Branching elements
Branching elements control the path that data takes through a workflow.
Branch on Coverage
Branch on Coverage (![]() ) controls the flow of read mappings based on coverage information from a coverage report. The input read mapping flows through the Pass or Fail output channel, depending on whether the coverage level in the report meets the defined condition (figure 14.65).
) controls the flow of read mappings based on coverage information from a coverage report. The input read mapping flows through the Pass or Fail output channel, depending on whether the coverage level in the report meets the defined condition (figure 14.65).
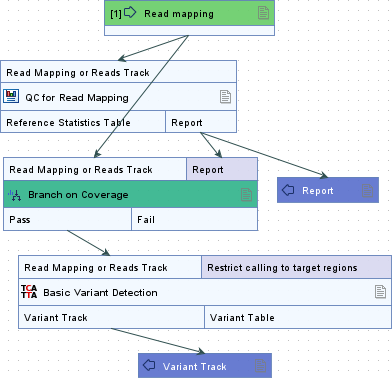
Figure 14.65: Read mappings that meet the condition specified in the Branch on Coverage element, based on coverage information in the associated report, flow through the Pass output channel and continue to the Basic Variant Detection step. Read mappings that do not meet the condition flow through the Fail output channel and are not processed further.
Reports generated by the following tools can be used with Branch on Coverage:
- QC for Targeted Sequencing
- QC for Read Mapping Note that zero coverage regions in these reports are ignored.
The following options can be configured (figure 14.66):
- Type Type of coverage:
Minimum,Median,AverageorMaximum. - Comparison Operator for evaluation:
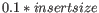 ,
, =or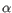 .
.
- Value Value used for comparison.

Figure 14.66: Configuration of a Branch on Coverage element.
Branch on Item Count
Branch on Item Count (![]() ) controls the flow of elements based on their item count or that of another element. The input element flows through the Pass or Fail output channel, depending on whether the item count meets the defined condition (figure 14.67).
) controls the flow of elements based on their item count or that of another element. The input element flows through the Pass or Fail output channel, depending on whether the item count meets the defined condition (figure 14.67).
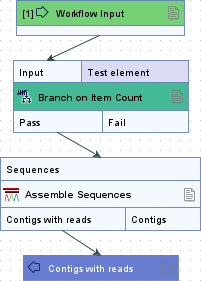
Figure 14.67: Sequences that meet the condition specified in the Branch on Item Count element flow through the Pass output channel and continue to the Assemble Sequences step. Sequences that do not meet the condition flow through the Fail output channel and are not processed further.
The following options can be configured (figure 14.68):
- Test element (Optional) Counts items in this element. If empty, counts items in the input element.
- Comparison Operator for evaluation:
 ,
, =or .
.
- Number of items Value used for comparison.
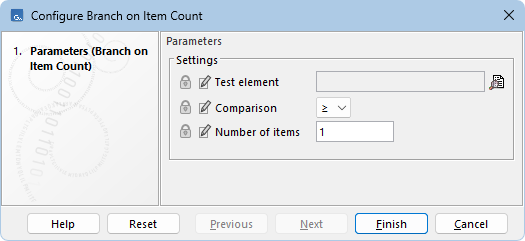
Figure 14.68: Configuration of a Branch on Item Count element.
Many element types containing countable items can be used with Branch on Item Count. Examples of countable items include sequences in a sequence list (![]() ) (
) (![]() ) or an alignment (
) or an alignment (![]() ), reads in a stand-alone read mapping (
), reads in a stand-alone read mapping (![]() ) or reads track (
) or reads track (![]() ), or number of features in an annotation track (
), or number of features in an annotation track (![]() ).
).
Branch on Sample Quality
Branch on Sample Quality (![]() ) controls the flow of data based on quality information from a sample report or a combined report. The input data flows through the Passed, Uncertain, or Failed output channel, depending on whether the report meets certain quality control conditions (figure 14.69).
) controls the flow of data based on quality information from a sample report or a combined report. The input data flows through the Passed, Uncertain, or Failed output channel, depending on whether the report meets certain quality control conditions (figure 14.69).
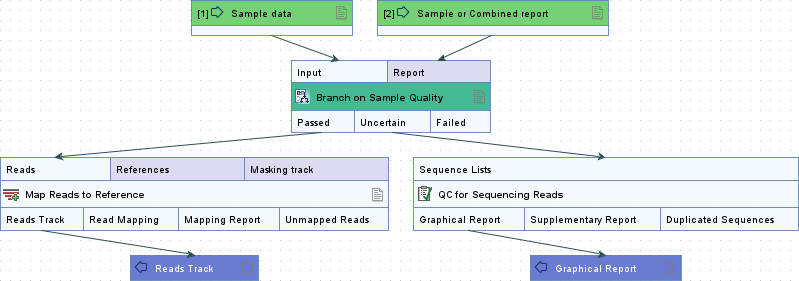
Figure 14.69: Sample data that meet the conditions specified in the "Quality control" subsection of the associated report flow through the Passed output channel and continue to the Map Reads to Reference step. Sample data that do not meet the conditions flow through the Uncertain output channel and continue to the QC for Sequencing Reads step, or through the Failed output channel and are not processed further, depending on which quality conditions are not met.
Reports generated by the following tools can be used with Branch on Sample Quality:
- Create Sample Report Used for configuring quality control conditions, which are added to the "Quality control" subsection of the sample report.
- Combine Reports Combined reports containing multiple sample reports with "Quality control" subsections can also be used as input.
For each quality condition configured in Create Sample Report, a color (red or yellow) can be assigned when the condition is not met. The branching element uses this information as follows:
- If a condition assigned red is not met, the data flows through the Failed channel.
- Otherwise, if a condition assigned yellow is not met, the data flows through the Uncertain channel.
- Otherwise, the data flows through the Passed channel.
If a report does not include the "Quality control" section, the data flows through the Passed channel.
The branching elements Branch on Item Count and Branch on Coverage also control the flow of data through a workflow based on quality measures. However, they do not have the same flexibility: they allow a single quality condition for a single data type, with data flowing into only two downstream paths.
