Find Best References using Read Mapping
The Find Best References using Read Mapping tool maps reads to a reference sequence list to identify the best matching reference i.e., the references for which the input reads hold more evidence.
If a host genome is provided, reads that map better to the host are filtered to not have them count toward results.
To start the tool, go to:
Tools | Microbial Genomics Module (![]() ) | Typing and Epidemiology (
) | Typing and Epidemiology (![]() ) | Find Best References using Read Mapping (
) | Find Best References using Read Mapping (![]() )
)
In the first dialog, select the sequences or sequence lists containing the sequencing reads, and click on Next.
In the References dialog, specify the following (figure 8.6):
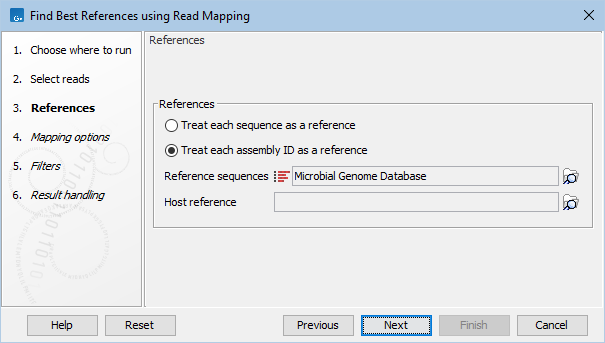
Figure 8.6: Select references.
- Treat each sequence as a reference. Each sequence makes up a separate reference.
- Treat each assembly ID as a reference. Sequences with the same assembly ID make up one reference and will be reported as such. This supports segmented references.
- Reference sequence. Select the reference sequence list.
The tool is able to handle duplicate references. If same-name references have identical sequences, only one of these will be included in analysis. If same-name references have different sequences, they will be renamed to ensure unique names. - Host reference. If relevant, provide a host reference to filter reads that map better to the host genome than to the reference sequences.
In the Mapping options dialog, specify settings for the read mapping (figure 8.7). The options are identical to those of the Map Reads to Reference tool and are described here: https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Mapping_parameters.html.
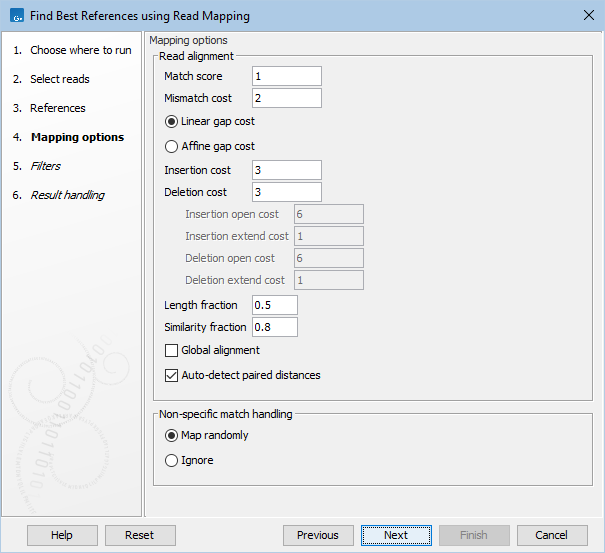
Figure 8.7: Select mapping options.
The Filters dialog holds the following options (figure 8.8):
- Minimum count. Minimum number of mapped reads required for a reference to be reported.
- Minimum relative abundance. Minimum relative abundance compared to most abundant reference required for a reference to be reported.
- Minimum fraction of reference covered. Minimum fraction of the reference sequence to be covered by at least one read for a reference to be reported.
- Minimum average coverage. Minimum average coverage for a reference to be reported. Average coverage: Number of nucleotides mapped to a reference divided by the reference length.
- Maximum number of references to report. The maximum number of references to report. References are ranked according to the number of mapped reads.
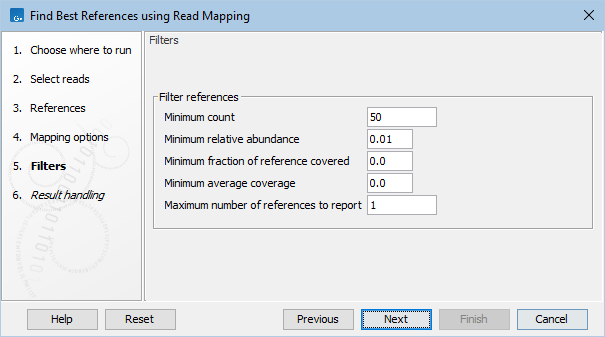
Figure 8.8: Select filtering options.
In the final step, specify the output:
- Create reference sequence list. A sequence list with the identified best-match reference sequences.
- Create reads track. A track of reads mapped to the reference sequence(s).
- Create reads track (host). A track of reads mapped to the host reference.
- Create report. A summary report (The Find Best References using Read Mapping Report).
Subsections
