Gap costs
The Create Alignment tool has three parameters concerning gap costs:
- Gap open cost. The price for introducing gaps in an alignment.
- Gap extension cost. The price for every extension past the initial gap.
- End gap cost. The price of gaps at the beginning or the end of the alignment.
One of the advantages of the CLC Main Workbench alignment method is that it provides flexibility in the treatment of gaps at the ends of the sequences. There are three possibilities:
Considerations for configuring the gap cost parameters:
- For most alignments it is a good idea to make the "Gap open cost" quite a bit higher than the "Gap extension cost". The default values are 10.0 and 1.0 for the two parameters, respectively.
- If you expect a lot of small gaps in your alignment, the "Gap open cost" should equal the "Gap extension cost".
- If you expect few but large gaps in your alignment, the "Gap open cost" should be set significantly higher than the "Gap extension cost".
- When aligning a long sequence with a short partial sequence, it is ideal to use free end gaps, since this will be the best approximation to the situation. The many gaps inserted at the ends are not due to evolutionary events, but rather to partial data.
- Many homologous proteins have quite different ends, often with large insertions or deletions. This confuses alignment algorithms, but using the "Cheap end gaps" option, large gaps will generally be tolerated at the sequence ends, improving the overall alignment. This is the default setting of the algorithm.
- When you know that there are no biologically distinct effects at the ends of the sequences, the best option is to treat end gaps like any other gaps.
Figures 16.3 and 16.4 illustrate the differences between the different end gap costs.
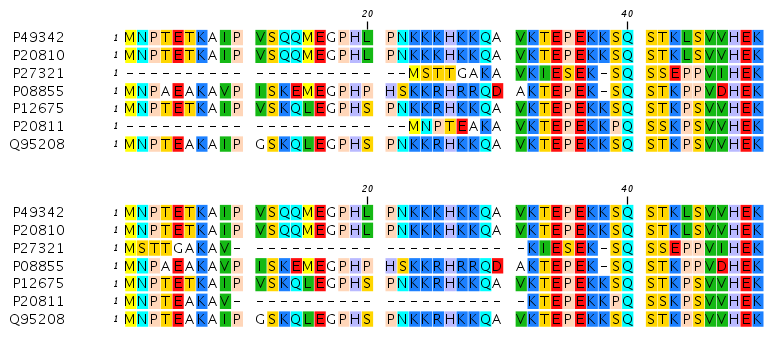
Figure 16.3: The first 50 positions of two different alignments of seven calpastatin sequences. The top alignment is made with cheap end gaps, while the bottom alignment is made with end gaps having the same price as any other gaps. In this case it seems that the latter scoring scheme gives the best result.
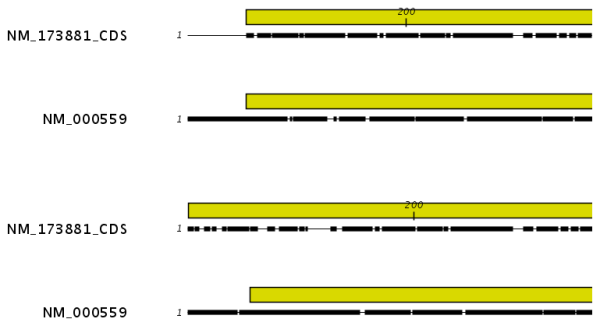
Figure 16.4: The alignment of the coding sequence of bovine myoglobin with the full mRNA of human gamma globin. The top alignment is made with free end gaps, while the bottom alignment is made with end gaps treated as any other. The yellow annotation represents the coding sequence. It is evident that free end gaps are ideal in this situation, as the start codons are aligned correctly in the top alignment. Treating end gaps as any other gaps in the case of aligning distant homologs where one sequence is partial leads to a spreading out of the short sequence as in the bottom alignment.
