Output from the Identify Variants workflow
The "Identify Variants" tool produces six different types of output:
- Read Mapping (
 ) The mapped sequencing reads. The reads are shown in different colors depending on their orientation, whether they are single reads or paired reads, and whether they map unambiguously. For the color codes please see the description of sequence colors in the CLC Genomics Workbench manual that can be found here: http://www.clcsupport.com/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=View_settings_in_Side_Panel.html.
) The mapped sequencing reads. The reads are shown in different colors depending on their orientation, whether they are single reads or paired reads, and whether they map unambiguously. For the color codes please see the description of sequence colors in the CLC Genomics Workbench manual that can be found here: http://www.clcsupport.com/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=View_settings_in_Side_Panel.html.
- Target Regions Coverage (
 ) The target regions coverage track shows the coverage of the targeted regions. Detailed information about coverage and read count can be found in the table format, which can be opened by pressing the table icon found in the lower left corner of the View Area.
) The target regions coverage track shows the coverage of the targeted regions. Detailed information about coverage and read count can be found in the table format, which can be opened by pressing the table icon found in the lower left corner of the View Area.
- Target Regions Coverage Report (
 ) The report consists of a number of tables and graphs that in different ways provide information about the targeted regions.
) The report consists of a number of tables and graphs that in different ways provide information about the targeted regions.
- Identified Variants (
 ) A variant track holding the identified variants. The variants can be shown in track format or in table format. When holding the mouse over the detected variants in the Genome Browser view a tooltip appears with information about the individual variants. You will have to zoom in on the variants to be able to see the detailed tooltip.
) A variant track holding the identified variants. The variants can be shown in track format or in table format. When holding the mouse over the detected variants in the Genome Browser view a tooltip appears with information about the individual variants. You will have to zoom in on the variants to be able to see the detailed tooltip.
- Genome Browser View Identify Variants (
 ) A collection of tracks presented together. Shows the annotated variants track together with the human reference sequence, genes, transcripts, coding regions, the mapped reads, the identified variants, and the structural variants (see figure 15.13).
) A collection of tracks presented together. Shows the annotated variants track together with the human reference sequence, genes, transcripts, coding regions, the mapped reads, the identified variants, and the structural variants (see figure 15.13).
It is important that you do not delete any of the produced files individually as some of the outputs are linked to other outputs. If you would like to delete the outputs, please always delete all of them at the same time.
Please have first a look at the mapping report to see if the coverage is sufficient in regions of interest (e.g. > 30 ). Furthermore, please check that at least 90% of reads are mapped to the human reference sequence. In case of a targeted experiment, please also check that the majority of reads are mapping to the targeted region.
Afterwards please open the Genome Browser View file (see 15.8).
The Genome Browser View includes the track of identified variants in context to the human reference sequence, genes, transcripts, coding regions, targeted regions and mapped sequencing reads.
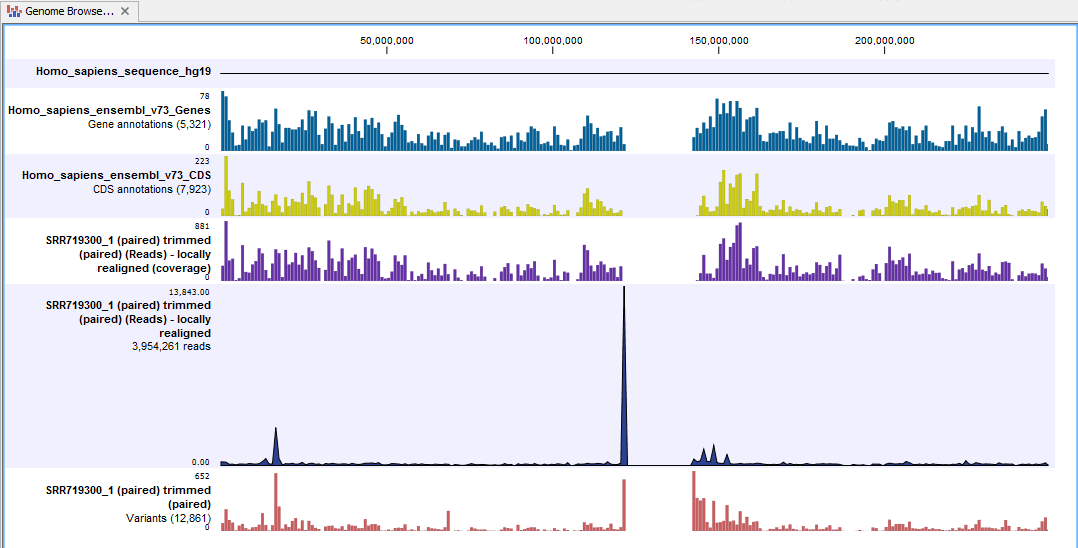
Figure 15.8: The Genome Browser View allows you to inspect the identified variants in the context of the human genome.
By double clicking on the variant track in the Genome Browser View, a table will be shown which includes information about all identified variants (see 15.9).
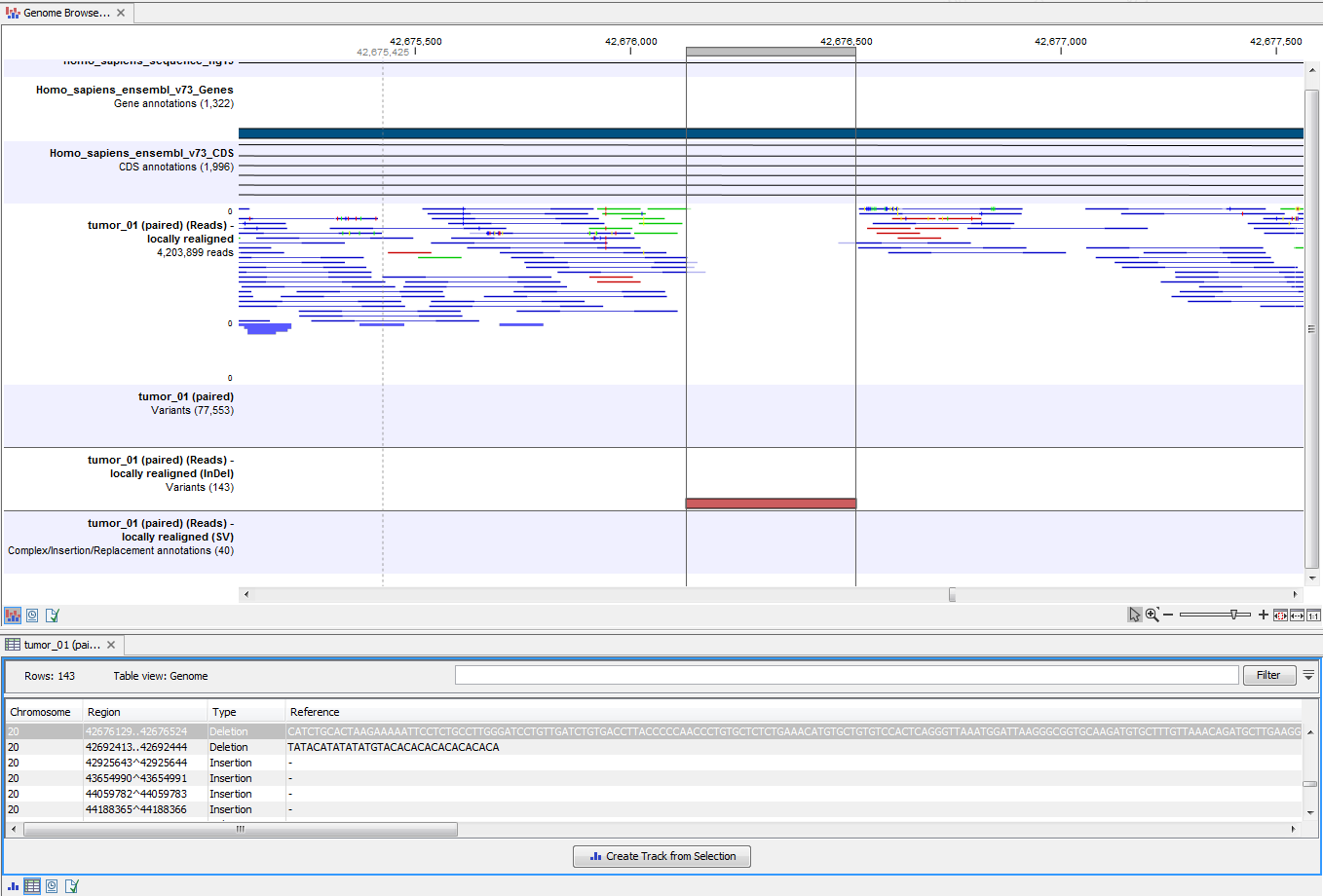
Figure 15.9: Genome Browser View with an open track table to inspect identified variants more closely in
the context of the human genome.
In case you like to change the reference sequence used for mapping as well as the human genes, please use the "Data Management".
