Create Mapping Graph
The Create Mapping Graph tool can create a range of different graphs from a read mapping track. To run the tool go to the toolbox:
Toolbox | Utility Tools (![]() ) | Tracks (
) | Tracks (![]() ) | Graphs (
) | Graphs (![]() ) | Create Mapping Graph (
) | Create Mapping Graph (![]() )
)
Select the read mapping as shown in figure 25.31 and click on the button labeled Next.
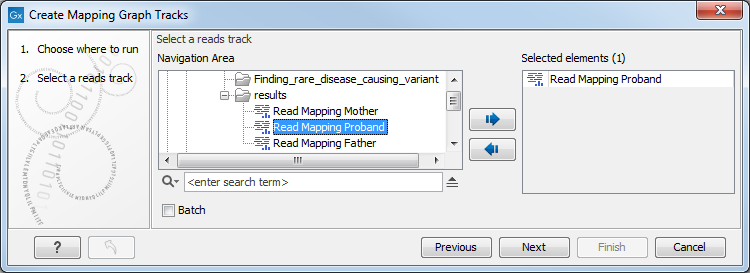
Figure 25.31: Mapping graph tracks containing different types of information can be created.
Select the graph track types to create, as shown in figure 25.32. One graph track is created for each type selected.
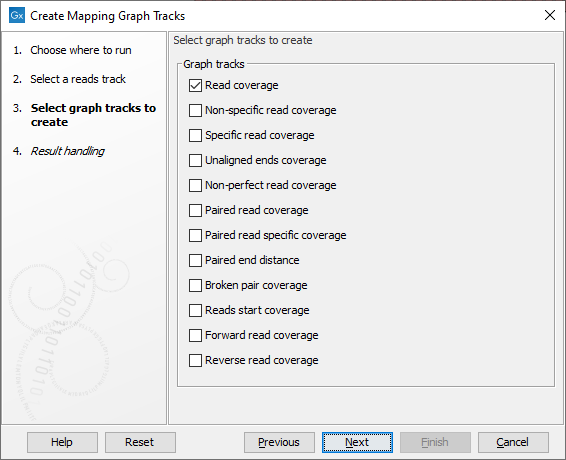
Figure 25.32: Choose the types of graph tracks to be created.
Each position in a graph track contains the values of the track type selected. These are:
- Read coverage The number of reads contributing to the alignment at the position. A more detailed definition is in Reference sequence statistics.
- Non-specific read coverage The number of reads mapped at the position that would map equally well to other places in the reference sequence.
- Specific read coverage The number of reads that map uniquely at the position, i.e. they do not map equally well to other places in the reference sequence.
- Unaligned ends coverage The number of reads with unaligned ends at the position. Unaligned ends arise when a read has been locally aligned and the there are mismatches or gaps relative to the reference sequence at the end of the read. Unaligned regions do not contribute to coverage in other graph track types.
- Non-perfect read coverage The number of reads at the position with one or more mismatches or gaps relative to the reference sequence.
- Paired read coverage The number of intact read pairs mapped to the position. Coverage is counted as one in positions where the reads of a pair overlap.
- Paired read specific coverage The number of intact paired reads that map uniquely at the position, i.e. they do not map equally well to other places in the reference sequence.
- Paired end distance The average distance between the forward and reverse reads of pairs mapped to the position.
- Broken pair coverage The number of broken paired reads mapped to the position. A pair is marked as broken if only one read in the pair matches the reference, if the reads map to different chromosomes, or if the distance or relative orientation between the reads is not within the expected values.
- Reads start coverage The number of reads with their start mapped to the position.
- Forward read coverage The number of reads mapping in forward direction. First and second read of a pair will be counted separately.
- Reverse read coverage The number of reads mapping in reverse direction. First and second read of a pair will be counted separately.
Click Next, choose where to save the generated output(s) and click on the button labeled Finish.
An example of three different outputs is shown in figure 25.33.
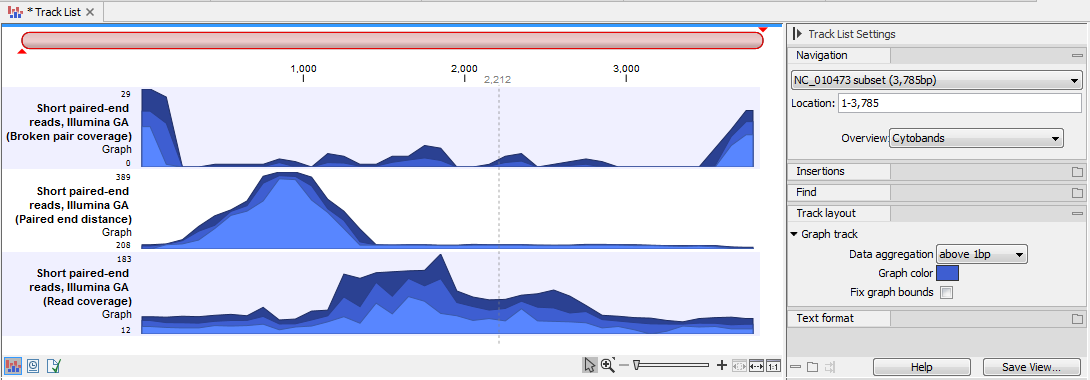
Figure 25.33: Three types of graph tracks are shown.
Note that the option "Fix graph bounds" found under Track layout in the Side Panel is useful to manually adjust the numbers on the y-axis.
When zoomed out, the graph tracks are composed of three curves showing the maximum, mean, and minimum value observed in a given region (see figure 25.36). When zoomed in all the way down to base resolution only one curve will be shown reflecting the exact observation at each individual position (figure 25.34).
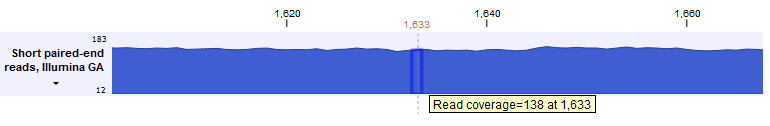
Figure 25.34: A graph track zoomed in.
