Maximum likelihood phylogeny
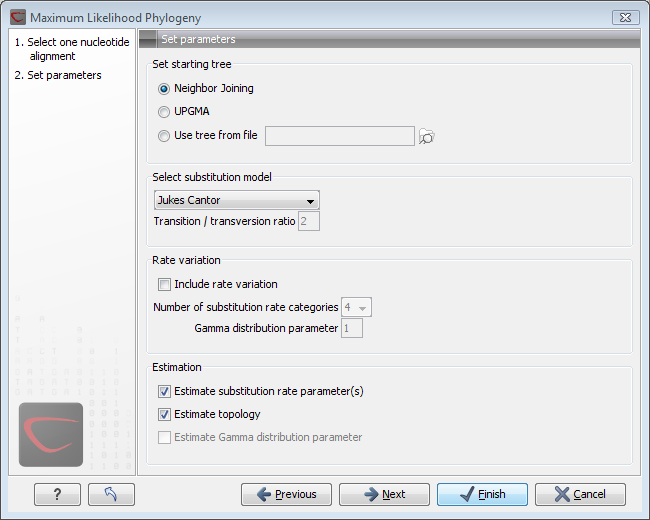
Figure 21.4: Adjusting parameters for ML phylogeny
Figure 21.4 shows the parameters that can be set for the ML phylogenetic tree reconstruction:
- Starting tree: the user is asked to specify a starting tree for the tree reconstruction.
There are three possibilities
- Neighbor joining
- UPGMA
- Use tree from file.
- Select substitution model: CLC Genomics Workbench allows maximum likelihood tree estimation to be performed under the assumption of one of four substitution models: the Jukes Cantor [Jukes and Cantor, 1969], the Kimura 80 [Kimura, 1980], the HKY [Hasegawa et al., 1985] and the GTR (also known as the REV model) [Yang, 1994a] models. All models are time-reversible. The JC and K80 models assume equal base frequencies and the HKY and GTR models allow the frequencies of the four bases to differ (they will be estimated by the observed frequencies of the bases in the alignment). In the JC model all substitutions are assumed to occur at equal rates, in the K80 and HKY models transition and transversion rates are allowed to differ. The GTR model is the general time reversible model and allows all substitutions to occur at different rates. In case of the K80 and HKY models the user may set a transtion/transversion ratio value which will be used as starting value or fixed, depending on the level of estimation chosen by the user (see below). For the substitution rate matrices describing the substitution models we use the parametrization of Yang [Yang, 1994a].
- Rate variation: in CLC Genomics Workbench substitution rates may be allowed to differ among the individual nucleotide sites in the alignment by selecting the include rate variation box. When selected, the discrete gamma model of Yang [Yang, 1994b] is used to model rate variation among sites. The number of categories used in the dicretization of the gamma distribution as well as the gamma distribution parameter may be adjusted by the user (as the gamma distribution is restricted to have mean 1, there is only one parameter in the distribution)
- Estimation estimation is done according to the maximum likelihood principle, that is, a search is performed for the values of the free parameters in the model assumed that results in the highest likelihood of the observed alignment [Felsenstein, 1981]. By ticking the estimate substitution rate parameters box, maximum likelihood values of the free parameters in the rate matrix describing the assumed substitution model are found. If the Estimate topology box is selected, a search in the space of tree topologies for that which best explains the alignment is performed. If left un-ticked, the starting topology is kept fixed at that of the starting tree. The Estimate Gamma distribution parameter is active if rate variation has been included in the model and in this case allows estimation of the Gamma distribution parameter to be switched on or off. If the box is left un-ticked, the value is fixed at that given in the Rate variation part. In the absence of rate variation estimation of substitution parameters and branch lengths are carried out according to the expectation maximization algorithm[Dempster et al., 1977]. With rate variation the maximization algorithm is performed. The topology space is searched according to the PHYML method [Guindon and Gascuel, 2003], allowing efficient search and estimation of large phylogenies. Branch lengths are given in terms of expected numbers of substitutions per nucleotide site.
