Secondary peak calling
CLC Genomics Workbench is able to detect secondary peaks - a peak within a peak - to help discover heterozygous mutations. Looking at the height of the peak below the top peak, the CLC Genomics Workbench considers all positions in a sequence, and if a peak is higher than the threshold set by the user, it will be "called".
The peak is called by changing the residue to an ambiguity character and by adding an annotation at this position.
To call secondary peaks:
select sequence(s) | Toolbox in the Menu Bar |
Molecular Biology Tools (![]() ) | Sequencing Data Analysis (
) | Sequencing Data Analysis (![]() )| Call
Secondary Peaks (
)| Call
Secondary Peaks (![]() )
)
This opens a dialog where you can alter your choice of sequences.
When the sequences are selected, click Next.
This opens the dialog displayed in figure 18.16.
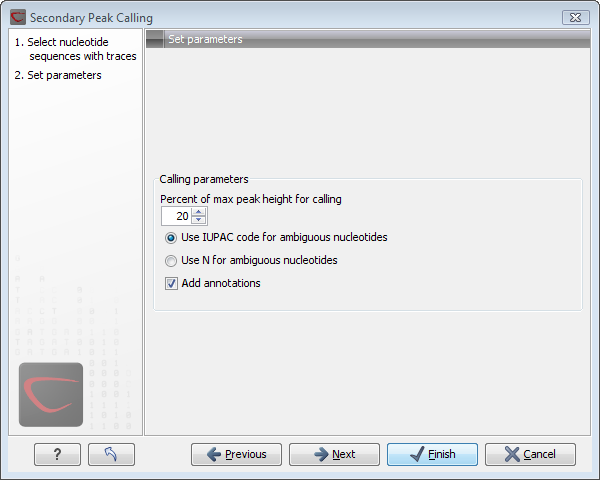
Figure 18.16: Setting parameters secondary peak calling.
The following parameters can be adjusted in the dialog:
- Percent of max peak height for calling. Adjust this value to specify how high the secondary peak must be to be called.
- Use IUPAC code / N for ambiguous nucleotides. When a secondary peak is called, the residue at this position can either be replaced by an N or by a ambiguity character based on the IUPAC codes (see the Appendix).
- Add annotations. In addition to changing the actual sequence, annotations can be added for each base which has been called.
Click Next if you wish to adjust how to handle the results. If not, click Finish. This will start the secondary peak calling. A detailed history entry will be added tothe history specifying all the changes made to the sequence.
