Cell Clonotypes tables
The Cell Clonotypes elements contain two table views, centered around the clonotypes (Both views contain the following information (see figure 13.8):
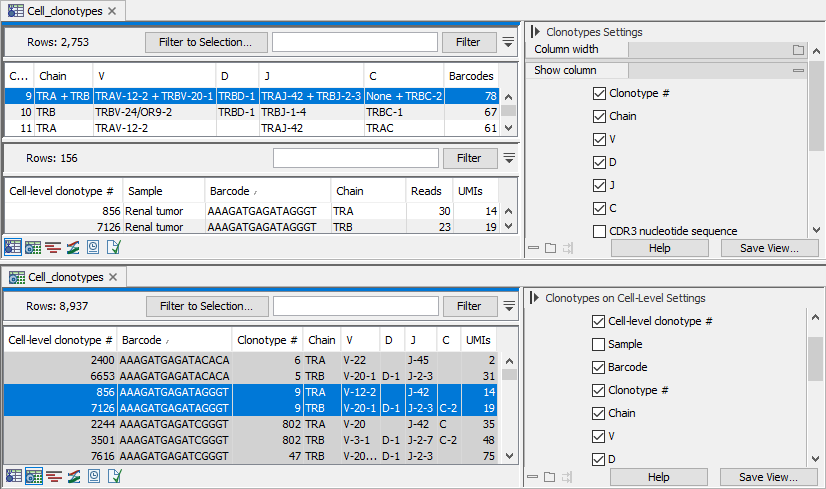
Figure 13.8: Views of the same TCR Cell Clonotypes element. Note that not all table columns are shown. Clonotype with number 9 is highlighted in both views. Top: View centered around the identified clonotypes, sorted after the number of barcodes. All identified chains for the clonotype are shown. For example, clonotype 9 contains both a TRA and TRB chain, while clonotypes 10 and 11 contain only a TRB and TRA chain, respectively. When a clonotype is selected, a second table lists the barcodes with the corresponding clonotype. Bottom: View centered around the barcodes, sorted by barcode. Rows with the same barcode have the same background color when the table is sorted after the barcode.
- Clonotype #. A unique number identifying the clonotype.
- Chain: Which chain the clonotype belongs to. Can be:
- For TCR Cell Clonotypes: TRA, TRB, TRA + TRB, TRG, TRD, and TRG + TRD;
- For BCR Cell Clonotypes: IGH, IGK, IGL, IGH + IGK, and IGH + IGL.
- V / D / J / C. The identified V, D, J and C reference segment(s), respectively. If a single unambiguous segment cannot be identified, the segments are separated by a comma.
- CDR3 nucleotide sequence. The nucleotide sequence for CDR3 including the V- and J region-encoded conserved motifs.
- CDR3 amino acid sequence. The translated amino acid sequence for the CDR3 nucleotide sequence, provided that it is in-frame.
- CDR3 length. The length of the CDR3 nucleotide sequence.
- Productive. One of three categories are used to characterize the CDR3 nucleotide sequence:
- Productive. Sequences that are in frame and do not contain a premature stop codon.
- Out-of-frame. Sequences that have a length that is not a multiple of three.
- Premature stop codon. Sequences that contain an in-frame premature stop codon.
Note that the Filter Cell Clonotypes can be used for retaining only the productive clonotypes, see Filter Cell Clonotypes for details.
The view centered around the identified clonotypes (![]() ) additionally contains:
) additionally contains:
- Barcodes. The number of barcodes with the given clonotype.
- Primary (%). The percentage of clonotypes that were the primary clonotype for their respective barcode, see Primary and secondary clonotypes.
Clicking on a row in this view opens a new table listing the corresponding barcodes (see figure 13.8).
The cell-level clonotypes view (![]() ) also provides (see figure 13.8):
) also provides (see figure 13.8):
- Cell-level clonotype #. A unique number identifying the barcode and clonotype.
- Sample / Barcode. The sample and barcode.
- Reads. The number of reads from the barcode that mapped to the contig from which the specific CDR3 sequence was detected.
- UMIs. The number of unique UMIs the aligned reads correspond to.
- Copy rank. Primary, Secondary or Subsequent, see Primary and secondary clonotypes.
To create a new element from a row selection in the table, use the Create Clonotypes from Selection option in the right-click menu.
