Mapping paired reads
- Auto-detect paired distances At the bottom of the dialog shown in figure 30.3 you can specify how Paired reads should be handled. You can read more about how paired data is imported and handled in General notes on handling paired data. If the sequence list used as input contains paired reads, this option will automatically be enabled - if it contains single reads, this option will not be applicable.
The CLC Genomics Workbench offers as the default choice to automatically calculate the distance between the pairs. If this is selected, the distance is estimated in the following way:
- A sample of 200,000 reads is extracted randomly from the full data set and mapped against the reference using a very wide distance interval.
- The distribution of distances between the paired reads is analyzed using a method that investigates the shape of the distribution and finds the boundaries of the peak.
- The full sample is mapped using this distance interval.
- The history (
 ) of the result records the distance interval used.
) of the result records the distance interval used.
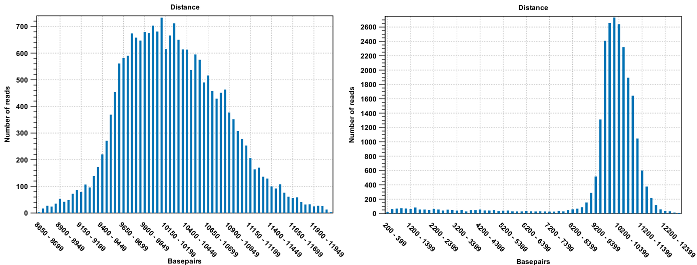
Figure 30.7: To the left: mapping with a narrower distance interval estimated by the workbench. To the right: mapping with a large paired distance interval (note the large right tail of the distribution).
Sometimes the automatic estimation of the distance between the pairs may return a warning "Few reads mapped as pairs so pair distance might not be accurate". This message indicates that fewer than 10.000 paired reads were available for estimation of the paired distance, hence the estimated distance may not be accurate. If in doubt, you may want to disable the option to automatically estimate paired distances and instead manually specify minimum and maximum distances between pairs on the input sequence list.
If the automatic detection of paired distances is not checked, the mapper will use the information about minimum and maximum distance recorded on the input sequence lists (see General notes on handling paired data).
If a large portion of pairs are flagged 'Broken' we recommend the following:
- Inspect the Detailed mapping report to deduce a distance setting interval - and compare this to the estimated distance used by the mapper (found in the mapping history).
- Open the paired reads list and set a broad paired distance in the Elements tab. Then run a new mapping with the 'auto-detect...' OFF. Make sure to have a report produced. Open this report and look at the Paired Distance Distribution graph. This will tell you the distances that your pairs did map with. Use this information to narrow down the distance setting and perhaps run a third mapping using this.
- Another cause of excessive amounts of broken pairs is misspecification of the read pair orientation. This can be changed in the Elements tab of the paired reads list prior to running a mapping.
See Detailed mapping report for further information.
When a paired distance interval is set, the following approach is used for determining the placement of read pairs:
- First, all the optimal placements for the two individual reads are found.
- Then, the allowed placements according to the paired distance interval are found.
- If both reads can be placed independently but no pairs satisfies the paired criteria, the reads are treated as independent and marked as a broken pair.
- If only one pair of placements satisfy the criteria, the reads are placed accordingly and marked as uniquely placed even if either read may have multiple optimal placements.
- If several placements satisfy the paired criteria, the pair is treated as a non-specific match (see Non-specific matches for more information.)
- If one read is uniquely mapped but the other read has several placements that are valid given the distance interval, the mapper chooses the location that is closest to the first read.
