Extract sequences
This tool allows the extraction of sequences from other types of data in the Workbench, such as sequence lists or alignments. The data types you can extract sequences from are:
- Alignments (
 )
)
- BLAST result (
 )
)
- BLAST overview tables (
 )
)
- sequence lists (
 )
)
- Contigs and read mappings (
 )
)
- Read mapping tables (
 )
)
- Read mapping tracks (
 )
)
- RNA-Seq mapping results (
 )
)
Note! When the Extract Sequences tool is run via the Workbench toolbox on an entire file of one of the above types, all sequences are extracted from the data used as input. If only a subset of the sequences is desired, for example, the reads from just a small area of a mapping, or the sequences for only a few blast results, then a data set containing just this subsection or subset should be created and the Extract Sequences tool should be run on that.
For extracting a subset of a mapping, please see Extract parts of a mapping that describes the function "Extract from Selection" that also can be selected from the right click menu (see figure 14.3).
For extracting a subset of a sequence list, you can highlight the sequences of interest in the table view of the sequence list, right click on the selection and launch the Extract Sequences tool.
The Extract Sequences tool can be launched via the Toolbox menu, by going to:
Toolbox | Classical Sequence Analysis (![]() ) | General Sequence Analysis (
) | General Sequence Analysis (![]() )| Extract Sequences (
)| Extract Sequences (![]() )
)
Alternatively, on all the data types listed above except sequence lists, the option to run this tool appears by right clicking in the relevant area; a row in a table or in the read area of mapping data. An example is shown in figure 14.3.
Please note that for mappings, only the read sequences are extracted. Reference and consensus sequences are not extracted using this tool. Similarly, when extracting sequences from BLAST results, the sequence hits are extracted, not the original query sequence or a consensus sequence.
"Note also, that paired reads will be extracted in accordance with the read group settings, which is specified during the original import of the reads. If the orientation has since been changed (e.g. using the Element Info tab for the sequence list) the read group information will be modified and reads will be extracted as specified by the modified read group. The default read group orientation is forward-reverse."
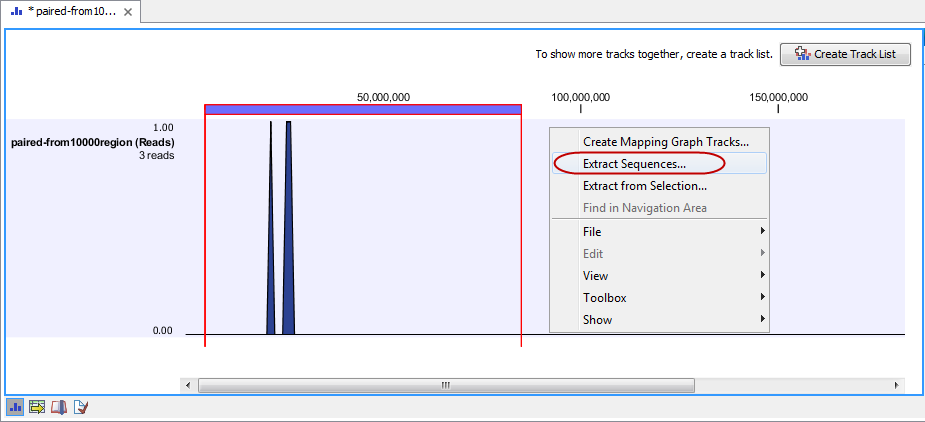
Figure 14.3: Right click somewhere in the reads track area and select "Extract Sequences".
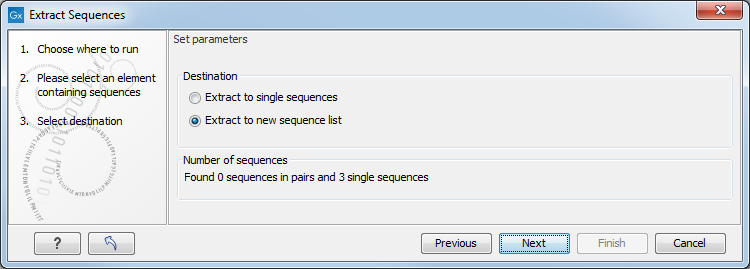
Figure 14.4: Choosing whether the extracted sequences should be placed in a new list or as single sequences.
The dialog allows you to select the Destination. Here you can choose whether the extracted sequences should be extracted as single sequences or placed in a new sequence list. For most data types, it will make most sense to choose to extract the sequences into a sequence list. The exception to this is when working with a sequence list, where choosing to extract to a sequence list would create a copy of the same sequence list. In this case, the other option would generally be chosen. This would then result in the generation of individual sequence objects for each sequence in the sequence list.
Below these options, in the dialog, you can see the number of sequences that will be extracted.
