Sanger sequencing data
The Sanger High-Throughput Sequencing Data Import tool is designed to handle the large volumes of Sanger data. Formats supported are ab, abi, ab1, scf and phd. Compressed data in gzip format is also supported (.gz).
Sanger sequencing data can also be imported using the standard Import (![]() ) tool (Import bioinformatics data). The following are key differences of the high throughput importer when compared to the standard importer:
) tool (Import bioinformatics data). The following are key differences of the high throughput importer when compared to the standard importer:
- It is designed to handle large volumes of data efficently.
- A given batch of sequences is imported to a single sequence list. The standard importer creates a single sequence element for each imported sequence.
- The chromatogram traces are removed (quality scores remain). This improves performance; trace data takes up a lot of disk space, and this can impact speed and memory consumption of downstream analyses.
- Paired reads are supported.
Sanger data can also be imported during a workflow run using on-the-fly import, described in Launching workflows individually and in batches. Both the standard importer ("Trace files") and the high throughput importer ("Sanger") are available using the on-the-fly import.
The configuration step when using the high throughput Sanger importer is shown in figure 7.14.
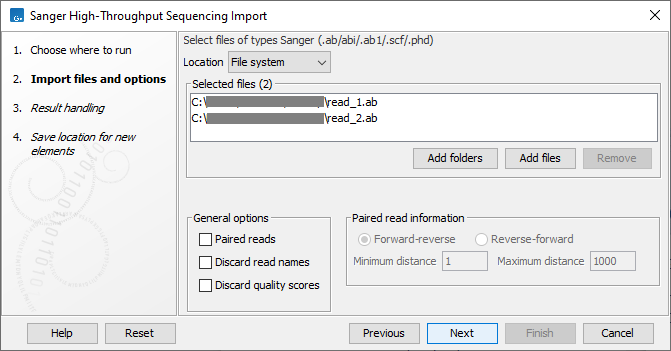
Figure 7.14: Selecting input and configuring a high throughput Sanger import
Configuring the import:
- Paired reads Import pairs of reads into a single sequence list. When enabled, the files selected for import will be sorted, and then the first and second file will be imported together as paired reads, the third and fourth file will be imported together as paired reads, etc. The selection of "Forward-reverse" or "Reverse-forward" in the "Paired read information" area determines whether the first file is treated as containing forward reads and the second file reverse reads, or vice versa. As an example, with two files:
sample1_fwdcontaining forward reads andsample1_revcontaining reverse reads, and selecting the "Forward-reverse" option, you would get a single sequence list, marked as containing paired reads, with the pairs in the expected orientation. Insert sizes can also be specified, using the "Minimum distance" and "Maximum distance" settings. Data sets with different insert sizes should be imported separately. Read more about handling paired data. - Discard read names Selecting this option saves disk space. Names of individual sequences are often irrelevant in large datasets.
- Discard quality scores Selecting this option can save substantial space, and can decrease memory consumption for downstream activities. Quality scores should be retained if they are relevant to your work. For example, quality scores are used for variant detection and can (optionally) be seen displayed in views of read mappings.
The next wizard step provides some options for handling the results. When the option to "Create subfolders per batch unit" is enabled, each sequence list created will be put into its own subfolder. This can be helpful for running analyses in batches and for organizing the results of subsequent analyses.
