BLAST search
BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) [McGinnis and Madden, 2004] is a program for quickly finding regions of similarity between two sequences. It is primarily used to search a sequence database to find database entries with regions of similarity to the sequences used to query the database. How similar regions need to be to be included in the results returned by BLAST is configurable.
Figure 16.1 shows an example of a BLAST result in the CLC Genomics Workbench.
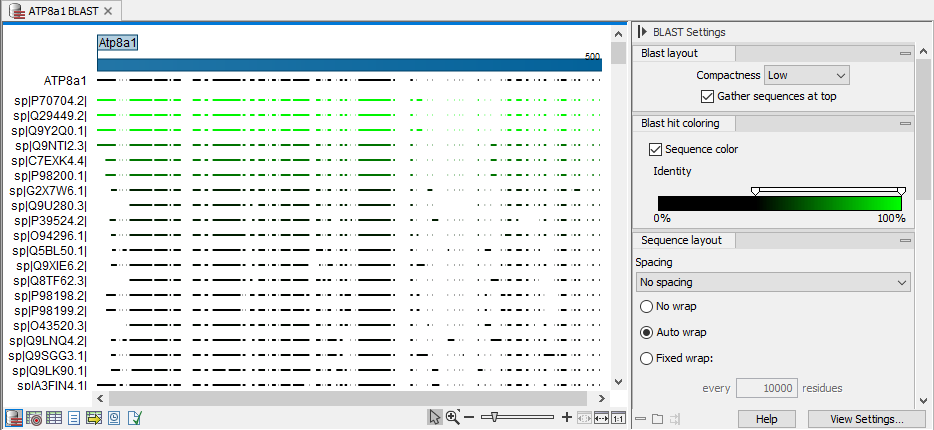
Figure 16.1: A BLAST search result open with linked views open. The graphical representation of the BLAST hits are in the upper area and the HSP table view is open below. Hovering the mouse cursor over a hit in the graphical view reveals a tooltip with additional information about that hit.
A brief introduction to the BLAST method is provided in Bioinformatics explained: BLAST.
Local BLAST searches versus remote searches at the NCBI
Using the CLC Genomics Workbench, BLAST searches can be run on the local machine or submitted to the NCBI to run on their servers to search databases hosted there.
Running BLAST searches on your local machine can have several advantages, such as:
- You can search against your own datasets by using:
- A BLAST database created using data already available in your Workbench.
- Sequence data selected from the Workbench Navigation Area.
- It does not rely on having a stable internet connection.
- You can use longer query sequences.
- It may be faster. This depends on the situation, with factors of particular relevance being that the query sequences are not sent over the external network, and that the search is run using local systems to search a locally held database. Whether this is faster locally or not will depend on the details of the search, details of the systems being used, and on how busy the NCBI servers are.
Using Blast at NCBI can be preferable in other circumstances, for example, when searching large databases, especially those not already available locally, or when relying on restricting searches based on Entrez queries.
Results of searches using the same query sequences, the same database and the same settings are expected to give the same or very similar results, whether run locally or at the NCBI as both rely on NCBI's BLAST+ executables. Small differences may occur, for example if the version of BLAST+, at the NCBI differs from that used by the CLC Genomics Workbench, and changes exist between these versions that affect search results.
Subsections
- BLAST against local data
- BLAST at NCBI
- Output from BLAST searches
- Local BLAST databases
- Manage BLAST databases
- Bioinformatics explained: BLAST
