Generate MSI Baseline
The Generate MSI Baseline tool can be used to generate microsatellite instability (MSI) baseline tracks that are used when running Detect MSI Status. The tool is available from the Tools menu:
Tools | Biomedical Genomics Analysis (![]() ) | Oncology Score Estimation (
) | Oncology Score Estimation (![]() ) | Generate MSI Baseline (
) | Generate MSI Baseline (![]() )
)
The tool can generate a baseline by:
- Using an annotation track containing microsatellite loci. The annotation track can be:
- A track containing specific loci targeted by the panel.
- A baseline track generated by this tool.
- Scanning the reference genome for microsatellite loci. This increases the tool's runtime.
The tool requires at least five read mappings from microsatellite stable (MSS) samples as input. For a reliable baseline we recommend at least 30 samples, since the Detect MSI Status tool uses a Z-test to compare a test sample to the baseline.
The following options can be adjusted (figure 8.7):
- MSI loci from track Generate baseline for microsatellite loci in an annotation track.
- MSI loci track An annotation track containing microsatellite loci.
Three MSI loci tracks are available in the Reference Data Manager, see QIAGEN Sets.
- msisensor2_loci_v1.0 contains 2828 mono- and dinucleotide loci from msisensor2, see https://github.com/niu-lab/msisensor2/.
- qiaseq_msi_9_loci_v1.0 contains 9 loci from the QIAseq MSI booster Panel (SDHS-10101-11981Z-48). These 9 loci are a subset of the 27 loci in qiaseq_msi_27_loci_v1.0.
- qiaseq_msi_27_loci_v1.0 contains 27 loci from the QIAseq MSI booster Panel (SDHS-10101-11981Z-48).
- MSI loci track An annotation track containing microsatellite loci.
Three MSI loci tracks are available in the Reference Data Manager, see QIAGEN Sets.
- Scan target regions or whole genome
Generate baseline for microsatellite loci that are automatically detected in the reference genome, by scanning the whole genome or just target regions.
Scanning the whole genome increases the runtime.
- Target regions track An optional annotation track containing non-overlapping target regions for scanning. Target regions can, for example, be regions in the genome that have coverage in the input MSS samples. Note that targeted DNA panels have their own specific target regions, typically covering hotspots and/or entire exons. As microsatellite loci are often intronic or intergenic, such panel target regions are generally unsuitable for scanning for microsatellite loci. Overlapping target regions can be collapsed using Collapse Overlapping Annotations, see Collapse Overlapping Annotations.
- Minimum locus length Only loci with a length equal to or greater than this value are kept.
- Maximum repeat unit size Only loci with the length of the repeat unit equal to or shorter than this value are kept. For example, 1 corresponds to only homopolymer loci.
- Minimum repeat times Only loci where the repeat unit appears at least this number of times are kept.
- Minimum read count A locus is included in the baseline if its length can be determined from at least this many reads in the input read mappings. The length can be determined when the read spans the locus and includes both the left and right flanking signatures.
- Flanking signature length The length of the flanking signatures. The flanking signature should be long enough to be unique in the read, but short enough to be present in as many reads as possible.
- Allow one mismatch in the flanking signature: When checked, the flanking signature can contain one SNP compared to the reference genome.
- Ignore broken pairs When checked, broken pairs in paired end reads are not used for baseline generation.
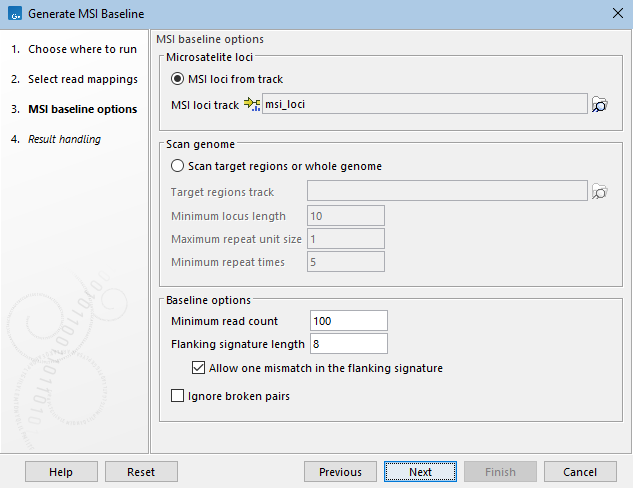
Figure 8.7: Parameters for Generate MSI Baseline.
If Scan target regions or whole genome is selected, the tool first identifies a list of candidate microsatellite loci, which are otherwise provided in the MSI loci track. Subsequently, the tool extracts all reads overlapping the loci and analyzes the locus length by identifying the flanking signatures in the reads. See Detect MSI Status for more details about how the locus length is determined. Finally, the loci are filtered in three steps. A locus is removed if:
- It does not meet the Minimum read count. The report lists the number of loci filtered out due to this under Loci with too few reads.
- One of the flanking signatures is identical to the locus sequence except for one mismatch. Such flanking signatures can lead to an incorrect locus length. The report lists the number of loci filtered out due to this under Loci with repeat unit in flanking signature.
- At least 25% of reads have a locus length of 3 bp or less. A high percentage of short locus lengths suggests that the flanking signatures have been incorrectly determined. The report lists the number of loci filtered out due to this under Loci with too many short reads.
Generate MSI Baseline outputs an MSI baseline track and a report summarizing the loci in the baseline (figure 8.8).
Undesired loci can be manually removed from the baseline track by:
- Opening its table view (
 ).
).
- Selecting the loci to be kept.
- Creating a new track using the Create Track from Selection button.
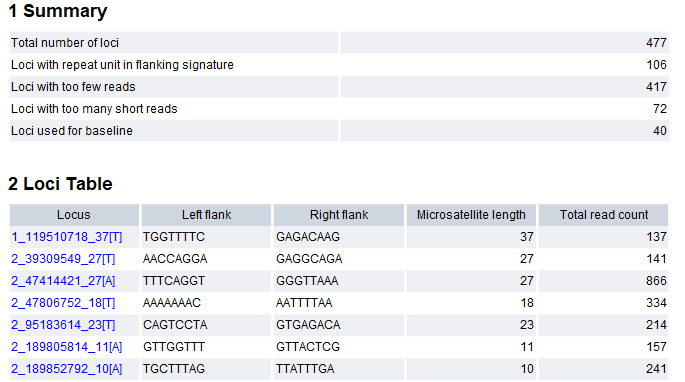
Figure 8.8: MSI baseline report obtained by scanning target regions for microsatellite sites.
The report contains a summary section with the number of unfiltered and filtered loci. The Total number of loci is either the number of loci in the provided MSI loci track, or the number of loci initially identified by scanning.
The loci table contains all loci in the baseline, with the following columns:
- Locus Locus name. This links to the plot showing the distribution of locus lengths. The name is obtained either from the provided MSI loci from track or has the form {chromosome name}_{start position}_{repeat times}[repeat unit] when scanning.
- Left flank Left flanking signature used for identifying the locus length.
- Right flank Right flanking signature used for identifying the locus length.
- Microsatellite length Length of the microsatellite locus in the reference genome.
- Total read count Total number of reads in which the locus length could be determined.
