Download MLST Scheme parameters
To run the Download MLST Scheme tool, go to:
Tools | Microbial Genomics Module (![]() ) | Databases (
) | Databases (![]() ) | MLST Typing (
) | MLST Typing (![]() ) | Download MLST Scheme (
) | Download MLST Scheme (![]() )
)
Select the scheme you wish to download in the Scheme to download drop-down menu (figure 14.5). To jump to specific schemes, click the drop-down menu once and type the first letters of the desired scheme, e.g., type "es" to reach the first Escherichia spp. scheme.
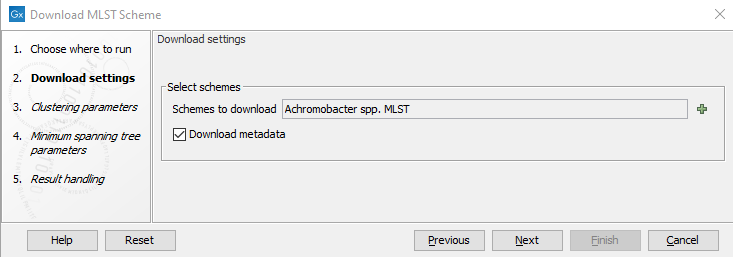
Figure 14.5: The Download MLST Scheme settings.
To download and extract metadata for all of the profiles in a scheme, tick the Download metadata option. Note that this can make the download take a long time.
Most of the schemes offered for download are classic (7-gene) schemes, but there are also core genome schemes available for several species, e.g.: N. gonorrhoeae, N. Meningitis, C. Jejuni / C. Coli, C. trachomatis, Vibrio cholerae, Listeria monocytogenes.
Some of the schemes may only contain allele and locus definitions and no profiles, i.e., sequence types.
Click on Next and accept the terms of use before proceeding to the Authorization step.
Authorize access through your account
To download MLST schemes using CLC Genomics Workbench, you must first authorize access to download data on you behalf. For this step, you must have a user account with the relevant MLST scheme provider (PubMLST or Pasteur) depending on which scheme you select. You must also have registered with the specific database in your account settings. How to create an account and register for specific databases is explained at https://pubmlst.org/site-accounts and https://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/register/.
- Click the Log in button (figure 14.6). This will open the relevant login page in an external browser.
Figure 14.6: Download MLST Scheme Authorization step. - If you were not already logged in in the browser, you must now do so. Depending on the scheme you are downloading, log in using your PubMLST or Institut Pasteur account (figure 14.7).
Note: Make sure you are registrered for the specific database you are trying to access. If you have an account, but have not registered for the specific database you are trying to download from, you will not be able to log in.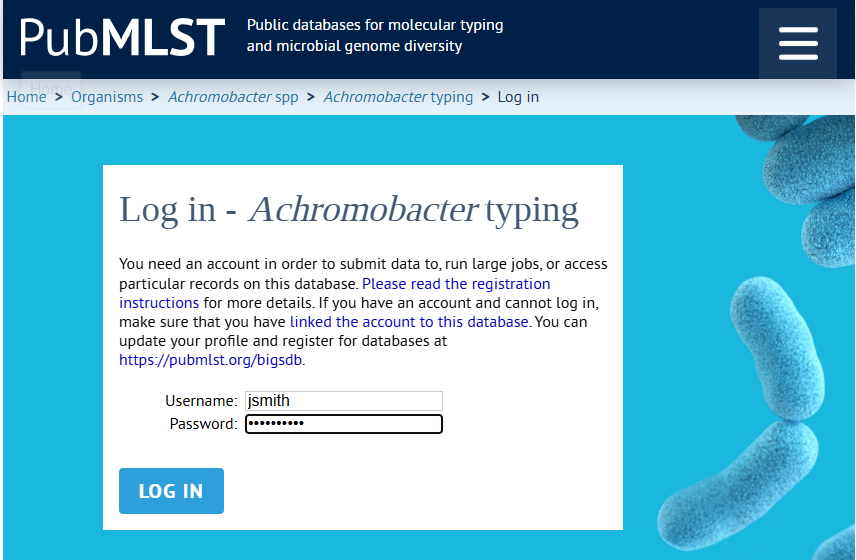
Figure 14.7: Log in to your account. In this case the PubMLST account is needed. - After logging in, you will be asked to authorize CLC Workbench to access data on your behalf (figure 14.8). Click "Authorize". This generates an access token and secret for use by CLC Workbench. No personal data about the account is shared. A verification code will be displayed after authorizing (figure 14.9).
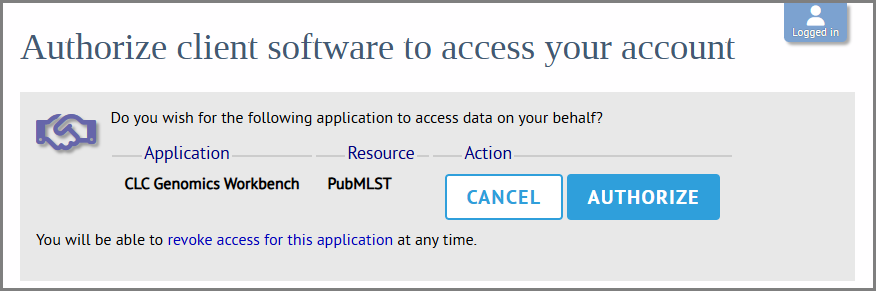
Figure 14.8: You will be asked to allow the Workbench to access your account. Click "Authorize".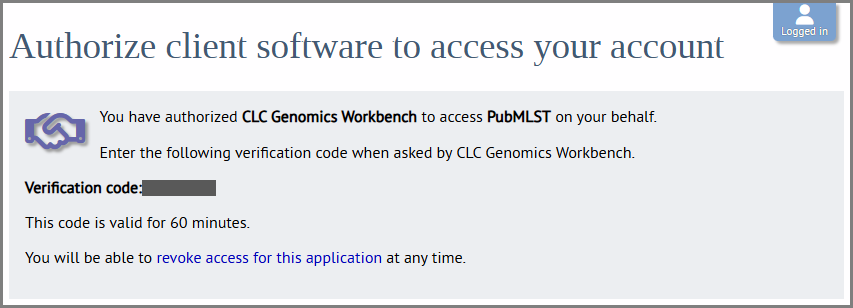
Figure 14.9: Following authorization a verification code will appear. Copy the code and return to the Workbench. - Copy the code, return to the Workbench, and paste it into the Verification code dialog box (figure 14.9). Click OK.
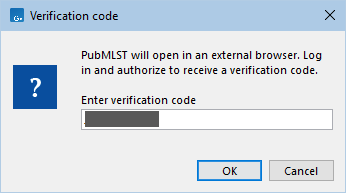
Figure 14.10: Paste or type the verification code into the dialog box.
When the verification code has been succesfully entered, you will be logged in and can proceed to the next steps. The browser window can also be closed. For following downloads from the same source, you need not authorize access again. Clicking the Log in button should automatically connect to the database on your behalf.
Clicking the Log out button will reset the token and secret, allowing you to log in using another account.
Minimum spanning tree parameters
The following options are available when creating a minimum spanning tree (figure 14.11):
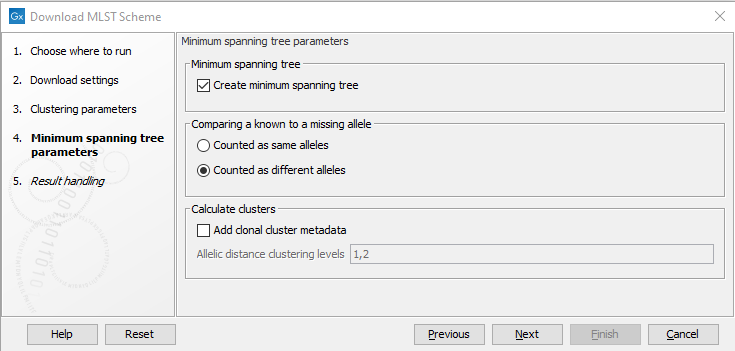
Figure 14.11: The minimum spanning tree parameters.
- Comparing a known to a missing allele. The minimum spanning tree is created using a distance matrix, where the distance is calculated between all pairs of sequence types. The distance is calculated as the number of loci where the allele assignment differs. But in some cases, a locus for a sequence type may not have an assigned allele (for instance, for the accessory genes in a wgMLST scheme). If this is the case, the behavior depends on this setting. If 'Counted as same alleles' is selected, a locus where at least one allele is missing for the pair being compared will be ignored (it will not count as a difference). If 'Counted as different alleles' is selected, a missing allele being compared to a known allele will increase the distance between the sequence types being compared.
- Add clonal cluster metadata. It is possible to assign cluster information to the scheme which will show up as metadata. The clustering is based on the minimum spanning tree, and will be similar to the clustering obtained by using the 'collapse branches' slider in the minimum spanning tree view - that is, the clustering will be single-linkage clustering - i.e. all nodes in cluster are within the specified threshold to at least one other node in the cluster. Each cluster will get a name chosen from the sequence type in the cluster with most connections.
- Add clonal cluster metadata. Specifies the level at which the clustering will be performed. It is possible to specify multiple, comma-separated values. E.g. '100,200' will assign clusters at allelic distances of 100 and 200 - this will create two new metadata columns, cc_100 and cc_200 with the new cluster information.
