Convert to Tracks
When working with tracks, information from standard sequences and mappings are split into specialized tracks with sequence, annotations and reads. This tool creates a number of tracks based on the input sequences:
Tools | Utility Tools (![]() ) | Tracks (
) | Tracks (![]() ) | Convert Tracks (
) | Convert Tracks (![]() ) | Convert to Tracks (
) | Convert to Tracks (![]() )
)
The following kinds of data can be converted to tracks: nucleotide sequences (![]() ), sequence lists (
), sequence lists (![]() ) and read mappings (
) and read mappings (![]() )/ (
)/ (![]() ). Select the input and click Next to specify which tracks should be created (see figure 27.21).
). Select the input and click Next to specify which tracks should be created (see figure 27.21).
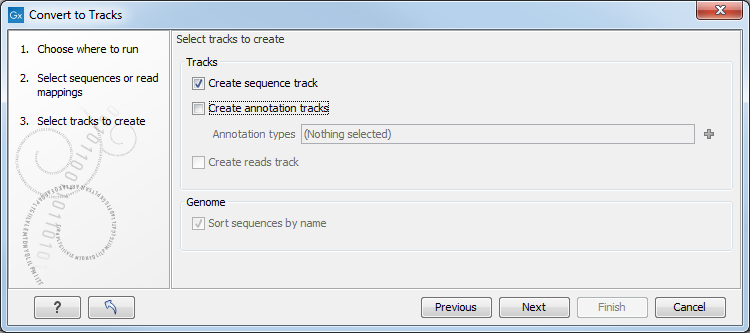
Figure 27.21: Converting data to tracks.
For sequences and sequence lists, you can Create a sequence track (for mappings, this will be the reference sequence) and a number of Annotation tracks. For each annotation type selected, a track will be created. For mappings, a Reads track can be created as well.
At the bottom of the dialog, there is an option to sort sequences by name. This is useful for example to order chromosomes in the menus etc (chr1, chr2, etc). Alphanumerical sorting is used to ensure that the part of the name consisting of numbers is sorted numerically (to avoid e.g. chr10 getting in front of chr2). When working with de novo assemblies with huge numbers of contigs, this option will require additional memory and computation time.
