Extract consensus sequence
For all kinds of read mappings, including those generated from de novo assembly or RNA-seq analyses, a consensus sequence can be extracted. In addition, you can extract a consensus sequence from a BLAST result as well. The consensus sequence extraction tool can be run in batch and as part of workflows.
To start the tool:
Toolbox | NGS Core Tools (![]() ) | Extract Consensus Sequence (
) | Extract Consensus Sequence (![]() )
)
This opens a dialog where you can select mappings,either in the form of tracks or read mappings, or BLAST results. Click Next to specify how the consensus sequence should be created (see figure 25.34).
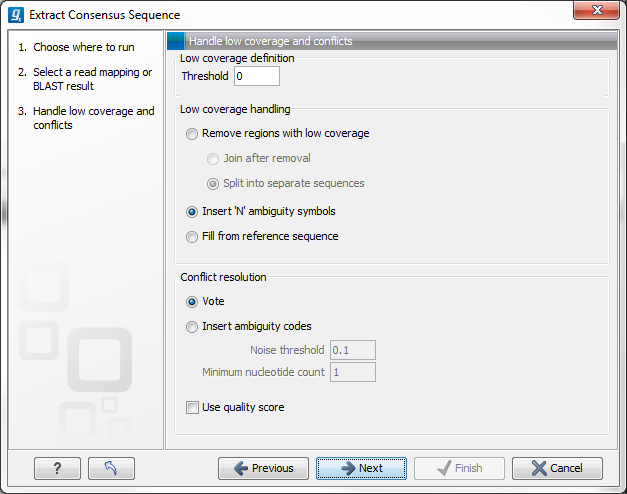
Figure 25.34: Specifying how the consensus sequence should be extracted.
It is also possible to extract a consensus sequence from a mapping view by right-clicking the name of the consensus or reference sequence or a selection on the reference sequence and select Extract Consensus Sequence (![]() ).
).
When extracting a consensus sequence, you can decide how to handle regions with low coverage (a definition of coverage can be found in Reference sequence statistics). The first step is to define a threshold for when coverage is considered low. The default value is 0, which means that low coverage is defined as no coverage (i.e. no reads align to the reference at this position). That means if you have one read covering a given position, it will only be that read that determines the consensus sequence. If you need to place higher confidence that the consensus sequence is correct, we advice to raise this value, to only construct a consensus sequence when there are more reads supporting it.
When the low coverage threshold is defined, there are several options for handling the low coverage regions:
- Remove regions with low coverage. When using this option, no consensus sequence is created for the low coverage regions. There are two ways of creating the consensus sequence from the remaining contiguous stretches of high coverage: either the consensus sequence is split into separate sequence when there is a low coverage region, or the low coverage region is simply ignored, and the high-coverage regions are directly joined (in this case, an annotation is added at the position where a low coverage region is removed in the consensus sequence produced, see below).
- Insert 'N' ambiguity symbols. This will simply add Ns for each base in the low coverage region. An annotation is added for the low coverage region in the consensus sequence produced (see below).
- Fill from reference sequence. This option will use the sequence from the reference to construct the consensus sequence for low coverage regions. An annotation is added for the low coverage region in the consensus sequence produced (see below).
In addition to deciding how to handle low coverage regions, you can also decide how to handle conflicts or disagreement between the reads:
- Vote. Whenever the reads disagree on the base at a given position, the vote resolution will let the majority of the reads decide which base is correct. In addition, you can specify to let the voting use the base calling quality scores from the reads. This is done be simply adding all quality scores for each base and let the sum determine which one is correct.
- Insert ambiguity codes. The problem with the voting option is that it will not be able to represent true biological heterozygous variation in the data. For a diploid genome, if two different alleles are present in an almost even number of reads, only one will be represented in the consensus sequence. With the option to insert ambiguity code, this can be solved. (The IUPAC ambiguity codes used can be found in the Appendix.) However, if an ambiguity code would always be inserted if just one read had a different base, there would be an ambiguity code whenever there was a sequencing error. In high-coverage NGS data that would be a big problem, because sequencing errors would be abundant. To solve this problem, you can specify a Noise threshold. The default value for this is 0.1 which means that for a base to contribute to the ambiguity code, it must be in at least 10 % of the reads at a given position. The Minimum nucleotide count specifies the minimum number of reads that are required before a nucleotide is included. Nucleotides below this limit are considered noise.
- Use quality score. In addition, you can select to use the base calling quality scores from the reads. This is done by simply adding all the quality scores for each base and let the sum determine which bases to consider.
Click Next to set the output option as shown in figure 25.35).
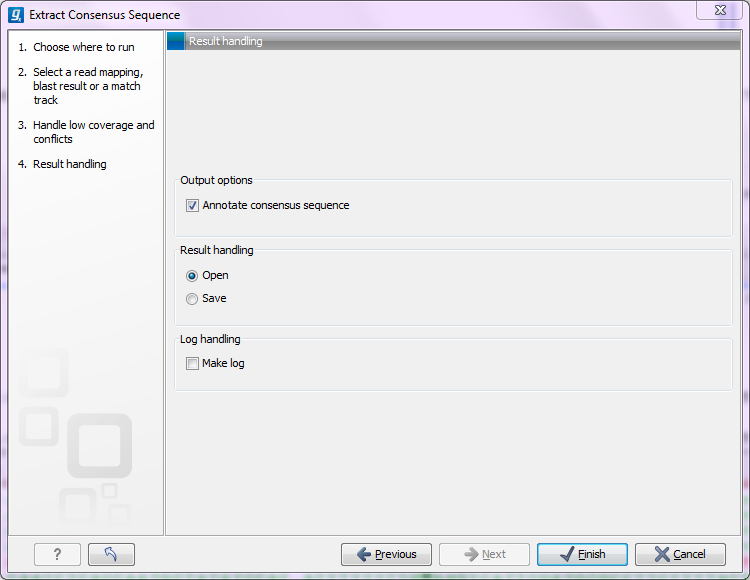
Figure 25.35: Choose to add annotations to the consensus sequence.
The annotations that can be added to the consensus sequence produced by this tool show both conflicts that have been resolved and low coverage regions (unless you have chosen to split the consensus sequence). Please note that for large data sets, this can amount to a very high number of annotations which will cause the tool to take longer time to complete, and the result will take up much more disk space.
Click Next if you wish to adjust how to
handle the results. If not, click Finish.
.
