Running an analysis directly from a Result Metadata Table
Analysis results from tools listed in the table of Create Result Metadata Table are automatically added to the Result Metadata Table as long as it was performed on samples associated with metadata. Content of the Result Metadata Table may be managed in similar ways as other tables in CLC Genomics Workbench (https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Filtering_tables.html), but it can also be used to start new analyses using the With selected (![]() ) button which provides the option of various downstream analysis of the selected dataset.
) button which provides the option of various downstream analysis of the selected dataset.
To perform an analysis on one or more samples, begins by selecting the relevant rows followed by finding the associated elements by clicking on the Find Associated Data (![]() ) button. All associated elements are then listed in window below called Metadata Elements. You can see an example in figure 20.8, where a Metadata Result Table includes 6 rows (Metadata, top view), while 30 elements are found to be associated to these 6 rows (Metadata Elements, bottom view).
) button. All associated elements are then listed in window below called Metadata Elements. You can see an example in figure 20.8, where a Metadata Result Table includes 6 rows (Metadata, top view), while 30 elements are found to be associated to these 6 rows (Metadata Elements, bottom view).
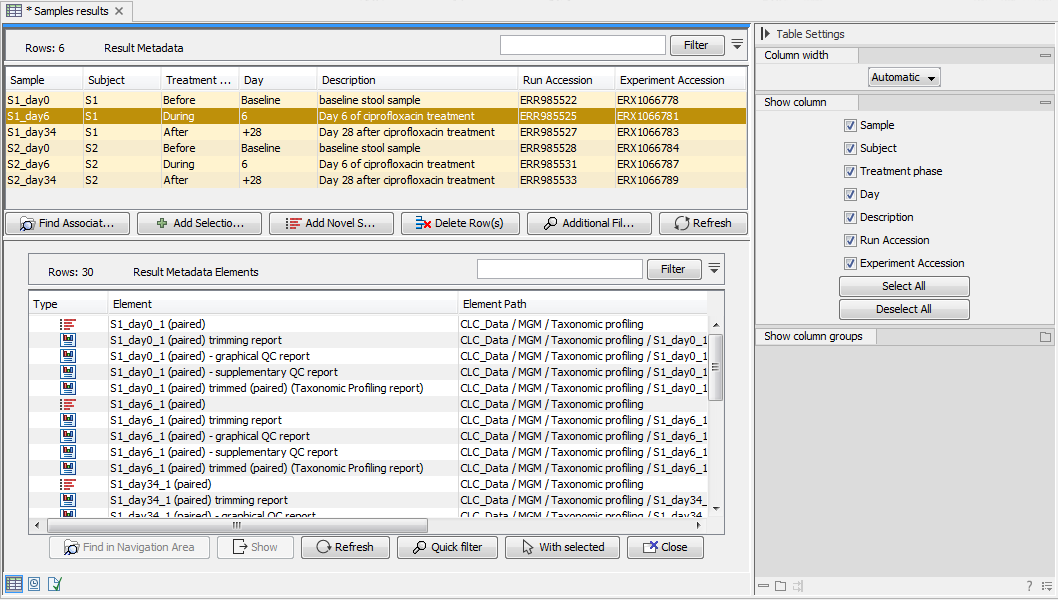
Figure 20.8: In total, 30 files are associated to the selected 6 sample rows within the Result Metadata Table.
As the number of samples, metadata and data elements increases over time, and the Result Metadata Table likely will include a mix of analyzed and novel samples, it is helpful to perform filtering steps to identify the elements you are looking for (see Filtering in Result Metadata Table). Once filtering is done, it is easy to select the remaining rows of data elements and click the With selected (![]() ) button to start tools such as Create K-mer Tree and Create SNP Tree, or initiate a workflow analyses using an opened and customized version of a workflow.
) button to start tools such as Create K-mer Tree and Create SNP Tree, or initiate a workflow analyses using an opened and customized version of a workflow.
Filtering in Result Metadata Table
Filtering is generally performed as a two step process: by picking or filtering firstly on the rows of the Result Metadata Table and secondly among the associated Metadata Elements.
Filtering can be done several ways, usually using a combination of the following options:
- Use the traditional table filtering function in top right corner. Filter for text elements, or unroll the banner by clicking on the icon (
 ) and use more specific filters options.
) and use more specific filters options.
- Tables can be sorted according to one or more columns, making it easier to find (and select) the desired elements. One example is to click on the Role column to find data elements with the same role.
- In the case of Metadata elements, use the Quick filter (
 ) button and select the desired filtering option. It is possible to choose among:
) button and select the desired filtering option. It is possible to choose among:
- Imported filters down to elements with the "Role" being Sample data. This can, for instance, be used for analyzing using an open and validated workflow based on one of the template workflows from the Workflows menu by clicking the With selected (
 ) button.
) button.
- Filter for SNP Tree filters down to elements with the "Role" being either Read mapping, Realigned mapping or Variants. Selection of the elements remaining after this filtering has been applied makes it easy to click the With selected (
 ) button and initiate the Create SNP Tree tool using the selected data as input.
) button and initiate the Create SNP Tree tool using the selected data as input.
- Filter for K-mer Tree filters down to elements with the "Role" being Trimmed reads. Selection of the elements remaining after this filtering has been applied makes it easy to click the With selected (
 ) button and initiate the Create K-mer Tree tool using the selected data as input.
) button and initiate the Create K-mer Tree tool using the selected data as input.
- Filter Re-mapped 'name of common reference' for SNP Tree, option available for elements generated with the Map to Specified Reference or manually added with the Use Genome as Result and based on a shared reference.
 ) followed by Clear Quick Filter.
) followed by Clear Quick Filter.
- Imported filters down to elements with the "Role" being Sample data. This can, for instance, be used for analyzing using an open and validated workflow based on one of the template workflows from the Workflows menu by clicking the With selected (
Filtering in a SNP-Tree creation scenario
To construct a SNP tree, all sample data must have been analyzed (i.e., reads mapped and variants called) using the same reference sequence. If we want to use all the samples that were generated by the Map to Specified Reference workflow on several occasions using a common reference sequence, we use the quick filtering options.
- Filter all samples where read mapping and variant calling was performed using a common reference by clicking on the icon (
 ) and using the following filter parameters: in the first drop-down menu, choose the column whose header is the reference sequence of interest; in the second drop-down menu, choose the term "contains"; and in the third window, write "true".
) and using the following filter parameters: in the first drop-down menu, choose the column whose header is the reference sequence of interest; in the second drop-down menu, choose the term "contains"; and in the third window, write "true".
- Select all remaining samples.
- Click on the Find Associated Data (
 ) button. This opens the Metadata elements table underneath the initial Metadata table with a certain amount of elements associated with the samples selected in the Metadata Result Table.
) button. This opens the Metadata elements table underneath the initial Metadata table with a certain amount of elements associated with the samples selected in the Metadata Result Table.
- Click on the Quick Filters (
 ) button in the Metadata Elements Table (bottom view) and select the Filter Re-mapped 'common reference' for SNP Tree option.
) button in the Metadata Elements Table (bottom view) and select the Filter Re-mapped 'common reference' for SNP Tree option.
- Select all the remaining elements.
- Click on the With selected (
 ) button and select the Create SNP Tree option. The Create SNP Tree wizard is displayed (see Create SNP Tree). The read mappings are preselected as input. The variant tracks and the Result Metadata Table are automatically preselected as parameters.
) button and select the Create SNP Tree option. The Create SNP Tree wizard is displayed (see Create SNP Tree). The read mappings are preselected as input. The variant tracks and the Result Metadata Table are automatically preselected as parameters.
