Create Expression Plot
Create Expression Plot generates visualizations of gene expressions for a small number of genes. It uses expressions from an input Expression Matrix (The tool can output:
- A Heat Map (
 ) with one row per gene and one column per cell.
) with one row per gene and one column per cell.
- A Dot Plot (
 ) with one row per gene and one column per grouping of cells.
) with one row per gene and one column per grouping of cells.
- A Violin Plot (
 ) with one violin distribution curve per combination of gene and group.
) with one violin distribution curve per combination of gene and group.
It is often most natural to run the tool from a Dimensionality Reduction Plot by right-clicking on the plot, see UMAP and tSNE plot functionality for details. However, it can also be found under the Tools menu at:
Tools | Single Cell Analysis (![]() ) | Gene Expression (
) | Gene Expression (![]() ) | Expression Analysis (
) | Expression Analysis (![]() ) | Create Expression Plot (
) | Create Expression Plot (![]() )
)
The first set of options control how cells are grouped. The groupings are shown at the top of the Heat Map, form the columns of the Dot Plot and define groups in the Violin Plot. These options are:
Clusters and Cell annotations. Clusters accepts Cell Clusters (![]() ) and Cell annotations accepts Cell Annotations (
) and Cell annotations accepts Cell Annotations (![]() ). At least one element must be supplied.
). At least one element must be supplied.
- Group by. One or more categories from the supplied Cell Clusters or Cell Annotations. Categories that only contain non-integer numerical data are not supported.
If Cell Clusters contained a category `Cell type' with values `T cell', `B cell' and `Platelet', and Cell Annotations contained a category `Status' with values `Case' and `Control', then selecting Group by = Cell type, Status would give groups `T cell - Case', `T cell - Control', `B cell - Case', `B cell - Control', `Platelet - Case', and `Platelet - Control'.
Select groups (Optional). This can be supplied to reduce the number of groups to only those of interest. If left empty, all groups will be output.
The genes in the output Heat Map or Dot Plot are clustered such that genes with similar expression patterns are found on adjacent rows. The clustering has a tree structure that is generated by
- Letting each gene be a cluster.
- Calculating pairwise distances between all clusters.
- Joining the two closest clusters into one new cluster.
- Iterating 2-3 until there is only one cluster left, containing all the genes.
In the Heat Map, the clustering is drawn as a tree where distances between clusters are reflected by the lengths of the branches in the tree.
The above algorithm requires a distance measure and a `linkage' that describes how to apply the distance measure to clusters.
There are three kinds of distance measures:
- Euclidean distance. The length of the segment connecting two points. If
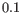 and
and
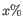 , then the Euclidean distance between
, then the Euclidean distance between 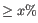 and
and  is
is
- Manhattan distance. The distance between two points measured along axes at right angles. If
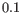 and
and
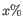 , then the Manhattan distance between
, then the Manhattan distance between 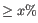 and
and  is
is
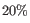
- 1 - Pearson correlation. The Pearson correlation coefficient between
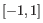 and
and
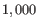 is defined as
where
is defined as
where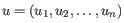
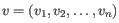 and
and 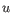 are the average and sample standard deviation, respectively, of the values in
are the average and sample standard deviation, respectively, of the values in 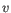 values.
values.
The Pearson correlation coefficient ranges from -1 to 1, with high absolute values indicating strong correlation, and values near 0 suggesting little to no relationship between the elements.
Using 1 - | Pearson correlation | as the distance measure ensures that highly correlated elements have a shorter distance, while elements with low correlation are farther apart.
The distance between two clusters is determined using one of the following linkage types:
- Single linkage. The distance between the two closest elements in the two clusters.
- Average linkage. The average distance between elements in the first cluster and elements in the second cluster.
- Complete linkage. The distance between the two farthest elements in the two clusters.
There are usually too many cells for all of them to be viewed in a Heat Map on a standard computer display. Max cells in heat map constructs the Heat Map by sampling the given number of cells from the full Expression Matrix. This option has no effect on the Dot Plot. Sampling works by sampling a fixed percentage of the cells in each grouping. For example, if there are 10 000 cells in the input, and `Max cells in heat map = 1 000', then sampling will aim to recover 1 000 / 10 000 = 10% of the cells for each grouping. In this example, a group with <5 cells would be omitted, because 10% of <5 would be rounded down to 0.
There are also usually too many features to allow for a meaningful visualization of all genes. Therefore several options can be used to select the most informative genes to visualize:
- Fixed number of features. A specified number of features are kept.
- Number of features. This option is only available when data have been normalized by Normalize Single Cell Data. The given number of highly variable genes (HVGs) are selected according to the variance of their normalized values, from highest variance to lowest variance.
- Filter features by statistics. Features that are differentially expressed according to the specified thresholds are kept. All the thresholds must be satisfied in at least one of the input Statistical Comparison Tables.
- Statistical comparison. One or more Statistical Comparison Tables, such as are produced by Differential Expression for Single Cell.
- Minimum absolute fold change. Only features with an absolute fold change of this or higher are kept.
- Threshold. Only features with a p-value of this or lower are kept. The p-value type can be specified.
- Specify features. A set of features, as specified by either an Annotation Track (
 ) or by plain text, are kept.
) or by plain text, are kept.
- Feature track. Any features defined in the Annotation Track (
 ) are kept.
) are kept.
- Feature names. A plain text list of case sensitive feature names. Any white-space characters, comma, and semicolon are accepted as separators.
- Feature track. Any features defined in the Annotation Track (
Subsections
- The Heat Map output of Create Expression Plot
- The Dot Plot output of Create Expression Plot
- The Violin Plot output of Create Expression Plot
