Downloading reads and metadata from SRA
At the bottom of the SRA results table are two buttons: Download Reads and Metadata and Show Metadata for Selection. The functionality of each is described in this section.
Download Reads and Metadata
Select the rows of interest in the results table and then click on Download Reads and Metadata to download and import reads and metadata from the selected runs.
Reads are imported into sequence lists. Import settings for reads from runs marked as paired are configurable, including the option to import technical reads in addition to biological reads.
Metadata is imported into a CLC Metadata Table. Each sequence list will have an association to the relevant row of the CLC Metadata Table. See Finding data elements based on metadata for details about data associations with CLC Metadata Tables. The CLC Metadata Table can be used directly to define the experimental design for differential expression analyses (Differential Expression for RNA-Seq) or edited, if desired (Editing Metadata tables).
Note: When the "Auto paired end distance detection" option is present in downstream analyses of paired data downloaded from SRA, we recommend it is enabled. This is because some SRA entries have an insert size that includes the length of the reads, while others exclude the length of the reads.
After clicking on Download Reads and Metadata, a wizard appears to guide you through the import of the selected runs.
Import Options
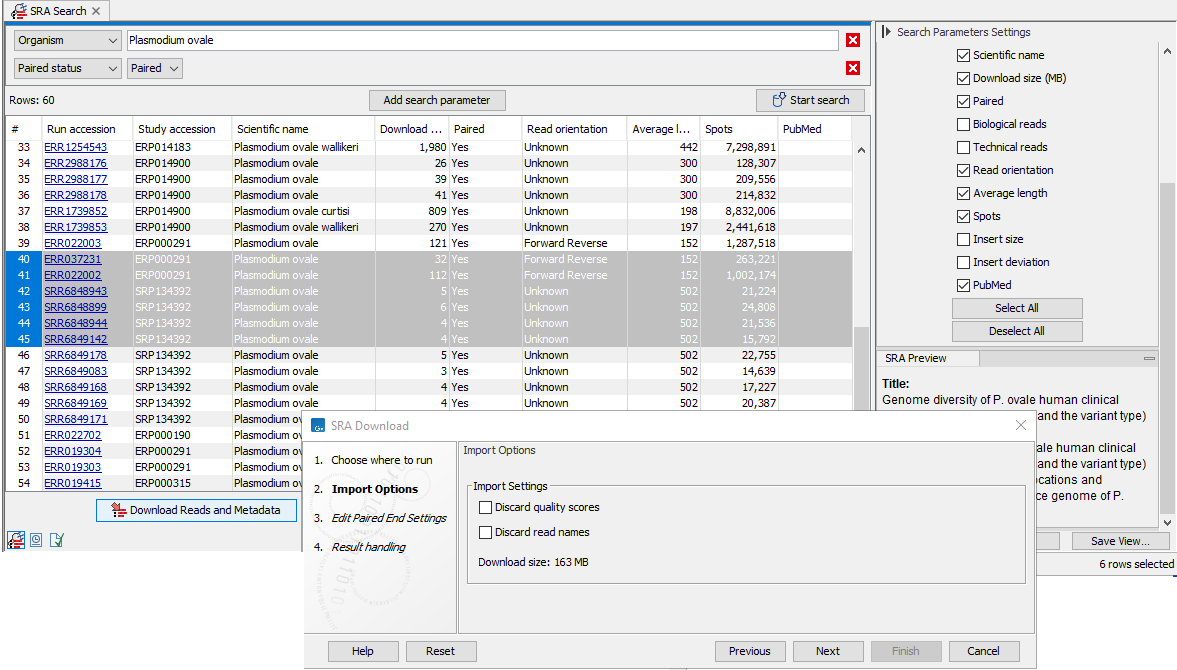
Figure 8.7: Import options in the SRA Download wizard
- Discard read names Check this option to save disk space. Individual read names are rarely relevant for NGS data.
- Discard quality scores Checking this option can reduce disk space usage and memory consumption. This should only be done if these scores are not relevant to your work. Quality scores are not used for RNA-Seq and expression analyses, but are used during variant detection and can be shown in views of read mappings.
Space requirements
During download and import: The Download size reported is the combined size of all the SRA format files that will be retrieved.
We recommend that at least twice the download size of the largest sample is available as temporary space during download and import.
If the SRA file is reference-compressed, a copy of the genome must also be retrieved before the reads can be imported, which will also require disk space.
For the imported data: The size of the sequence lists after import will often be comparable in size to the SRA files downloaded (often between half to twice the size). The size depends on multiple factors, including whether compression has been turned off, whether read names and quality scores were retained, and whether you imported technical reads as well as biological reads, where relevant.
A few examples of SRA file sizes relative to imported sequence list sizes are given below. Relative sizes may differ on your system depending on your settings.
| Description | SRA file | After import, with read names and qual. scores | After import, no read names or quality scores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single end reads | 84 MB | 110 MB | 32 MB |
| Paired end biological reads | 107 MB | 138 MB | 59 MB |
| 2 technical reads and 1 biological read, only the biological imported | 1311 MB | 760 MB | 208 MB |
Edit Paired End Settings
If at least one of the selected runs is marked as paired, the next wizard step allows you to review and edit the paired end settings (figure 8.8).Values in shaded cells can be configured by selecting rows and clicking on the "Edit Selected Rows" button. The settings in the edit dialog when you click on OK are applied to all the selected rows, so we recommend selecting either a single row, or sets of rows where the information should be the same.
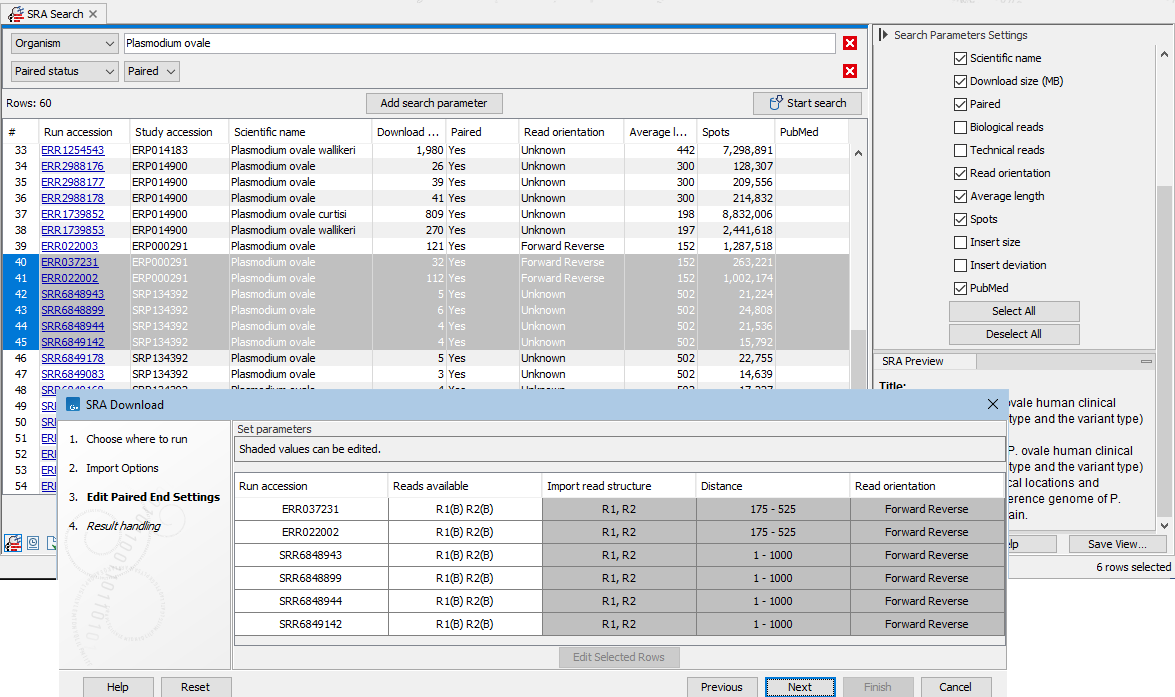
Figure 8.8: Paired end information includes the reads available for that run, as well as the read structure, distance and read orientation. Values in shaded cells can be configured by selecting rows and clicking on the "Edit Selected Rows" button.
- Reads available Most entries consist of two reads, both biological (figure 8.8). These are presented as
R1(B) R2(B), where B stands for "biological".When there are 3 or more reads, 1 or 2 of these are expected to be biological. E.g.
I1(T) R1(B) R2(T) R3(B)(figure 8.10).Mouse over a cell in the Reads available column to see details about the reads, including the number of reads, their average length and the standard deviation of the length (figure 8.11).
- Import read structure Importing just biological reads is the default. To configure this setting, specify the reads to import using the names given in the "Reads available" column, e.g.
I1,R1, etc. Use a space to separate reads that should be concatenated on import. Use a comma to separate reads to import as the first sequence in a pair and reads to import as the second sequence in a pair.For example:
R2, R1A sequence list containing paired reads is imported. The first member of each pair is from R2 and the second from R1.I1 R1 R2A sequence list containing single reads is imported. Each sequence in the list is a concatenation of I1, R1 and R2, in that order (figure 8.12).R2 R1, R3A sequence list containing paired reads is imported. The first member of each pair is a concatenation of R2 and R1, in that order. The second member is the corresponding R3 read. This could represent a situation where R1 contains forward reads, R3 contains reverse reads, and R2 contains molecular indices.
If "Use SRA Defaults" appears in this column, we recommend explicitly defining the read structure. See Troubleshooting SRA downloads for further details.
- Distance The minimum and maximum distance depend on whether an "Insert Size" and an "Insert Deviation" were supplied to SRA by the depositor.
- If no insert size was supplied, we set the minimum to 1 and the maximum to 1,000.
- If an insert size was supplied, we do the following calculation:
-
- If no deviation was supplied, we estimate this to be
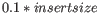 and perform the same calculation as above.
and perform the same calculation as above.
- Read orientation The orientation to use when importing paired reads.
For runs marked as paired with 2 biological reads per spot and no read structure information, we use the SRA default, which is to handle the reads as Forward Reverse pairs (figure 8.8).
N/A values in the Distance and Read orientation columns are expected when only one of the reads is biological (figure 8.9). If the read structure is edited such that paired reads will be imported, values will appear in these columns.
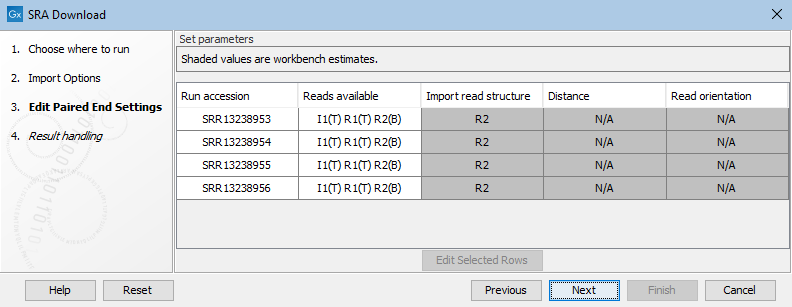
Figure 8.9: Only R2 is biological, so by default a sequence list containing single sequences from R2 would be imported.
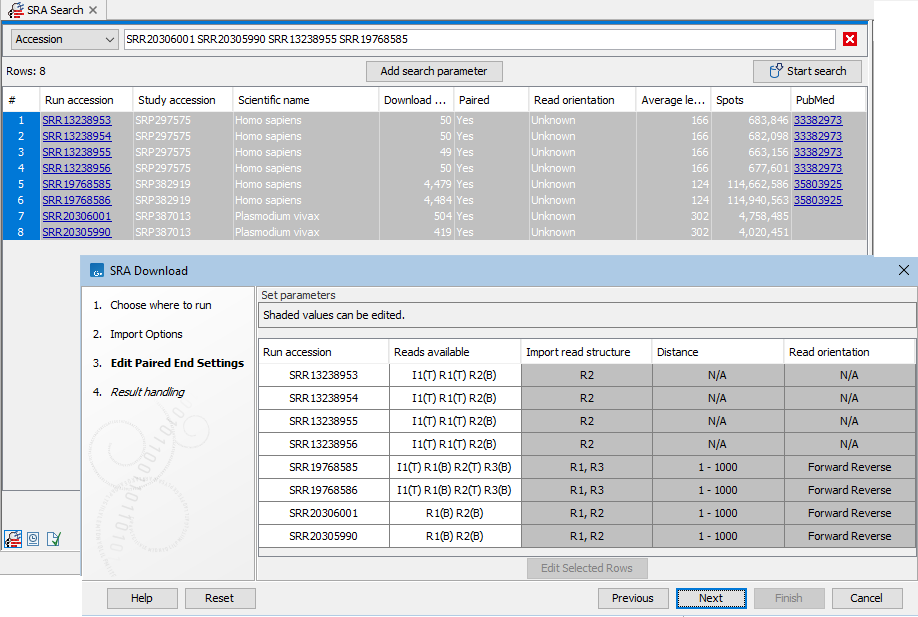
Figure 8.10: Paired end information includes the reads available for that run, as well as the read structure, distance and read orientation. Reads specified as technical by the SRA submitter are marked with (T), while other reads are marked with (B) for biological. The first 4 entries listed in the SRA Download wizard are examples for runs marked as paired with only one read specified as biological. These are imported as single end reads by default.
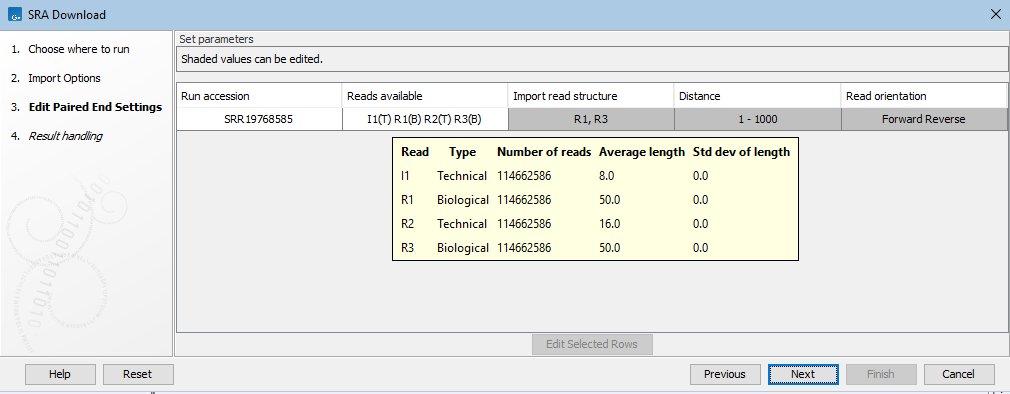
Figure 8.12: Mousing over an entry in the Reads available column in the Edit Paired End Settings wizard step reveals a tooltip with details for each read in that run.
When the settings match your expectations, click on Next to select where to save the data, and then start the download.
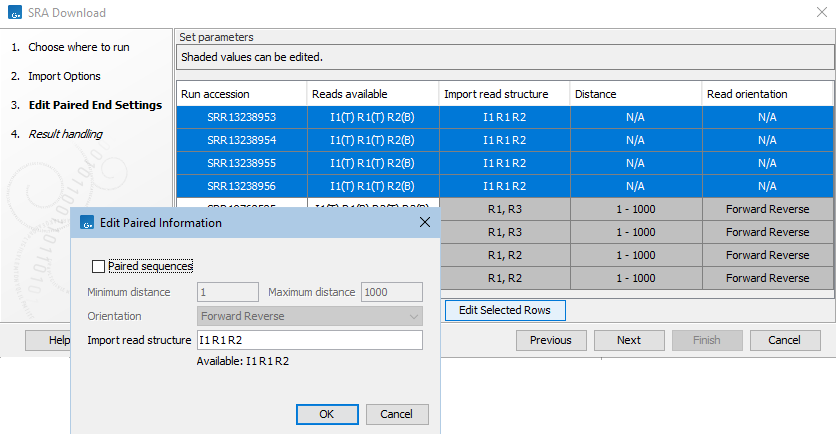
Figure 8.11: The read structure for import has been edited in the first 4 entries listed in the SRA Download wizard, using the settings shown in the Edit Paired Information dialog. Technical reads from I1 and R1 will be prepended to R2 reads and these sequences imported into a single end sequence list.
Show Metadata for Selection
Information about SRA entries of interest can be downloaded to a CLC Metadata Table without downloading the sequence data. Select the rows of interest in the results table and then click on Show Metadata for Selection. Sequence data can be downloaded later if desired.
The first columns of the resulting CLC Metadata Table contain the same database identifiers as in the original results table. Later columns contain details associated with the biosample, which are pulled from SRA. In the side panel, to the right, the columns to show in the table can be configured.
Tips relating to retrieving sequence data later using the CLC Metadata Table:
- CLC Metadata Tables can be filtered so that only relevant rows are shown (Filtering tables).
- To copy just the accessions from the visible rows in the table, and retrieve these entries from SRA:
- Select only the "Run Accession" column in the side panel settings. (It can be fastest to click on the "Deselect All" button at the bottom of the column listing in the side panel and then re-select Run Accession.)
- Select all the rows and then go to Edit | Copy in the top level menu (or use Ctrl + C).
- In Search for Reads in SRA, choose "Accession" in the search options area and paste the copied accessions into that field using Edit | Paste from the top level menu (or use Ctrl + V).
- Remove the text "Run Accession" from the start of the pasted text.
- Run the search at SRA.
- Downloading reads using Search for Reads in SRA creates a new CLC Metadata Table with the resulting sequence lists associated to the relevant rows. Sequence lists can be associated with any CLC Metadata Table you wish. For more details, see Associating data elements with metadata.
