The Layout panel
The following options are available: Node layout
- Show sequence type names: show the names of the sequence types for the nodes in the tree. If nodes are collapsed, only the first few names will be shown.
- Scale nodes: makes the nodes large or smaller.
- Node radius: either 'Sequence type count' or 'Isolate count'. A sequence type may have multiple isolates and metadata entries. This setting determines whether the node radius is based on the number of sequence types or isolates.
Branch layout
- Show allelic distance: shows the distance between different nodes in the tree. The distance is calculated as the number of loci where the allele assignment differs. Note that loci may have missing assignments. In this case, the distance calculation depends on the choice made when building the scheme (see Create MLST Scheme)).
- Collapse branches: It is possible to reduce the complexity of the tree by clustering together nodes that are within a specific allelic threshold of each other. When setting a threshold, clusters will be formed where all nodes in a cluster are within the specified threshold to at least one other node in the cluster (single-linkage clustering). See (figure 10.10) for an example of a tree where nodes have been collapsed.
- Scale branches: This parameter can be adjusted to make the branches longer. Note that the force-directed layout is primarily controlled by the repulsive force, so adjusting this parameter will not always have a proportional impact. Also note that due to the large span in allelic distances for cg- and wg-MLST schemes, the layout algorithm tries to fit an ideal branch length that is proportional to the square-root of the allelic distance.
- Reset layout: Pressing this button will reset the layout: this is done by first creating an initial radial layout, where no branches are crossed, and then applying a force-directed layout. If the graph is uncollapsed, pressing the Reset layout button will reset to the default layout created during scheme building.
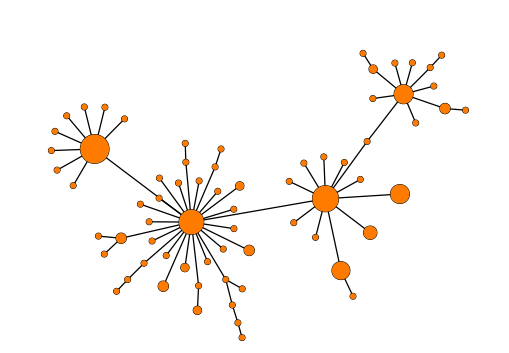
Figure 10.10: Collapsing nodes in a Minimum Spanning Tree.
