Extracting reads from mappings
Reads can be extracted from stand-alone read mappings in multiple ways:
- Extract from Selection. Available from the right-click menu of the reference sequence or consensus sequence (figure 21.17). A new stand-alone read mapping consisting of just the reads that are completely covered by the selected region will be created. Options are available to specify the nature of the extracted reads in the 'Specify reads to be included' wizard step, see below.
- Extract Sequences. Available from the right-click menu of the coverage graph or a read (figure 21.18), or from the Tools menu. It extracts all reads to a sequence list or individual sequences. See Extract sequences.
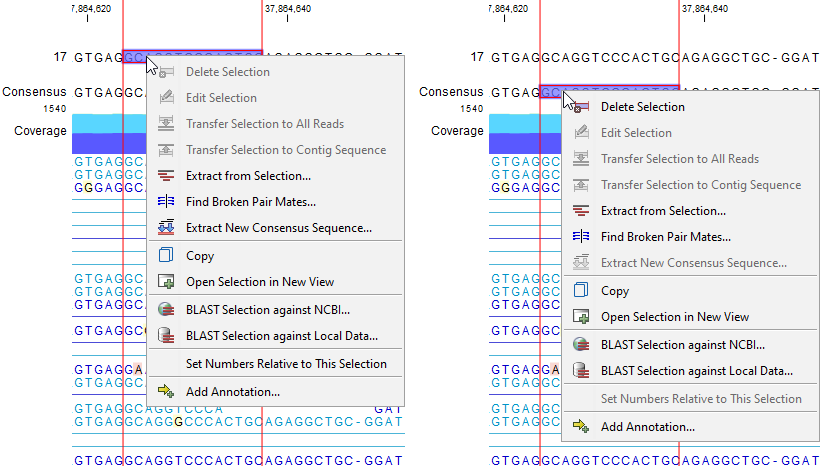
Figure 21.17: Right-click on the selected region on the reference sequence (left) or consensus sequence (right) in a stand-alone read mapping for revealing the available options.
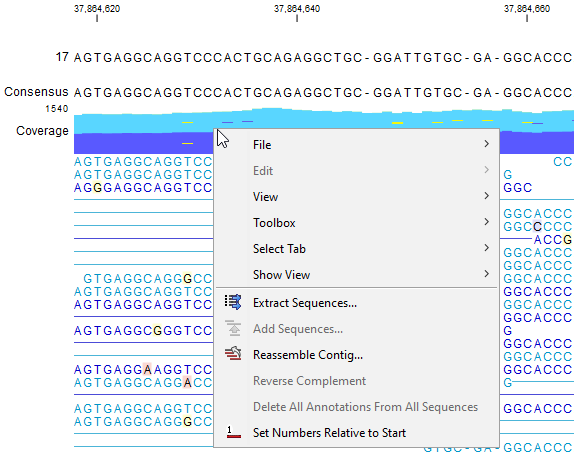
Figure 21.18: Right-click on the coverage graph or reads for revealing the available options.
The 'Specify reads to be included' wizard step of Extract from Selection offers the following options (figure 21.19):
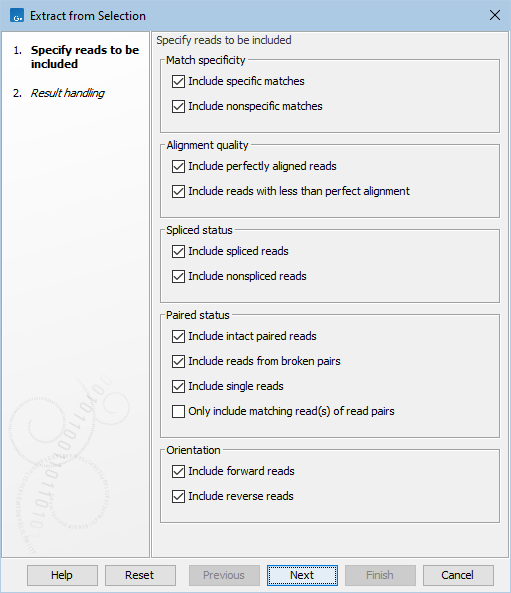
Figure 21.19: Options to include or exclude specific types of reads.
- Match specificity
- Include specific matches Reads that mapped best to just a single position of the reference genome.
- Include non-specific matches Reads that have multiple, equally good alignments to the reference genome. These reads are colored yellow by default in read mappings.
- Alignment quality
- Include perfectly aligned reads Reads where the full read is perfectly aligned to the reference genome. Reads that extend beyond the end of the reference are not considered perfectly aligned, because part of the read does not match the reference.
- Include reads with less than perfect alignment Reads with mismatches, insertions or deletions, or with unaligned ends.
- Spliced status
- Include spliced reads Reads mapped across an intron.
- Include non spliced reads Reads not mapped across an intron.
- Paired status
- Include intact paired reads Paired reads mapped within the specified paired distance.
- Include reads from broken pairs Paired reads where only one of the reads mapped, either because only one read in the pair matched the reference, or because the distance or relative orientation of its mate was wrong.
- Include single reads Reads marked as single reads (as opposed to paired reads). Reads from broken pairs are not included. Reads marked as single reads after trimming paired sequence lists are included.
- Only include matching read(s) of read pairs If only one read of a read pair matches the criteria, then only include the matching read as a broken pair. For example if only one of the reads from the pair is inside the overlap region, then this option only includes the read found within the overlap region as a broken read. When both reads are inside the overlap region, the full paired read is included. Note that some tools ignore broken reads by default.
- Orientation
- Include forward reads Reads mapped in the forward direction.
- Include reverse reads Reads mapped in the reverse direction.
Note that excluding forward or reverse reads will generate broken pairs if reads in pairs are mapped in opposite directions, regardless of the Only include matching read(s) of read pairs option.
