Nested PCR
Nested PCR is a modification of Standard PCR, aimed at reducing product contamination due to the amplification of unintended primer binding sites (mispriming). If the intended fragment can not be amplified without interference from competing binding sites, the idea is to seek out a larger outer fragment which can be unambiguously amplified and which contains the smaller intended fragment. Having amplified the outer fragment to large numbers, the PCR amplification of the inner fragment can proceed and will yield amplification of this with minimal contamination.
Primer design for nested PCR thus involves designing two primer pairs, one for the outer fragment and one for the inner fragment.
In Nested PCR mode the user must thus define four regions a Forward primer region (the outer forward primer), a Reverse primer region (the outer reverse primer), a Forward inner primer region, and a Reverse inner primer region. These are defined by making a selection on the sequence and right-clicking the selection. If areas are known where primers must not bind (e.g. repeat rich areas), one or more No primers here regions can be defined.
It is required that the Forward primer region, is located upstream of the Forward inner primer region, that the Forward inner primer region, is located upstream of the Reverse inner primer region, and that the Reverse inner primer region, is located upstream of the Reverse primer region.
In Nested PCR mode the Inner melting temperature menu in the Primer parameters panel is activated, allowing the user to set a separate melting temperature interval for the inner and outer primer pairs.
After exploring the available primers (see Graphical display of primer information) and setting the desired parameter values in the Primer parameters preference group, the Calculate button will activate the primer design algorithm.
After pressing the Calculate button a dialog will appear (see figure 16.9).

Figure 16.9: Calculation dialog
The top and bottom parts of this dialog are identical to the Standard PCR dialog for designing primer pairs described above.
The central part of the dialog contains parameters pertaining to primer pairs and the comparison between the outer and the inner pair. Here five options can be set:
- Maximum percentage point difference in G/C content (described above under Standard PCR) - this criteria is applied to both primer pairs independently.
- Maximal difference in melting temperature of primers in a pair - the number of degrees Celsius that primers in a pair are all allowed to differ. This criteria is applied to both primer pairs independently.
- Maximum pair annealing score - the maximum number of hydrogen bonds allowed between the forward and the reverse primer in a primer pair. This criteria is applied to all possible combinations of primers.
- Minimum difference in the melting temperature of primers in
the inner and outer primer pair - all comparisons between the melting temperature of primers
from the two pairs must be at least this different, otherwise the primer set is excluded. This option is
applied to ensure that the inner and outer PCR reactions can be initiated at
different annealing temperatures. Please note that
to ensure flexibility there is no directionality indicated when
setting parameters for melting temperature differences between
inner and outer primer pair, i.e. it is not specified whether the inner pair should have a lower or higher
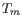 . Instead this is determined by the allowed temperature
intervals for inner and outer primers that are set in the primer
parameters preference group in the side panel. If a higher
. Instead this is determined by the allowed temperature
intervals for inner and outer primers that are set in the primer
parameters preference group in the side panel. If a higher 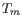 of inner primers is desired, choose a
of inner primers is desired, choose a 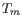 interval for inner primers which has higher
values than the interval for outer primers.
interval for inner primers which has higher
values than the interval for outer primers.
- Two radio buttons allowing the user to choose between a fast and an accurate algorithm for primer prediction.
Subsections
