Advanced filtering
Advanced filtering makes it possible to go beyond simple text searches by using structured filter criteria. Criteria can be grouped, enabling the construction of complex filters, and can also be saved for later use, either within tables or in Filter on Custom Criteria.
For general information, see Filtering tables.
Defining filter criteria
Each filter criterion consists of a column name, an operator, and a value. Filter criteria can be added by:
- Clicking the Add button.
- Right-clicking on a value in the table and choosing the Table filters option from the menu that appears. Predefined criteria for that column and value combinations are listed (figure 9.4). Selecting one of these adds it to the list of filters at the top of the table.
To remove a filter criterion, click on the (![]() ) icon, use the Delete key or choose Delete from the right-click menu. To remove all criteria, click the Clear button.
) icon, use the Delete key or choose Delete from the right-click menu. To remove all criteria, click the Clear button.
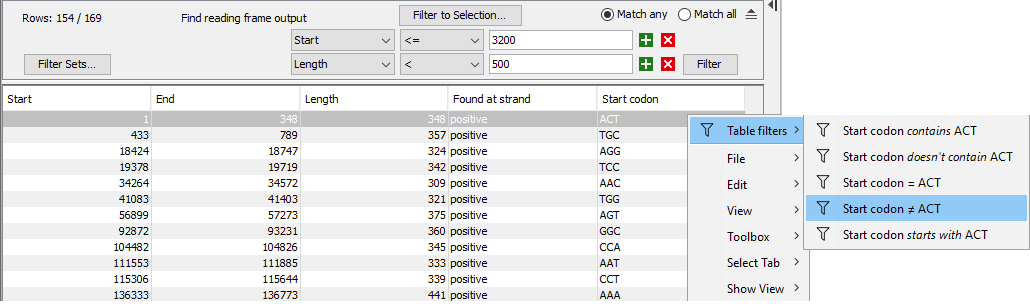
Figure 9.4: Right-click on a cell value and choose "Table filters" to reveal predefined criteria that can be added to the list of filters for this table.
The available operators depend on the column type. Columns containing numbers include comparison operators such as "<=", while columns containing text provide operators for text matching, such as "starts with". Note that:
- Text matching is case insensitive.
- Values for "is in list" and "is not in list" operators can be separated by comma, semicolon or white-space.
- The number of digits displayed after the decimal separator can be set in the View preferences. As a result, a number may have more digits than are shown in the table view. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid using the "=" operator when filtering non-integer values.
Applying filter criteria
Match all and Match any specify whether a row matches the configured filter criteria only if all criteria are satisfied, or if satisfying a single criterion is sufficient (figure 9.5). Keep and Remove specify whether rows that match the criteria are included or excluded.
The configured filter criteria, together with the Match all, Match any, Keep, and Remove options, form a filter set. The filter sets can be saved and reused. To apply the filter set to the table and show only the included rows, click the Filter button (figure 9.5).
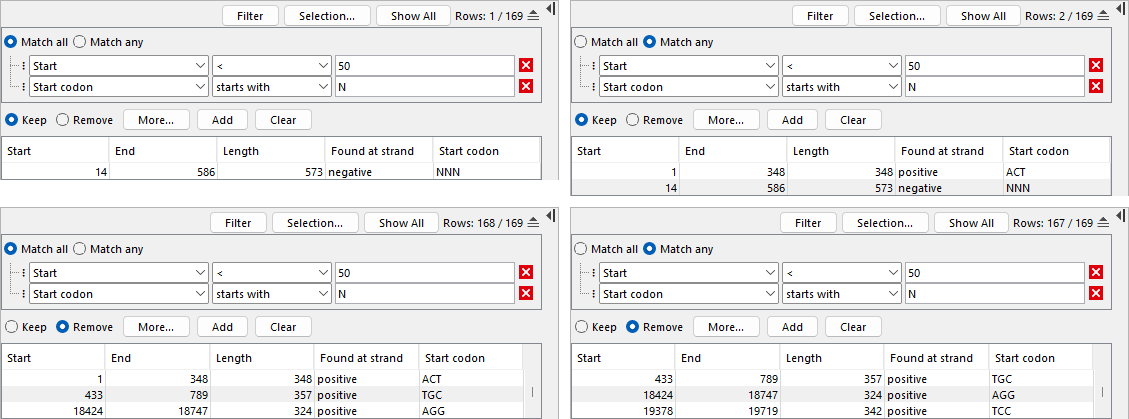
Figure 9.5: Advanced filter using two criteria. Panels show the following options. Left: "Match all". Only one row satisfies both criteria; it is visible with "Keep" (top), while the other 168 rows are visible with "Remove" (bottom). Right: "Match any". Two rows satisfy at least one criterion; they are visible with "Keep" (top), while the other 167 rows are visible with "Remove" (bottom).
Adding a match status
Click the More... button below the filter criteria, and choose Add match status to display a "Match status" column, without affecting which rows are shown (figure 9.6). The values in this column indicate if the row is included or excluded by the filter set, according to the Keep and Remove options:
- Green and empty if the row is included by the filter set.
- Red if the row is excluded by the filter set.
The column also lists:
- The criteria that are not satisfied, if Keep is selected.
- The criteria that are satisfied, if Remove is selected.
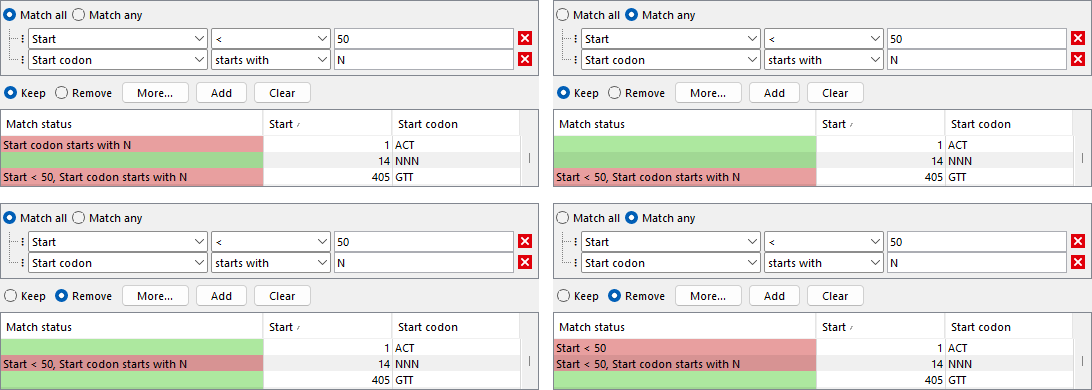
Figure 9.6: The match status of the filter set can be displayed without affecting which rows are shown. Panels show the following options. Left: "Match all". Right: "Match any". Top: "Keep". Bottom: "Remove".
The "Match status" column is only updated when clicking Add match status. This can be useful for further filtering the table to incrementally refine the filter set (figure 9.7).
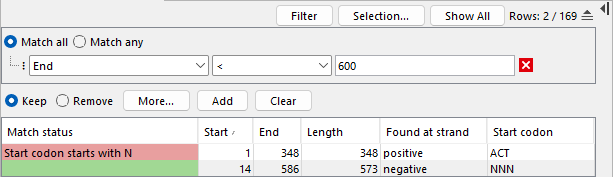
Figure 9.7: After adding the "Match status" column, the table is further filtered using a new criterion.
To show the match status for all rows when a filter set is already applied, click the Show All button. To remove the "Match status" column, click the More... button and choose Remove match status.
Adding the match status affects only the table view and does not modify the underlying table content. Use Filter on Custom Criteria to annotate certain element types non-interactively and generate a new table.
Subsections
