Expression settings
Expression settings are defined in the dialog shown in figure 33.51.
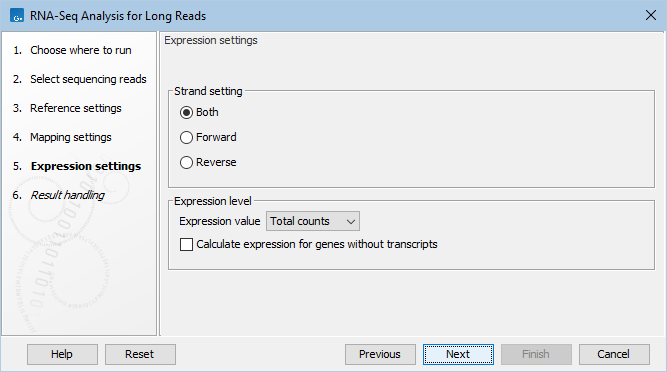
Figure 33.51: Set strand setting and define how expression values should be calculated.
These parameters determine the way expression values are counted.
- Strand setting
- Both. Reads are mapped both in the same and reversed orientation as the transcript from which they originate. This is the default.
- Forward. Reads are mapped in the same orientation as the transcript from which they originate.
- Reverse. Reads are mapped in the reverse orientation as the transcript from which they originate.
- Expression value. This parameter describes how expression per gene or transcript can be defined in different ways on both levels:
- Total counts. When the reference is annotated with genes only, this value is the total number of reads mapped to the gene. For un-annotated references, this value is the total number of reads mapped to the reference sequence. For references annotated with transcripts and genes, the value reported for each gene is the number of reads that map to the exons of that gene. The value reported per transcript is the total number of reads mapped to the transcript.
- Unique counts. This is similar to the above, except only reads that are uniquely mapped are counted.
- TPM. (Transcripts per million). This is computed as
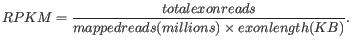 , where the sum is over the RPKM values of all genes/transcripts.
, where the sum is over the RPKM values of all genes/transcripts.
- RPKM. This is a normalized form of the "Total counts" option (see more under Definition of RPKM below.
All values are present in the output. The choice of expression value only affects how Expression Tracks are visualized in the track view but the results will not be affected by this choice as the most appropriate expression value is automatically selected for the analysis being performed. For detection of differential expression this is the "Total counts" value, and for the other tools this is a normalized and transformed version of the "Total counts" as described below.
- Calculate expression for genes without transcripts. For genes without annotated transcripts, the RPKM cannot be calculated since the total length of all exons is needed. By selecting this option, the length of the gene will be used in place of an "exon length". If the option is not checked, there will be no RPKM value reported for those genes.
RPKM, Reads Per Kilobase of exon model per Million mapped reads, is defined in this way [Mortazavi et al., 2008]:
For prokaryotic genes and other non-exon based regions, the calculation is performed in this way:
- Total exon reads.
- This value can be found in the column with header Total exon reads in the expression track. This is the number of reads that have been mapped to exons (either within an exon or at the exon junction). When the reference genome is annotated with gene and transcript annotations, the mRNA track defines the exons, and the total exon reads are the reads mapped to all transcripts for that gene. When only genes are used, each gene in the gene track is considered an exon. When an un-annotated sequence list is used, each sequence is considered an exon.
- Exon length.
- This is the number in the column with the header Exon length in the expression track, divided by 1000. This is calculated as the sum of the lengths of all exons (see definition of exon above). Each exon is included only once in this sum, even if it is present in more annotated transcripts for the gene. Partly overlapping exons will count with their full length, even though they share the same region.
- Mapped reads.
- The sum of all mapped reads as listed in the RNA-Seq analysis report. For more information on how expression is calculated in this case, see above.
