Output from Detect Regional Ploidy
The tool produces the following outputs:
- A locus-level ploidy track (
 ) containing all loci (CNV targets and SNPs) and their detected ploidy state.
) containing all loci (CNV targets and SNPs) and their detected ploidy state.
- A region-level ploidy track (
 ) where neighboring loci sharing the ploidy state are merged to contiguous regions.
) where neighboring loci sharing the ploidy state are merged to contiguous regions.
- A report (
 ) providing the optimized parameters, an overview of ploidy states, as well as plots for relative log coverage ratios (RLRs) and B-allele frequencies.
) providing the optimized parameters, an overview of ploidy states, as well as plots for relative log coverage ratios (RLRs) and B-allele frequencies.
Locus-level ploidy track
The table view (![]() ) shows one locus per row. In addition to standard information, it contains the following:
) shows one locus per row. In addition to standard information, it contains the following:
- Name. One of:
- Coverage ratio. The locus is a CNV target.
- B-allele frequency. The locus is a somatic SNP with a B-allele frequency, that is heterozygous in normal cells since the same SNP is found in the known variant track (germline or database).
- Reference allele. The locus is a SNP from the Variant database that is not present in the somatic variant track.
- Ploidy state. The predicted ploidy state from table 10.1.
- LOH. The LOH status.
- RLR. The relative log coverage ratio.
- The following are copied from the input tracks:
- From the target-level CNV track: Fold-change (adjusted) and p-value.
- From the somatic variant track: Count, Coverage, and Frequency.
- from the variant database, if relevant: Population frequency.
Loci not included in regions due to Centromeres, Remove outliers, Minimum loci count and/or Minimum length (Mb) are excluded from this track.
Region-level ploidy track
The table view (![]() ) shows one region per row. In addition to standard information, it contains the following:
) shows one region per row. In addition to standard information, it contains the following:
- Name. The predicted ploidy state from table 10.1.
- LOH, Minor copy number, and Major copy number. According to table 10.1.
- Number of targets. The number CNV targets included in the region.
- Number of variants. The number of somatic SNPs included in the region, as well as database SNPs without overlapping somatic variants if using Variant database.
Report
The report has the following sections:
- Parameter estimates. Contains the estimated purity, and if relevant, normalization factor, along with their confidence intervals (CI).
Low purity or a wide purity confidence interval indicates uncertain ploidy states predictions.
- Ploidy states. An overview of how many loci and regions are predicted to be in each ploidy state.
- Genomic plots. Plots for all chromosomes jointly and separately showing:
- Copy number (figure 10.7) of the predicted ploidy states, according to table 10.1.

Figure 10.7: The minor and major copy number of the predicted ploidy states for all chromosomes. - Relative log coverage ratio (figure 10.8) for the CNV targets.
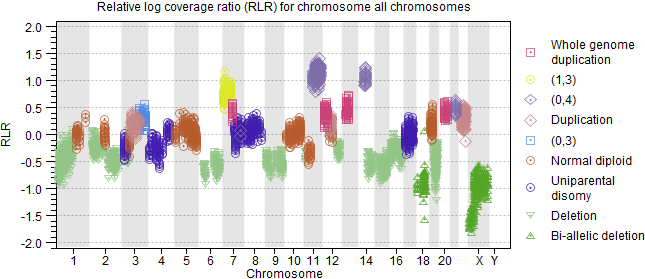
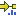
Figure 10.8: Relative log coverage ratio for the CNV targets for all chromosomes. - B-allele frequency (figure 10.9) for the somatic SNPs.

Figure 10.9: B-allele frequency for the somatic SNPs for all chromosomes.
Loci not included in regions due to Centromeres, Remove outliers, Minimum loci count and/or Minimum length (Mb) are excluded from these plots.
- Copy number (figure 10.7) of the predicted ploidy states, according to table 10.1.
- Relative log coverage ratio. Table and plot showing the expected and actual RLR for each ploidy state and CNV target plotted against the base coverage, i.e. the normalized baseline coverage (figure 10.10).
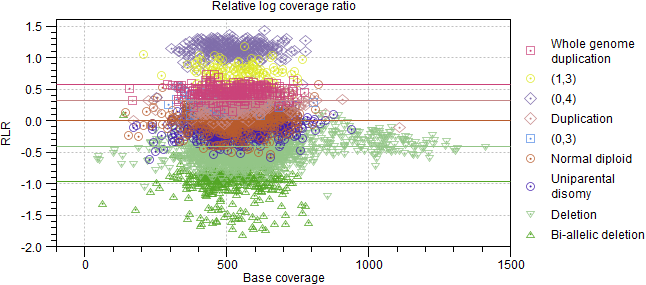
Figure 10.10: Relative log coverage ratio for each CNV target. Expected values are displayed as horizontal lines. - B-allele frequency. Table and plot showing the expected and actual B-allele frequency for each ploidy state and somatic SNP (figure 10.11).
Figure 10.11: B-allele frequency for each somatic SNP. Expected values are displayed as horizontal lines.
