Model Testing
Model Testing is used to determine the best substitution model for tree building using Maximum Likelihood Phylogeny.
The Model Testing tool offers four different statistical analyses:
- Hierarchical likelihood ratio test (hLRT)
- Bayesian information criterion (BIC)
- Minimum theoretical information criterion (AIC)
- Minimum corrected theoretical information criterion (AICc)
to test the substitution models:
- Jukes-Cantor
- Felsenstein 81
- Kimura 80
- HKY
- GTR (also known as the REV model)
To launch Model Testing, go to:
Tools | Alignments and Trees (![]() ) | Model Testing (
) | Model Testing (![]() )
)
Select the same alignment that will be used for tree construction using Maximum Likelihood Phylogeny.
In the Model Testing launch wizard step, configure the model testing options (figure 17.3):
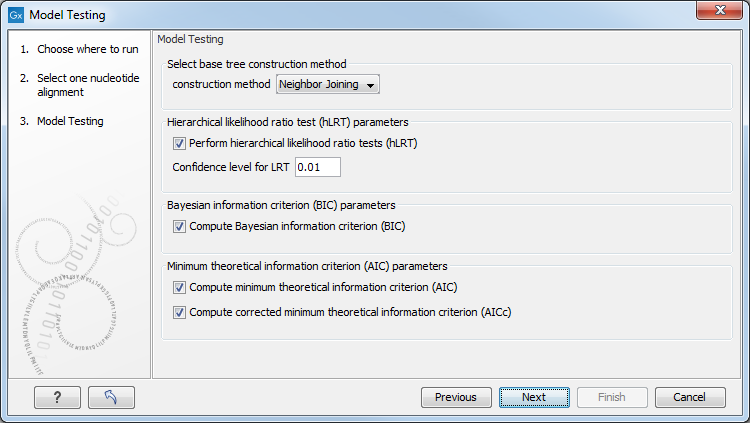
Figure 17.3: Specify parameters for model testing.
- Select base tree construction method
- Tree construction method. The distance-based method to use for construction of a base tree (a guiding tree), Neighbor Joining or UPGMA. The topology of the base tree is used in the hierarchical likelihood ratio test (hLRT), and the tree is used as the starting point for topology exploration in Bayesian information criterion (BIC), Akaike information criterion (or minimum theoretical information criterion) (AIC), and AICc (AIC with a correction for the sample size) ranking.
- UPGMA. Assumes constant rate of evolution.
- Neighbor Joining. Well suited for trees with varying rates of evolution.
- Tree construction method. The distance-based method to use for construction of a base tree (a guiding tree), Neighbor Joining or UPGMA. The topology of the base tree is used in the hierarchical likelihood ratio test (hLRT), and the tree is used as the starting point for topology exploration in Bayesian information criterion (BIC), Akaike information criterion (or minimum theoretical information criterion) (AIC), and AICc (AIC with a correction for the sample size) ranking.
- Hierarchical likelihood ratio test (hLRT) parameters
- Perform hierarchical likelihood ratio test (hLRT). A statistical test of the goodness-of-fit between two models that compares a relatively more complex model to a simpler model to see if it fits a particular dataset significantly better.
- Confidence level for LRT. The confidence level used in the likelihood ratio tests.
- Bayesian information criterion (BIC) parameters
- Compute Bayesian information criterion (BIC). Rank substitution models based on Bayesian information criterion (BIC). Formula used is BIC = -2ln(L)+Kln(n), where ln(L) is the log-likelihood of the best tree, K is the number of parameters in the model, and ln(n) is the logarithm of the length of the alignment.
- Minimum theoretical information criterion (AIC) parameters
- Compute minimum theoretical information criterion (AIC). Rank substitution models based on minimum theoretical information criterion (AIC). Formula used is AIC = -2ln(L)+2K, where ln(L) is the log-likelihood of the best tree, K is the number of parameters in the model.
- Compute corrected minimum theoretical information criterion (AIC). Rank substitution models based on minimum corrected theoretical information criterion (AICc). Formula used is AICc = -2ln(L)+2K+2K(K+1)/(n-K-1), where ln(L) is the log-likelihood of the best tree, K is the number of parameters in the model, n is the length of the alignment. AICc is recommended over AIC roughly when n/K is less than 40.
The output from Model Testing is a report that lists all test results in table format. For each tested model, a recommendation is made whether to use rate variation or not. Topology variation is recommended in all cases. The statistical test results usually agree on the models to recommend, although differences may occur.
The most appropriate model for downstream use will generally be the one identified as the best by the most tests.
