Taxonomic Profiling parameters
To run the Taxonomic Profiling tool, go to
Tools | Microbial Genomics Module (![]() ) | Metagenomics (
) | Metagenomics (![]() ) | Taxonomic Analysis (
) | Taxonomic Analysis (![]() ) | Taxonomic Profiling (
) | Taxonomic Profiling (![]() )
)
In the first dialog, select the sequence list to analyze (figure 6.19).
Figure 6.19: Select a sequence list as input.
When sequences are selected, click Next, and you will see the dialog in (figure 6.20).
Select reference databases:
- Reference index. The database of reference genomes that you are analyzing for.
- Filter host reads. If this is checked, reads that map better to the specified host genome are filtered and will not count toward taxonomic results.
- Host genome index. The host genome, or background genome, represents the reference sequences that may be present in your sample, but that are not the target of your analysis. As an example, to analyze the microbiome from human gut samples, you would specify the human reference index to filter reads that map against the human genome.
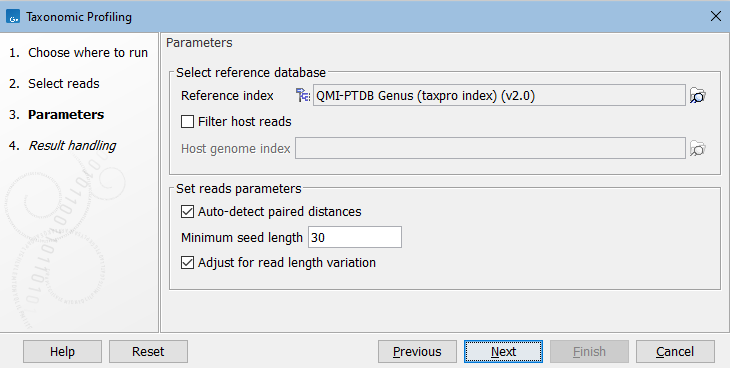
Figure 6.20: Set the parameters for taxonomic profiling.
Curated reference databases and taxonomic profiling indexes are available with the Download Curated Microbial Reference Database tool (Download Curated Microbial Reference Database). Alternatively, you can use the Download Custom Microbial Reference Database tool (Download Custom Microbial Reference Database) to create your own custom reference database. To create indexes from reference databases and host genomes, use the Create Taxonomic Profiling Index tool (Create Taxonomic Profiling Index).
Metagenome indexes, available from Download Curated Microbial Reference Database tool (Download Curated Microbial Reference Database) or created with Create Whole Metagenome Index (Create Whole Metagenome Index), are not supported.
Under Set reads parameters, the following options are available:
- Auto-detect paired distances. For paired data, this default choice will automatically calculate the distance between reads in pairs as follows:
- A sample of 100,000 reads is extracted randomly from the full data set and mapped against the reference index using a very wide distance interval.
- The distribution of distances between the paired reads is analyzed using a method that investigates the shape of the distribution and finds the 0.5% boundaries of the peak. These values make up the distance interval. If fewer than 10,000 reads are mapped as pairs, the range is calculated using the standard deviation.
- The full sample is mapped using the calculated distance interval.
- The history of the result records the distance interval used.
- Minimum seed length. The minimum number of nucleotides with which a read must map to a reference sequence for it to be considered a valid match. Increasing this value will give higher precision of called taxa (true positives). Lowering it will result in more taxa being called, but at the cost of precision (more false positives).
Apart from the Minimum seed length parameters, reads are mapped with standard read mapping parameters (see https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Mapping_parameters.html). - Adjust for read length variation. This option is recommended for data sets with varying read lengths to adjust for skewed read distribution between taxa. If checked, abundance and coverage values are adjusted by weighting the reads assigned to a taxon by the number of nucleotides mapped to the taxon. Calculation of abundance and coverage with and without this option checked is explained in Taxonomic Profiling abundance table.
