Property viewer
The Property viewer, found in the Side Panel, lists detailed information about the atoms that the mouse hovers over. For all atoms the following information is listed:- Name The particular atom name, if given in input.
- Element The element type (C, N, O,...).
- Hybridization The atom hybridization assigned to the atom.
- Charge The atomic charge as given in the input file. If charges are not given in the input file, some charged chemical groups are automatically recognized and a charge assigned.
- Molecule The name of the molecule the atom is part of.
- Chain For proteins and nucleic acids, the name of the chain the atom belongs to is listed.
- Residue For proteins and nucleic acids, the name and number of the residue the atom belongs to is listed.
For atoms in molecules imported from a PDB file, extra information is given:
- Temperature Here is listed the b-factor assigned to the atom in the PDB file. The b-factor is a measure of uncertainty or disorder in the atom position; the higher the number, the higher the disorder.
- PDB index Each atom listed in the PDB file is given an index number, which is listed in the second column of the ATOM or HETATOM entries in the PDB file.
- Source line The line number in the PDB text file where the atom information appears.
If an atom is selected, the Property view will be frozen with the details of the selected atom shown. If then a second atom is selected (by holding down Ctrl while clicking), the distance between the two selected atoms is shown. If a third atom is selected, the angle for the second atom selected is shown. If a fourth atom is selected, the dihedral angle measured as the angle between the planes formed by the three first and three last selected atoms is given.
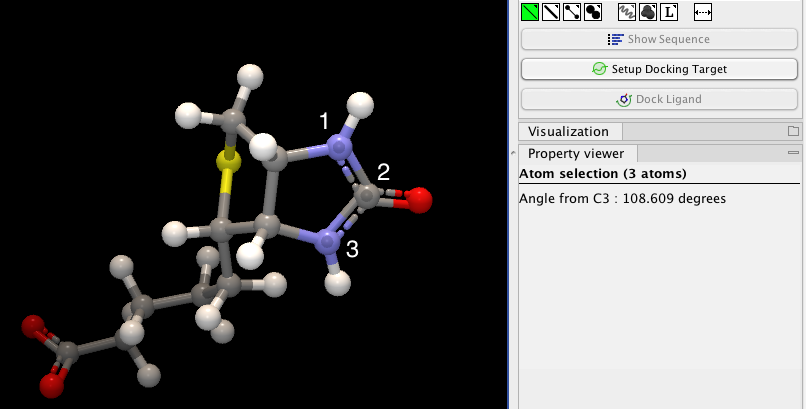
Figure 13.12: Selecting two, three, or four atoms will display the distance, angle, or dihedral angle, respectively.
If a molecule is selected in the Project Tree, the Property view shows information about this molecule:
- Atoms Number of atoms in the molecule.
- Weight The weight of the molecule in Daltons.
