Analyze QIAseq xHYB Viral Panel Data (Human host)
The Analyze QIAseq xHYB Viral Panel Data (Human host) template workflow trims reads, identifies the best match reference, and calls viral variants. It is suitable for analysis of samples from human hosts generated with the QIAseq xHYB viral panels:
- QIAseq xHYB Respiratory Panel
- QIAseq xHYB Viral STI Panel
- QIAseq xHYB Adventitious Agent Panel
- QIAseq xHYB MPXV Panel
- QIAseq xHYB HepC Panel
QIAGEN reference data set
The QIAseq xHYB Viral Panels and QIAseq xHYB HepC Panel Reference Data Sets contain reference data relevant to this template workflow. The data can be downloaded and managed using the Reference Data Manager. To download the data, open the Reference Data Manager by clicking on the Manage Reference Data (![]() ) button in the top Toolbar, go to the QIAGEN Sets Reference Data Library tab, and locate the relevant set. Data from the Reference Data Sets that have not already been downloaded can be downloaded when the workflow is run.
) button in the top Toolbar, go to the QIAGEN Sets Reference Data Library tab, and locate the relevant set. Data from the Reference Data Sets that have not already been downloaded can be downloaded when the workflow is run.
Like the template workflow, the Reference Data Sets are designed for human samples. They include both a human host taxonomic profiling index and a sequence list with human control genes for use in the workflow step Map Reads to Human Control Genes. For analysis of samples not from human hosts: If a non-human host is relevant for your application, you can create a host taxonomic profiling index from your host reference genome using Create Taxonomic Profiling Index, see Create Taxonomic Profiling Index.
Workflow customization
You can create a copy of the template workflow and edit it to fit your specific application, see Template workflows. This could be useful e.g., in the following cases:
- Your sample is from a non-human source. Since the workflow element Map Reads to Human Control Genes is relevant for human data only, it can be deleted. In addition, if a host genome is not relevant for you application, open the Taxonomic Profiling workflow element, and uncheck Filter host reads.
- You expect mixed or co-infections in your samples. The workflow analysis and reporting is made in such a way that only one viral species is expected per sample. You can configure the Filter references parameters in the Find Best References using Read Mapping workflow element to allow for detection of multiple species according to your preferences.
Launching the workflow
The Analyze QIAseq xHYB Viral Panel Data (Human host) template workflow is available at:
Workflows | Template Workflows (![]() ) | Microbial Workflows (
) | Microbial Workflows (![]() ) | QIAseq Analysis (
) | QIAseq Analysis (![]() ) | Analyze QIAseq xHYB Viral Panel Data (Human host) (
) | Analyze QIAseq xHYB Viral Panel Data (Human host) (![]() )
)
Launch the workflow and step through the wizard.
- Select the sequence list(s) containing the reads to analyze.
- Select a reference data set or select "Use specified data elements". The latter runs the workflow using default elements, which can be viewed by clicking the "workflow roles" text just above the option.
- Define batch units. For details, see Running part of a workflow multiple times.
- Check that batching is as intended.
- Verify or select the viral taxonomic profiling index (figure 2.36).
- Verify or select the host taxonomic profiling index.
- Select the viral reference database(s). If in the first step you selected e.g., the QIAseq xHYB Viral Panels reference set, you can now select which of the available viral reference databases from that set to apply (2.37). If you chose to use the specified data elements, select a reference database.
- Verify or select the control genes.
- If your reads contain adapters, add an appropriate Trim adapter list (see Adapter trimming). This is optional and not needed if the QIAseq xHYB Microbial Hyb Kit was used.
- Specify Low Frequency Variant Detection settings, see figure 2.38.
- Specify Extract Consensus sequence settings (figure 2.39).
- In the "Create Full Sample Report" step various summary items have been set. These are guidelines to help evaluate the quality of the results.
- Finally, select a location to save outputs to.
Figure 2.36: Select viral taxonomic profiling index.
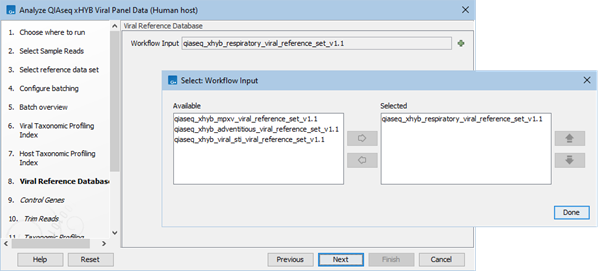
Figure 2.37: Select one or more viral reference databases.
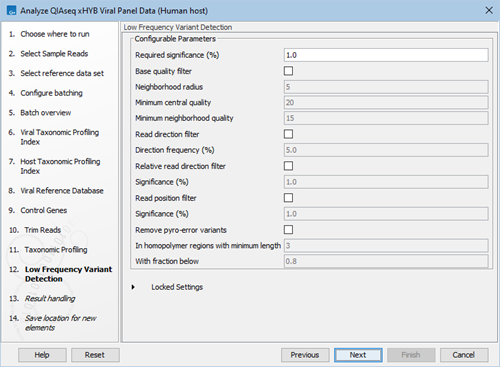
Figure 2.38: Low frequency variant detection parameters.
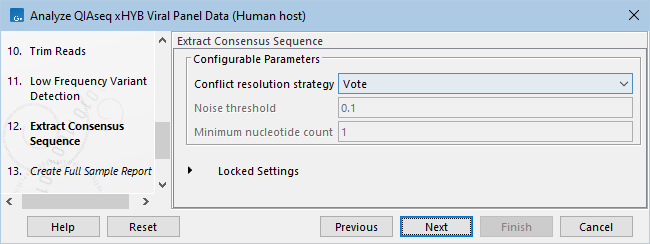
Figure 2.39: Extract Consensus Sequence parameters.
Workflow tools and outputs
The Analyze QIAseq xHYB Viral Panel Data (Human host) template workflow consists of the following tools.
- QC for Sequencing Reads. Performs basic quality control of the sequencing reads. The output, which is included in a combined report, can be used to evaluate the quality of the sequencing reads. See QC for Sequencing Reads.
- Trim Reads. Removes adapter sequences and low quality nucleotides. The appropriate settings for the Trim Reads tool depends on the protocol used to generate the reads. See Trim Reads.
- Taxonomic Profiling. Used to filter viral reads from the sample reads. See Taxonomic Profiling. Host reads i.e., reads that map to the host taxonomic profiling index, do not count toward the taxonomic profiling result, but are used as input for Map Reads to Human Control Genes. Viral reads - reads that map to the viral taxonomic profiling index - are subsampled and later used as input for Find Best References using Read Mapping.
- Map Reads to Human Control Genes. Maps the host reads output from Taxonomic Profiling to the host taxonomic profiling index, to a reference of human control genes. See Map Reads to Reference. This serves as a QC step to verify mapping to the human control genes. For human samples, you expect to see mapping of reads to all human control genes.
- Find Best References using Read Mapping. Maps the viral reads output from Taxonomic Profiling to the selected viral reference database to identify which reference sequence is the "Best match". See Find Best Reference using Read Mapping.
- Remove Duplicate Mapped Reads. Removes duplicate reads derived from PCR amplification (or other enrichment) during sample preparation from the mapping. See Remove Duplicate Mapped Reads. The output reads track is used as input for Local Realignment.
- Local Realignment. Improves the alignment of the reads in the reads track. See Local Realignment.
- Low Frequency Variant Detection. Calls variants in the read mapping that are present at low frequencies. See Low Frequency Variant Detection.
- Filter on Custom Criteria and Filter against Known Variants. Remove variants that fall below a set of thresholds. For this workflow, coverage >30 and frequency >20% is required. See Variant filtering.
- Amino Acid Changes. Uses the called variants to generate a track of amino acid changes. See Amino Acid Changes.
- Create Mapping Graph and Identify Graph Threshold Areas. Creates a track with regions with coverage below a threshold. For this workflow, the threshold is set to 30. See Create Mapping Graph and Idnetify Graph Threshold Areas.
- Extract Consensus Sequence. Makes a consensus sequence from the read tracks from Local Realignment. See Extract Consensus Sequence.
- QC for Read Mapping. Performs quality control of the read mapping. See QC for Read Mapping.
- Refine Abundance Table. Aggregates the abundance table from Taxonomic Profiling on species-level. See Refine Abundance Table.
- Merge Abundance Tables. Merges the sample-specific abundance tables to one combined abundance table. See Merge Abundance Tables.
- Create Sample Report. Creates a single report per sample that contains all tool reports. Also allows for setting of Summary items to highlight possible issue during analysis. See Create Sample Report.
The sample-specific outputs provided by this workflow are:
- Sample report. The sample report is curated to contain the most important information for analysis interpretation. All full reports are linked throughout the Sample report or can be found in the QC & Reports folder. The Sample report icon will be colored based on whether Summary item thresholds were met. See the "Quality control" section in the sample report for specifics.
- Refined abundance table. The abundance of viral species, along with their full taxonomy. See Taxonomic Profiling abundance table and Refine Abundance Table.
- Consensus sequence. Viral consensus sequence(s), extracted from the Best match read mapping track.
- Track list. Collection of all the tracks in the "Tracks" folder, except for the Read mapping human control genes track.
- Viral Reads. Folder containing sequence list(s) of reads that mapped to the viral taxonomic profiling index.
- Tracks. Folder containing all tracks output during analysis.
- Read mapping human control genes. The host reads mapped against the control gene reference.
- Best match sequence. The "Best match" reference sequence as identified by the Find Best References using Read Mapping tool.
- Best match CDS track. The CDS track extracted from the "Best match" reference sequence as identified by the Find Best References using Read Mapping tool.
- Best match read mapping. Reads mapped to the "Best match" viral reference. Output from Local Realignment.
- Low coverage areas. List of low coverage regions in the Best match read mapping output.
- Annotated variant track. List of detected variants left after filtering, annotated with amino acid changes.
- Amino acid track. List of amino acid changes.
- Read mapping human control genes. The host reads mapped against the control gene reference.
- QC & Reports. Folder containing the individual reports generated during the analysis.
- All reports from the sample report are found here in their full length.
The combined outputs provided by this workflow are:
- Combined report. Combined report of all sample reports. The combined report contains all quality control information and analysis results, including the result best matching reference as detected by Find Best Reference using Read Mapping.
The combined report icon will be colored based on whether Summary item thresholds were met in each sample. See the "Quality control" section in the combined report for specifics.
- Merged refined abundance table. The abundance of viral species for all samples in the workflow run. See Taxonomic Profiling abundance table and Refine Abundance Table. In this analysis, Taxonomic Profiling is only used for filtering viral reads. However, if the best matching reference species does not align with the most abundant species in the abundance table, or if another species has a high relative abundance compared to the best match, it may be a sign of a mixed or co-infection. As mentioned previously, this workflow does not support multiple species detection, but alterations can be made to investigate such a case further.
