Create Tree
Create Tree uses distance estimates computed from a multiple sequence alignment to create a tree. Alignments can be generated using Create Alignment or the alignment tools available in the Additional Alignments plugin, or they can be imported.
The tree can be constructed using either Neighbor Joining or UPGMA in combination with Jukes-Cantor or Kimura distance correction.
To launch Create Tree, go to:
Tools | Alignments and Trees (![]() ) | Create Tree (
) | Create Tree (![]() )
)
The tool accepts one alignment as input.
In the Tree Construction launch wizard step, select the construction method and a distance measure, and choose whether to perform bootstrapping (figure 17.2):
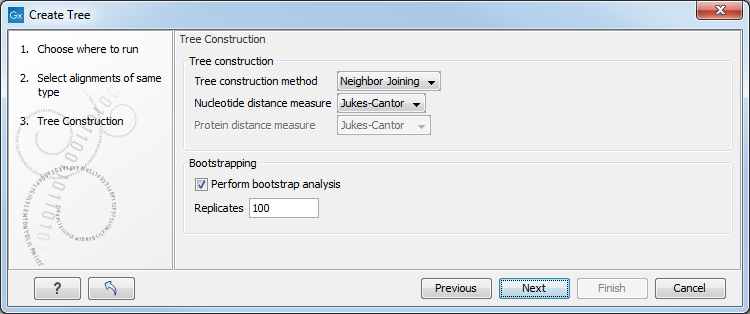
Figure 17.2: The Tree Construction launch wizard step.
- Tree construction
- Tree construction method. Specify which distance-based method to use for tree construction, Neighbor Joining or UPGMA:
- UPGMA. Assumes constant rate of evolution.
- Neighbor Joining. Well suited for trees with varying rates of evolution.
- Nucleotide distance measure.
- Jukes-Cantor. Assumes equal base frequencies and equal substitution rates.
- Kimura 80. Assumes equal base frequencies but distinguishes between transitions and transversions.
- Protein distance measure.
- Jukes-Cantor. Assumes equal amino acid frequency and equal substitution rates.
- Kimura protein. Assumes equal amino acid frequency and equal substitution rates. Includes a small correction term in the distance formula that is intended to give better distance estimates than Jukes-Cantor.
- Tree construction method. Specify which distance-based method to use for tree construction, Neighbor Joining or UPGMA:
- Bootstrapping
- Perform bootstrap analysis. Check this option to perform a bootstrap analysis.
- Replicates. The number of replicates used in the bootstrap analysis. The default value (100 replicates) is usually enough to distinguish between reliable and unreliable nodes in the tree.
