Advanced options
The free energy minimization algorithm
includes a number of advanced options:
- Avoid isolated base pairs. The algorithm filters out isolated base pairs (i.e. stems of length 1).
- Apply different energy rules for Grossly Asymmetric Interior Loops (GAIL). Compute the minimum free energy applying different rules for Grossly Asymmetry Interior Loops (GAIL).
A Grossly Asymmetry Interior Loop (GAIL) is an interior loop that is
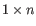 or
or 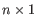 where
where 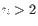 (see
http://www.bioinfo.rpi.edu/~zukerm/lectures/RNAfold-html/rnafold-print.pdf).
(see
http://www.bioinfo.rpi.edu/~zukerm/lectures/RNAfold-html/rnafold-print.pdf).
- Include coaxial stacking energy rules. Include free energy increments of coaxial stacking for adjacent helices [Mathews et al., 2004].
- Apply base pairing constraints. With base pairing constraints, you can easily add experimental constraints to your folding algorithm.
When you are computing suboptimal structures, it is not possible to
apply base pair constraints. The possible base pairing constraints
are:
- Force two equal length intervals to form a stem.
- Prohibit two equal length intervals to form a stem.
- Prohibit all nucleotides in a selected region to be a part of a base pair.
- Maximum distance between paired bases. Forces the algorithms to only consider RNA structures of a given upper length by setting a maximum distance between the base pair that opens a structure.
Subsections
