Find and Model Structure
Find and Model Structure is used to find suitable protein structures for representing the peptide sequence that is provided as input. The tool produces a table of results, from which structures can be downloaded and opened, or they can be used as a template to create a structure model (homology model) of the input sequence.
|
Note: This analysis involves a BLAST search against a database of 3D protein structures. Download this database by running the Download 3D Protein Structure Database tool. |
Running Find and Model Structure
To run Find and Model Structure, go to:
Tools | Classical Sequence Analysis (![]() ) | General Sequence Analysis (
) | General Sequence Analysis (![]() ) | Find and Model Structure (
) | Find and Model Structure (![]() )
)
The steps carried out during the analysis are described later in this section.
The Find and Model Structure output table
Find and Model Structure produces a table that lists the identifiers of suitable protein structures for representing the peptide sequence provided as input. Click an identifier in the "Available Structures" column to open a menu with options to download and open the structure or to download the structure and use it as the template for creating a homology model (figure 20.12). These options are described in detail in Create structure model.
The other columns in the table contain additional information about the database hits including their rank, described further below.
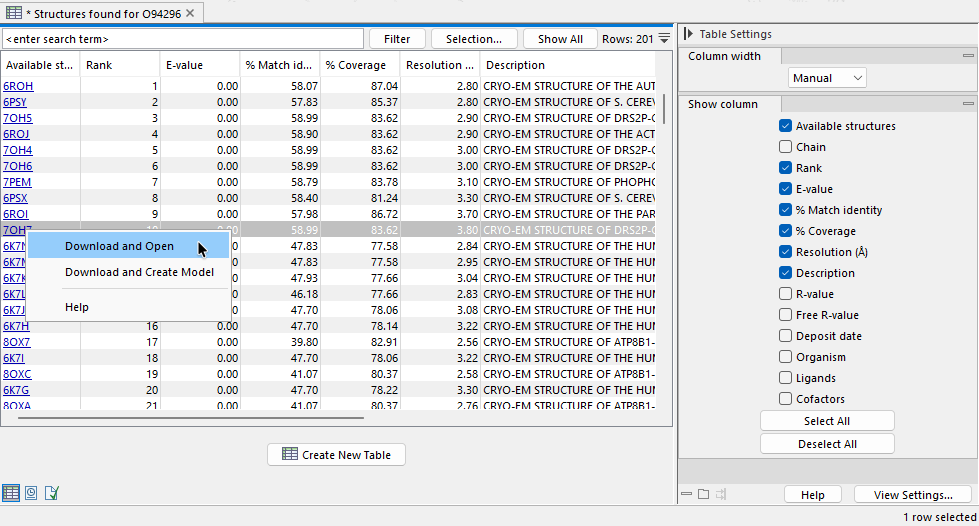
Figure 20.12: Each structure in the results table can be downloaded and opened, or downloaded and used as a template to create a homology model.
How Find and Model Structure works
A Find and Model Structure analysis involves three steps:
- A BLAST search is run. A local BLAST search is run against a 3D protein structure sequence database using the input peptide sequence as the query.
The maximum allowed E-value for hits is 0.0001 and a maximum of 2500 hits are retrieved. Read more about BLAST in Bioinformatics explained: BLAST.
- Low quality hits are filtered away Hits returned by the BLAST search are filtered to remove results where:
- The PDB structure has a resolution lower than 4 Å. Such structures cannot be expected to represent a trustworthy atomistic model.
- The BLAST hit identity, i.e. the percentage of identical amino acids in the aligned region of the query and the database entry, is lower than 20%. Such entries are unlikely to result in accurate models.
- Remaining structures are ranked. A Template quality score is calculated for the structures still under consideration and this value is used to rank the results. The rank is reported in the "Rank" column of the results (figure 20.12).
The calculation of Template quality scores is described in Evaluating the rank of available structures.
Subsections
