Analyze QIAseq xHYB NTM-ID Panel Data (Human host)
This workflow has been incorporated into the workflow Analyze QIAseq xHYB Mycobacterium tuberculosis and NTM-ID Panel Data (Human host). Please run that workflow instead.
This workflow has been deprecated and will be retired in a future version of the software. It has been moved to the Legacy Template Workflows (![]() ) folder of the Toolbox, and its name has "(legacy)" appended to it. If you have concerns about the future retirement of this workflow, please contact QIAGEN Bioinformatics Support team at ts-bioinformatics@qiagen.com.
) folder of the Toolbox, and its name has "(legacy)" appended to it. If you have concerns about the future retirement of this workflow, please contact QIAGEN Bioinformatics Support team at ts-bioinformatics@qiagen.com.
The Analyze QIAseq xHYB NTM-ID Panel Data (Human host) (legacy) template workflow detects and types species from the Mycobacteriaceae family. It is suitable for analysis of samples from human hosts generated with the QIAseq xHYB NTM-ID Panel and can detect both the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Non-Tuberculosis Mycobacteria (NTM) by targeting the 65-kDa heat shock protein (hsp65) gene.
If the QIAseq xHYB NTM-ID Panel was used in conjunction with the QIAseq xHYB Mycobacterium tuberculosis Panel, use the template workflow Analyze QIAseq xHYB Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Panel Data (Human host) (legacy) instead.
To analyze samples not from human hosts, you can create a copy of the workflow and edit it to fit your specific application, see Template workflows. Since the workflow element QC for Targeted Sequencing is relevant for human data only, you should delete this. In addition, if a host genome is not relevant for you application, you can remove the "Host reference" input from the Find Best References using Read Mapping step.
Once the workflow copy is customized, you can install it to make it available from under the Workflows menu (see Workflow installation).
QIAGEN Reference Data Set
The QIAseq xHYB NTM-ID Panel Reference Data Set contains reference data relevant for this template workflow. It includes a non-redundant reference database of the hsp65 gene, used for detection and typing of Mycobacteriaceae. Like the template workflow, the reference data set is designed for human samples, and additionally contains a human host reference and an annotation track of human control gene regions.
Data in the QIAseq xHYB NTM-ID Panel set not already downloaded can be downloaded during the launch of the workflow. It can also be downloaded, as well as managed, using the Reference Data Manager, which can be opened by clicking on the Manage Reference Data (![]() ) button in the Toolbar. Click on the QIAGEN Sets Reference Data Library tab in the Reference Data Manager and search for the set by entering terms from its name in the search field.
) button in the Toolbar. Click on the QIAGEN Sets Reference Data Library tab in the Reference Data Manager and search for the set by entering terms from its name in the search field.
For analysis of samples not from human hosts: If a non-human host is relevant for your application, you can download a host genome using Download Custom Microbial Reference Database.
The workflow analysis
The raw reads are trimmed for low quality, read-through adapter sequences, and G homopolymers. If a Trim adapter list is supplied, these adapters will also be trimmed.
Trimmed reads are mapped to the references of Mycobacteriaceae hsp65 genes and the human host reference simultaneously using Find Best References using Read Mapping. Due to the high level of similarity between hsp65 genes from different Mycobacteriaceae species, the reads are mapped with stringent mapping parameters.
This results in an intial set of hsp65 reads and possible references. If more than one possible reference is detected for the sample reads, the analysis will try to refine the references by only looking at non-ambiguous reads mapping to this subset of the references. This helps to resolve false positive species calls as a result of the high level of similarity within the target gene.
While the detected species may contain a "variant" name (e.g. "Mycobacterium tuberculosis variant bovis"), be advised that the hsp65 gene is usually not specific enough for strain level typing - only species level typing. For mixed infections involving more than one Mycobacteriaceae species, the lower detection limit is 3% abundance relative to the most abundant species.
After reference refinement, all of the hsp65 reads will be re-mapped to the final refined list of references, and the detected species and read mapping statistics are output in the report.
The human control gene regions are used for QC for Targeted Sequencing. The QIAseq xHYB NTM-ID Panel contains probes for these regions as an indicator of succesful hybrid capture.
Launching the workflow
The Analyze QIAseq xHYB NTM-ID Panel Data (Human host) (legacy) workflow is available at:
Workflows | Template Workflows (![]() ) | Legacy Template Workflows (
) | Legacy Template Workflows (![]() ) | Analyze QIAseq xHYB NTM-ID Panel Data (Human host) (legacy) (
) | Analyze QIAseq xHYB NTM-ID Panel Data (Human host) (legacy) (![]() )
)
Launch the workflow and step through the wizard.
- Select the sequence list(s) containing the sample reads. If selecting multiple inputs from different samples, check the Batch option, see Running workflows in batch mode.
- Select a reference data set or select "Use specified data elements". The latter runs the workflow using default elements, which can be viewed by clicking the "workflow roles" text just above the option.
- If Batch was checked in step 1, choose whether batch units should be defined based on organization of the input data, or by provided metadata. In the next step, review the batch units resulting from your selections above.
- If your reads contain adapters, add an appropriate Trim adapter list. Click Next.
- The parameters for filtering references can be changed (figure 21.4). This might be necessary if the expected Mycobacteriaceae species is present in the sample at a very low abundance. The default settings are expected to work in most cases. For more information about the filters, see Find Best References using Read Mapping.
- In the "Create Sample Report" step various summary items have been set. These are guidelines to help evaluate the quality of the results (see Create Sample Report). Thresholds can be changed, if the defaults are too stringent for the input samples.
- Finally, select a location to save outputs to.
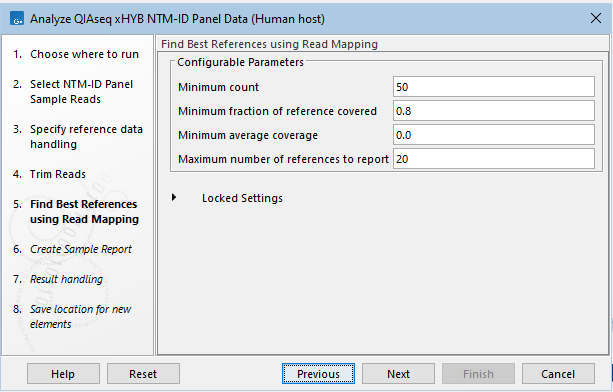
Figure 21.4: Parameters for filtering references can be changed.
Workflow outputs and how to interpret
The outputs provided by the workflow are:
- QC & Reports. Folder containing the individual reports generated during the analysis.
- All reports from the sample report are found here in their full length.
- Mycobacteriaceae full mapping statistics table, which the Mycobacteriaceae mapping report is based on.
- Outputs. Folder containing results from the analysis.
- Human host read mapping. Track to see mapping of the human host reads and from which the QC for human control genes report section was derived.
- Mycobacteriaceae reads. (Only if a positive result was detected). Sequence lists (single and paired) containing reads from the input that mapped to the hsp65 references before refinement of references.
- Mycobacteriaceae read mapping. (Only if a positive result was detected). Reads track of the reads mapped to the final hsp65 references.
- Typing Report. The sample report is curated to contain the most important information for analysis interpretation. All full reports are linked throughout the Sample report or can be found in the QC & Reports folder. The Sample report icon will be colored based on whether Summary item thresholds were met (see the "Quality control" section in the sample report for specifics):
- A green dot on the report icon indicates detection of at least one Mycobacteriaceae species, and all quality control thresholds passed.
- A yellow dot on the report icon indicates detection of at least one Mycobacteriaceae species, but not all quality control thresholds passed.
- A red dot on the report icon indicates no detection of Mycobacteriaceae species. The report must be opened to determine whether quality control thresholds passed.
The Typing Report is the main output of the workflow. This allows for easy overview of the analysis results, both in terms of quality control and detected Mycobacteriaceae for the sample. An example of the report can be seen in figure 21.5.
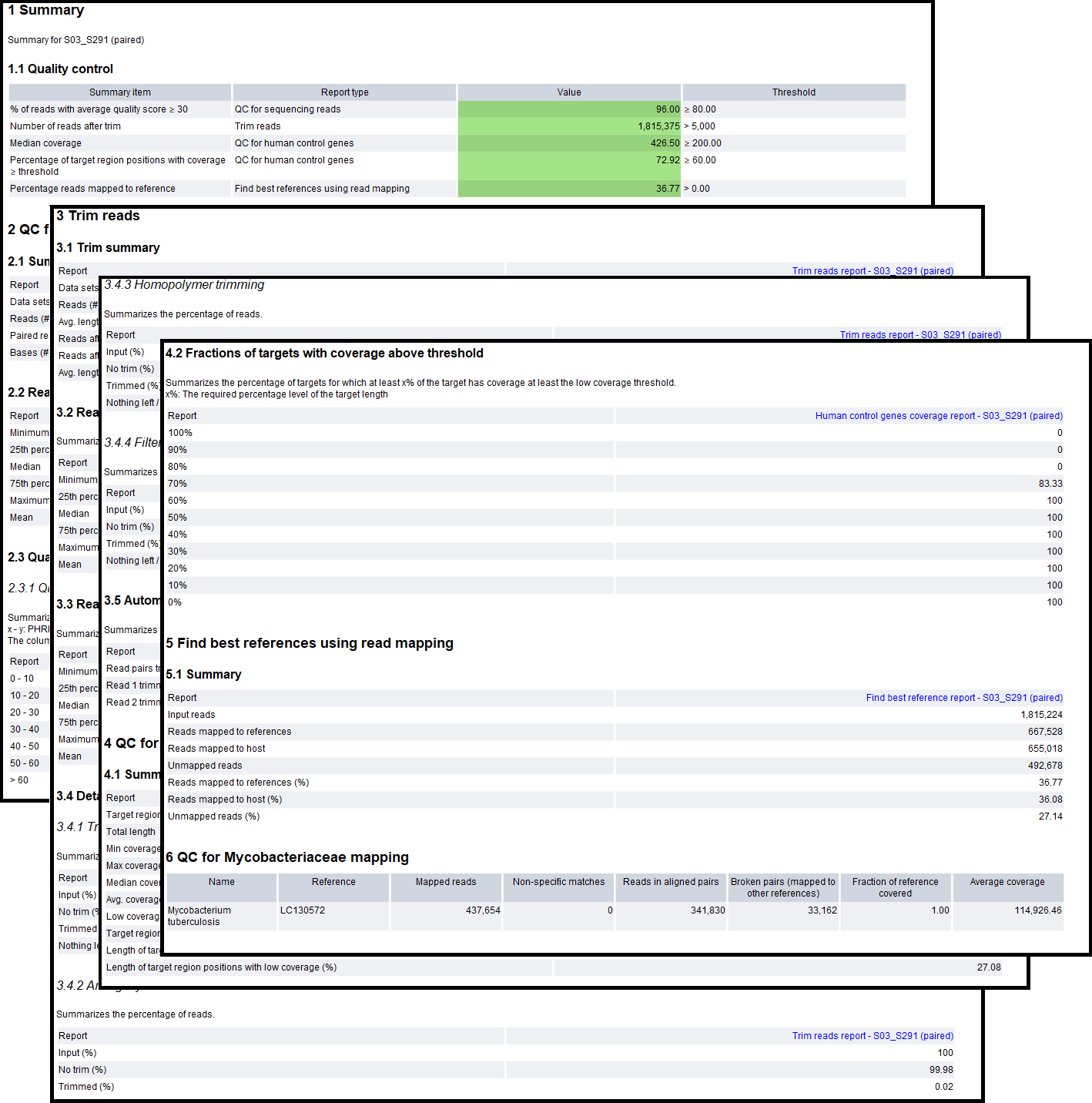
Figure 21.5: An example report from the Analyze QIAseq xHYB NTM-ID Panel Data (Human host) (legacy) workflow.
The report contains the following sections:
- Sections 1-4 contain quality metrics for the analysis:
- Summary. A summary of the QC summary items and whether they passed (green) or failed (yellow). The "Percentage reads mapped to reference" will be red if no Mycobacteriaceae species was detected.
- QC for sequencing reads. A summary of the number of raw reads and their quality. If the reads are of too low quality, the results may be unreliable.
- Trim reads. A summary of the read trimming. If the percentage of reads after trim is low or the average read length after trimming is considerably lower than before trimming, it may be a sign that something is wrong with the sample reads.
- QC for human control genes. A summary of the host reads mapping to the human control genes. The fraction of the regions covered is expected to be more than half, and with relatively high median coverage due to the hybrid capture method used. If not, something may have gone wrong during the sample prep, or the sample was not made with the QIAseq xHYB NTM-ID Panel.
- Sections 5 and 6 contain detection results for the analysis:
- Find best references using read mapping. Contains a summary of how many of the input reads mapped to the hsp65 references vs. the host and how many were unmapped. These are the mapping statistics before refinement of the references, and may not match the number of reads mapped to the reference(s) in the following sections. To see more details of the results prior to refinement, see the "Find best reference report" in the "QC & Reports" folder.
- QC for Mycobacteriaceae mapping. (Only if a positive result was detected). Contains the name of the reference(s) detected after refinement of references and mapping statistics for the reads mapped to them. See below for details about the columns.
The "QC for Mycobacteriaceae mapping" table report contains the following columns:
- Name. The name of the Mycobacteriaceae species reference detected.
- Reference. The accession number of the reference.
- Mapped reads. The number of reads mapped to the reference.
- Non-specific matches. The number of reads that mapped equally well to multiple positions in the set of detected references.
- Reads in aligned pairs. The number of reads mapped in pairs to the reference.
- Fraction of reference covered. The fraction of the reference covered by at least one read.
- Average coverage. The number of nucleotides mapped to the reference divided by the reference length.
