MGI/BGI
Choosing the MGI/BGI import will open the dialog shown in figure 7.16. This data type can also be imported using the on-the-fly import functionality available in workflows, described in Launching workflows individually and in batches.
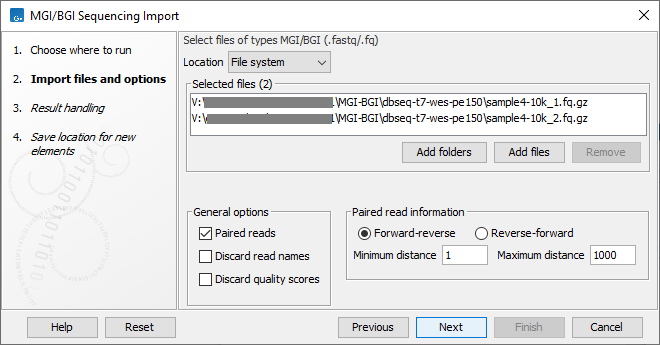
Figure 7.16: Importing data from MGI/BGI.
The following file formats from the MGI and BGI systems can be imported:
- Fastq (
.fastq/.fq). Quality scores are expected to be in the NCBI/Sanger format (see Quality scores in the Illumina platform). Compressed data in gzip format is also supported (.gz).
The General options to the left are:
- Paired reads. The Workbench will pair up files based on the names of the first read. At the bottom of the dialog, you can choose if read 1 and read 2 are Forward-reverse or Reverse-forward. As an example, you could have a data set with two files where the names of the first reads are
@sample1/1and@sample1/2. With Forward-reverse ordering the reads from the file with@sample1/1are forward and the reads from the file with@sample1/2are reverse. Note that you can specify the insert sizes when importing paired read data. If you have data sets with different insert sizes, you should import each data set individually in order to be able to specify different insert sizes. Read more about handling paired data. - Discard read names. For high-throughput sequencing data, the naming of the individual reads is often irrelevant given the huge amount of reads. This option allows you to discard this option to save disk space.
- Discard quality scores. Quality scores are visualized in the mapping view and they are used for SNP detection. If this is not relevant for your work, you can choose to Discard quality scores. One of the benefits from discarding quality scores is that you will gain a lot in terms of reduced disk space usage and memory consumption.
