Sanger sequencing data
Although traditional sequencing data (with chromatogram traces like abi files) is usually imported using the standard Import (- All the sequences will be put in one sequence list (instead of single sequences).
- The chromatogram traces will be removed (quality scores remain). This is done to improve performance, since the trace data takes up a lot of disk space and significantly impacts speed and memory consumption for further analysis.
- Paired data is supported.
For all formats, compressed data in gzip format is also supported (.gz).
The dialog for importing data Sanger sequencing data is shown in figure 6.11.
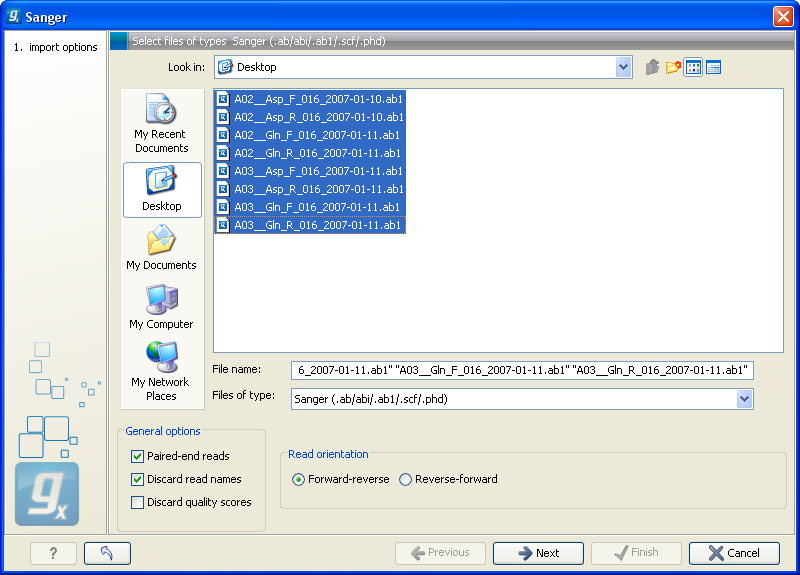
Figure 6.11: Importing data from Sanger sequencing.
The General options to the left are:
- Paired reads. The Workbench will sort the files before import and then assume that the first and second file belong together, and that the third and fourth file belong together etc. At the bottom of the dialog, you can choose whether the ordering of the files is Forward-reverse or Reverse-forward. As an example, you could have a data set with two files:
sample1_fwdfor the forward read andsample1_revfor the reverse reads. Note that you can specify the insert sizes when running the mapping and the assembly. If you have data sets with different insert sizes, you should import each data set individually in order to be able to specify different insert sizes. Read more about handling paired data. - Discard read names. For high-throughput sequencing data, the naming of the individual reads is often irrelevant given the huge amount of reads. This option allows you to discard this option to save disk space.
- Discard quality scores. Quality scores are visualized in the mapping view and they are used for SNP detection. If this is not relevant for your work, you can choose to Discard quality scores. One of the benefits from discarding quality scores is that you will gain a lot in terms of reduced disk space usage and memory consumption.
Click Next to adjust how to handle the results. We recommend choosing Save in order to save the results directly to a folder, since you probably want to save anyway before proceeding with your analysis. There is an option to put the import data into a separate folder. This can be handy for better organizing subsequent analysis results and for batch processing.
