Fixpoints
Particular regions of an alignment can be forced to be aligned to each other in two ways:
- Add fixpoint annotations to these regions.
- Check the Use fixpoints option when running the Create Alignment tool.
To add a fixpoint (figure 24.6):
- Open the alignment.
- Select the region you want to use as a fixpoint.
- Right-click on the selection.
- Choose Set Alignment Fixpoint Here.
This will add an annotation of type "Alignment fixpoint" with name "Fixpoint" to the alignment.
To add the same fixpoint annotation to multiple sequences in the alignment, right-click the annotation and select Copy Annotation to Other Sequences.... It is also possible to select the same region across multiple sequences in the alignment by holding down the Shift or Ctrl key (![]() on Mac) while clicking on the sequences.
on Mac) while clicking on the sequences.
Regions with fixpoint annotations with the same name are aligned to each other. Where there are multiple fixpoints of the same name on sequences, the first fixpoints on each sequence will be aligned to each other, the second on each sequence will be aligned to each other, and so on.
To adjust the name of a fixpoint annotation:
- Right-click on the fixpoint annotation.
- Choose Edit Annotation... (
 ).
).
- Type the new name in the "Name" field under "Properties".
An example where assigning different names to fixpoints is useful: Given three sequences, A, B, and C, where A and B each have one copy of a domain while sequence C has two copies of the domain, you can force sequence A to align to the first copy of the domain in sequence C and sequence B to align to the second copy of the domain in sequence C by naming the fixpoints accordingly. E.g. if the fixpoints in sequence C were named 'fp1' and 'fp2', the fixpoint in sequence A was named 'fp1' and the fixpoint in sequence B was named 'fp2', then when these sequences are aligned using fixpoints, the fixpoint in sequence A would be aligned to the first copy of the domain in sequence C, while the fixpoint in sequence B would be aligned to the second copy of the domain in sequence C.

Figure 24.6: Select a region and right-click on it to see the option to set a fixpoint.
The result of an alignment using fixpoints is shown in figure 24.7.
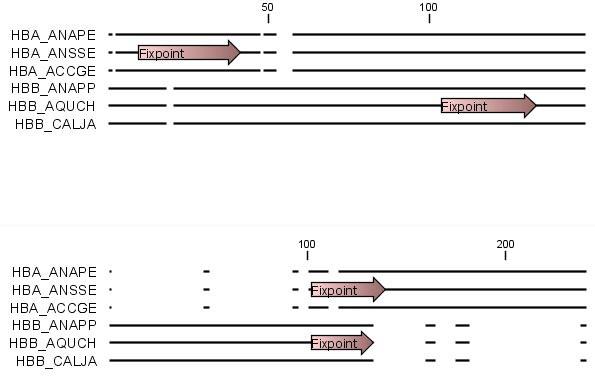
Figure 24.7: Fixpoints have been added to 2 sequences in an alignment, where the first 3 sequences are very similar to each other and the last 3 sequences are very similar to each other (top). After realigning using just these 2 fixpoints (bottom), the alignment now shows clearly the 2 groups of sequences.
