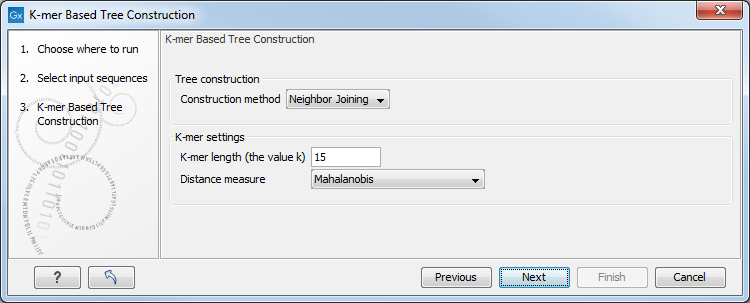
Figure 25.1: The Tree Construction launch wizard step.
- Tree construction
- Construction method. The distance-based method to use for tree construction, Neighbor Joining or UPGMA:
- UPGMA. Assumes constant rate of evolution.
- Neighbor Joining. Well suited for trees with varying rates of evolution.
- Construction method. The distance-based method to use for tree construction, Neighbor Joining or UPGMA:
- K-mer settings
- K-mer length (the value k). A k-mer length between 3 and 50.
- Distance measure. The distance measure used to compute the distances between two counts of k-mers. See K-mer based distance estimation for further details on the three options.
- Euclidan squared.
- Fractional common K-mer count.
- Mahalanobis.
