Result Metadata
Metadata refers to information about data. In the context of the CLC Microbial Genomics Module, this usually means information about samples. For example a set of reads could come from a particular specimen at a particular time point with particular characteristics. The specimen, time and characteristics would be metadata for that set of reads.
What is metadata used for?
Core uses of metadata in CLC software include:
- Defining batch units when launching workflows in batch mode, described in https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Running_workflows_in_batch_mode.html.
- Distributing data to the relevant input channels in a workflow when using Collect and Distribute elements, described in https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Control_flow_elements.html.
- Finding and selecting data elements based on sample information (in a CLC Metadata Table). Workflow Result Metadata Tables are of particular use when reviewing results generated by workflows run in batch mode and are described in https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Workflow_Result_Metadata_tables.html.
- Running tools where characteristics of the data elements are relevant. An example is Differential Abundance Analysis, described in Differential Abudance Analysis.
Metadata tables
An example of a CLC Metadata Table generated by the CLC Workbench is shown in figure 20.3. Each column represents a property of a sample (e.g., identifier, sample depth, geographic location, temperature) and each row contains information relevant to a sample. A single column can be designated the key column. That column must contain unique entries.
Each row can have associations with one or more data elements, such as sequence lists, taxonomic profiling abundance tables, variant tracks, etc.
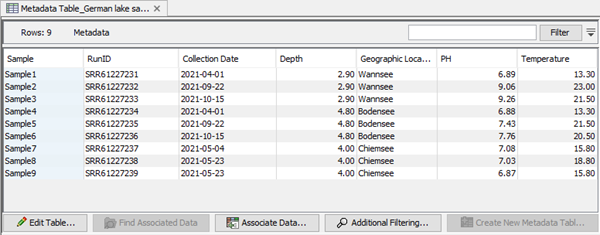
Figure 20.3: A CLC Metadata Table, with the key column highlighted in blue.
Creating metadata tables
CLC Metadata Tables can be created in several ways, including:
- Import metadata from an Excel, CSV or TSV format file using the Import Metadata (
 ) tool. You can associate already imported data with your metadata during import, or do this later.
The process of importing metadata and associating data is described in the CLC Genomics Workbench user manual, https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Importing_metadata.html.
) tool. You can associate already imported data with your metadata during import, or do this later.
The process of importing metadata and associating data is described in the CLC Genomics Workbench user manual, https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Importing_metadata.html.
- Use a workflow to import a sample and its metadata at the same time. A template workflow for importing sequence data with associated metadata can be found in the Preparing Raw Data folder in the Template Workflows folder under the Workflows menu. It is described in the CLC Genomics Workbench user manual, https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Import_with_Metadata.html.
For more ways to create CLC Metadata Tables and information on how to work with CLC Metadata Tables in general, see the Metadata section of the CLC Genomics Workbench user manual, https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Metadata.html.
In addition to standard CLC Metadata Tables, the CLC Microbial Genomics Module makes use of a special type of metadata table; the Result Metadata Table. As opposed to CLC Metadata Tables, Result Metadata Tables can be updated with selected types of analysis results e.g., antibiotic resistance. This is described in Create Result Metadata Table.
Subsections
- Create a Result Metadata Table
- Running an analysis directly from a Result Metadata Table
- Extend Result Metadata Table
- Use Genome as Result
