Filter Samples Based on Number of Reads
In order to cluster accurately samples, they should have comparable coverage. Sometimes, however, DNA extraction, PCR amplification, library construction or sequencing has not been entirely successful, and a fraction of the resulting sequencing data will be represented by too few reads. These samples should be excluded from further analysis using the Filter Samples Based on Number of Reads tool.
To run the tool, go to
Tools | Microbial Genomics Module (![]() ) | Metagenomics (
) | Metagenomics (![]() ) | Amplicon-Based Analysis (
) | Amplicon-Based Analysis (![]() ) | Filter Samples Based on Number of Reads (
) | Filter Samples Based on Number of Reads (![]() )
)
The tool requires that the input reads from each sample must be either all paired or all single. This check ensures that the samples are comparable, as the number of reads before merging paired reads is twice as great as the number of merged reads.
The threshold for determining whether a sample has sufficient coverage is specified by the parameters minimum number of reads and minimum percent from the median. The algorithm filters out all samples whose number of reads is less than the minimum number of reads or less than the minimum percent from the median times the median number of reads across all samples.
The primary output is a table describing how many reads are in a particular sample and if they passed or failed the quality control (see figure 5.2).
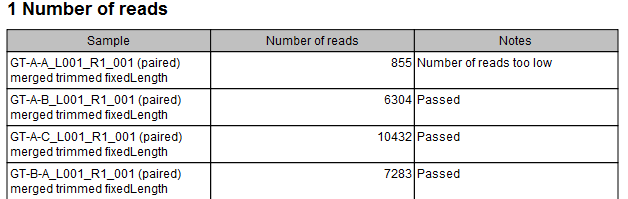
Figure 5.2:
Output table from the Filter Samples Based on Number of Reads tool.
In the next wizard window you can decide to Copy samples with sufficient coverage as well as to Copy the discarded samples. Copying the samples with sufficient coverage will give you a new list of sequences that you can use in your following analyses.
