Create expression clones (LR)
The final step in the Gateway cloning work flow is to recombine the entry clone into a destination vector to create an expression clone, the so-called LR reaction:
Toolbox | Cloning and Restriction Sites (![]() )| Gateway Cloning (
)| Gateway Cloning (![]() ) | Create Expression Clone (
) | Create Expression Clone (![]() )
)
This will open a dialog where you can select one or more entry clones (see how to create an entry clone). If you wish to perform separate LR reactions with multiple entry clones, you should run the Create Expression Clone in batch mode.
When you have selected your entry clone(s), click Next.
This will display the dialog shown in figure 30.24.
Figure 30.24: Selecting one or more destination vectors.
Clicking the Browse (![]() ) button opens a dialog where you can select a destination vector. You can download donor vectors from Invitrogen's web site: http://tools.invitrogen.com/downloads/Gateway%20vectors.ma4 and import into the CLC Cancer Research Workbench. Note that the Workbench looks for the specific sequences of the attR sites in the sequences that you select in this dialog (see how to change the definition of sites in Technical information about modifying Gateway cloning sites). Note that the CLC Cancer Research Workbench only checks that valid attR sites are found - it does not check that they correspond to the attL sites of the selected fragments at this step. If the right combination of attL and attR sites is not found, no entry clones will be produced.
) button opens a dialog where you can select a destination vector. You can download donor vectors from Invitrogen's web site: http://tools.invitrogen.com/downloads/Gateway%20vectors.ma4 and import into the CLC Cancer Research Workbench. Note that the Workbench looks for the specific sequences of the attR sites in the sequences that you select in this dialog (see how to change the definition of sites in Technical information about modifying Gateway cloning sites). Note that the CLC Cancer Research Workbench only checks that valid attR sites are found - it does not check that they correspond to the attL sites of the selected fragments at this step. If the right combination of attL and attR sites is not found, no entry clones will be produced.
When performing multi-site gateway cloning, the CLC Cancer Research Workbench will insert the fragments (contained in entry clones) by matching the sites that are compatible. If the sites have been defined correctly, an expression clone containing all the fragments will be created. You can find an explanation of the multi-site gateway system at http://tools.invitrogen.com/downloads/gateway-multisite-seminar.html
Click Next if you wish to adjust how to handle the results. If not, click Finish.
The output is a number of expression clones depending on how many entry clones and destination vectors that you selected. The attL and attR sites have been used for the recombination, and the expression clone is now equipped with attB sites as shown in figure 30.25.
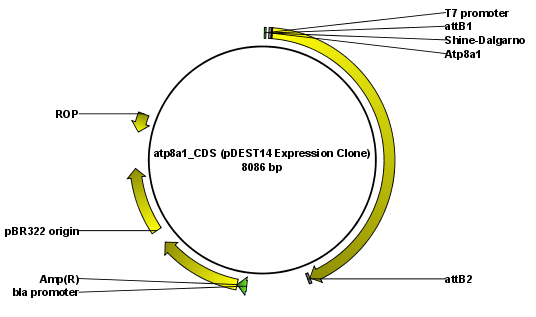
Figure 30.25: The resulting expression clone opened in a circular view.
You can choose to create a sequence list with the bi-products as well.
For a destination vector to be recognized, apart from the appropriate att sites, it must contain the ccdB gene. This must be present either as a 'ccdB' annotation, or as the exact sequence:
ATGCAGTTTAAGGTTTACACCTATAAAAGAGAGAGCCGTTATCGTCTGTTTGTGGATGTACAGAGTGATATT
ATTGACACGCCCGGGCGACGGATGGTGATCCCCCTGGCCAGTGCACGTCTGCTGTCAGATAAAGTCTCC
CGTGAACTTTACCCGGTGGTGCATATCGGGGATGAAAGCTGGCGCATGATGACCACCGATATGGCCAGT
GTGCCGGTCTCCGTTATCGGGGAAGAAGTGGCTGATCTCAGCCACCGCGAAAATGACATCAAAAACGCC
ATTAACCTGATGTTCTGGGGAATATAA
If the ccdB gene is not present or if the sequence is not identical to the above, a solution is to simply add a 'ccdB' annotation. Select the relevant part of the sequence, right-click and choose 'Add Annotation'. Name the annotation 'ccdB'.
