Distance-based methods
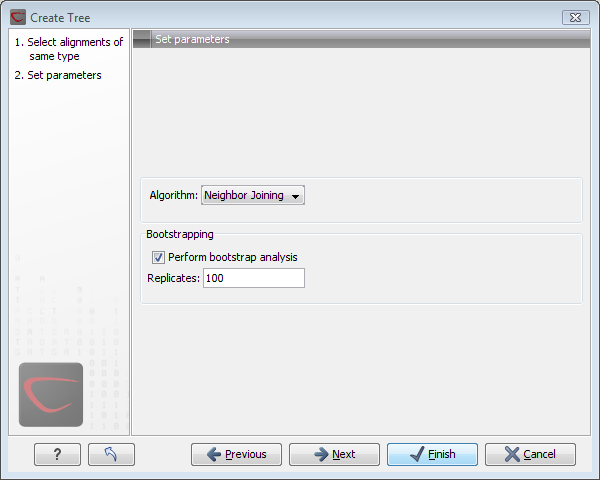
Figure 21.2: Adjusting parameters for distance-based methods.
Figure 21.2 shows the parameters that can be set for the distance-based methods:
The distance-based methods make use of Jukes-Cantor distances.
- Algorithms
- The UPGMA method assumes that evolution has occurred at a constant rate in the different lineages. This means that a root of the tree is also estimated.
- The neighbor joining method builds a tree where the evolutionary rates are free to differ in different lineages. CLC Genomics Workbench always draws trees with roots for practical reasons, but with the neighbor joining method, no particular biological hypothesis is postulated by the placement of the root. Figure 21.3 shows the difference between the two methods.
- To evaluate the reliability of the inferred trees, CLC Genomics Workbench allows the option of doing a bootstrap analysis. A bootstrap value will be attached to each branch, and this value is a measure of the confidence in this branch. The number of replicates in the bootstrap analysis can be adjusted in the wizard. The default value is 100.
For a more detailed explanation, see Bioinformatics explained.
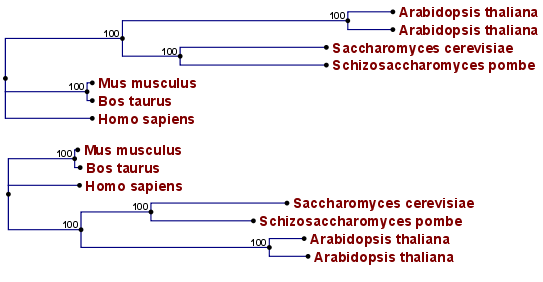
Figure 21.3: Method choices for phylogenetic inference.
The bottom shows a tree found by neighbor joining, while the top
shows a tree found by UPGMA. The latter method assumes that the
evolution occurs at a constant rate in different lineages.
