Identify QIAseq Hybrid Capture Causal Inherited Variants in Trio
The Identify QIAseq Hybrid Capture Causal Inherited Variants in Trio template workflow is designed to support the analysis of data generated with hybrid capture QIAseq Human Exome and QIAseq xHYB Human kits. The workflow identifies putative disease causing, inherited variants in a family of three, where there is an affected parent, unaffected parent and a proband.
The first steps of the workflow involve trimming off any remaining PCR adapters. This is followed by mapping the trimmed reads to the human reference sequence. The Structural Variant Caller then generates a guidance track that is used in the Local Realignment tool to improve the mapping. The improved mapping is then input to the Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection tool. The resulting variants are filtered to remove those located outside defined target regions. Remaining variants are then annotated with information such as the relation to repeat/homopolymer regions or gene elements. Finally, a series of filtering steps removes variants likely to be artifacts.
The putative disease causing variants are identified by creating a list of variants present in both affected individuals and subtracting all variants in the unaffected individual. Additional checks are then carried out, allowing variants to be classified, for example as de novo variants, recessive variants, etc. The variants are output, along with reports and other associated results.
The Identify QIAseq Hybrid Capture Causal Inherited Variants in Trio template workflow can be found at:
Template Workflows | Biomedical Workflows (![]() ) | QIAseq Sample Analysis (
) | QIAseq Sample Analysis (![]() ) | QIAseq DNA workflows (
) | QIAseq DNA workflows (![]() ) | Identify QIAseq Hybrid Capture Causal Inherited Variants in Trio (
) | Identify QIAseq Hybrid Capture Causal Inherited Variants in Trio (![]() )
)
If you are connected to a CLC Server via the CLC Workbench, you will be asked where you would like to run the analysis. We recommend that you run the analysis on a CLC Server when possible.
Separate dialog steps are presented for providing the sample data for the proband, the affected parent and the unaffected parent. The names of the steps in the left hand side of the wizard indicate the data that should be entered in that step. For example, sequencing reads for the proband would be selected in the step shown in figure 12.32.
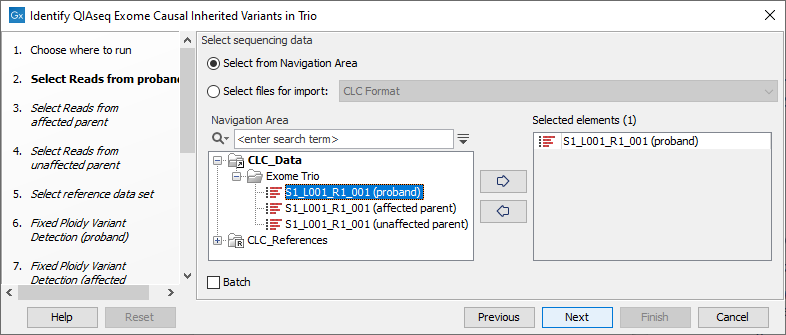
Figure 12.32: The sequence reads for the proband are specified at the "Select reads from proband" wizard step.
The following dialog helps you set up the relevant Reference Data Set. If you have not downloaded the Reference Data Set yet, the dialog will suggest the relevant data set and offer the opportunity to download it using the Download to Workbench button.
Note that if you wish to Cancel or Resume the Download, you can close the template workflow and open the Reference Data Manager where the Cancel, Pause and Resume buttons are available.
If the Reference Data Set was previously downloaded, the option "Use the default reference data" is available and will ensure the relevant data set is used. You can always check the "Select a reference set to use" option to be able to specify another Reference Data Set than the one suggested.
Both Map Reads to Reference and Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection are configured in separate dialog steps for the proband, the affected parent and the unaffected parent samples. The names of the steps in the left hand side of the wizard, and near the top of each dialog, indicate which sample the parameters apply to. For example, the first wizard steps for Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection, displayed in figure 12.33, has the word "proband" in the title near the top of the dialog.
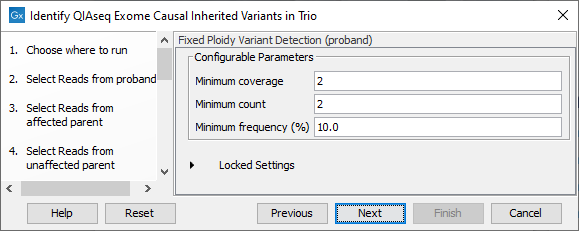
Figure 12.33: Configuration of Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection tool for the proband sample analysis. This tool is configured separately for the anlaysis of each family member.
In the Map Reads to Reference dialog, it is possible to configure masking. A custom masking track can be used, but by default, the masking track is set to GenomeReferenceConsortium_masking_hg38_no_alt_analysis_set, containing the regions defined by the Genome Reference Consortium, which serve primarily to remove false duplications, including one affecting the gene U2AF1.
The Fixed Ploidy Variant Detection settings:
- Minimum coverage: Only variants in regions covered by at least this many reads are called.
- Minimum count: Only variants that are present in at least this many reads are called.
- Minimum frequency: Only variants that are present at least at the specified frequency (calculated as 'count'/'coverage') are called.
In the next two wizard steps, individual filtering settings can be specified for SNVs and Indels for the proband.
In the final wizard step, choose to Save the results of the workflow and specify a location in the Navigation Area before clicking Finish.
Launching using the QIAseq Panel Analysis Assistant
The workflow is not available in the QIAseq Panel Analysis Assistant.
Subsections
