Taxonomic Profiling
The Taxonomic Profiling tool is designed to determine which known organisms are in a whole shotgun metagenomic sample, and how abundant they are. To this end, the tool will map each input read to a reference database of complete genomes. If a host organism genome is provided, the mapping phase will disregard reads that it deems to have originated from the host. Paired reads that cannot map as an intact pair to the reference database will also be dismissed. If a read is found to map to the reference database, it will be assigned to the lowest common ancestor of all mapping positions with the highest mapping score. After the mapping phase, the tool performs qualification and quantification of the abundance of each qualified taxon, and finally compiles the results into an abundance table.
The purpose of the qualification phase is to determine whether a particular taxon is represented in a sample. The qualification is based on a confidence score that a reference did not receive its reads by pure chance. Any taxon with a confidence score < 0.995 will be ignored and the reads assigned to it will be reassigned to its closest qualified ancestor. By construction the confidence score is very close to 1.0 except on the Kingdom level of the taxonomy, thus it is not reported.
The purpose of the quantification phase is to estimate how abundant the qualified taxa are. It is based on the number of reads assigned to that taxon. For data sets with varying read length, the abundance values may optionally be adjusted to correct for a skewed read distribution between taxa (see below).
The detection limit of the tool is now controlled by the single read mapping parameter "Minimum seed length". Increasing this value will give higher precision in the taxa called (true positives), while lowering it will give more taxa called at the cost of precision (more false positives).
To run the Taxonomic Profiling tool, go to
Metagenomics (![]() ) | Taxonomic Analysis (
) | Taxonomic Analysis (![]() ) | Taxonomic Profiling (
) | Taxonomic Profiling (![]() ).
).
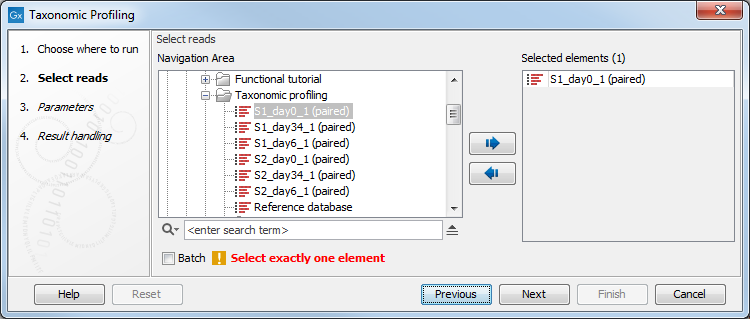
You can select only one read file to analyze (figure 6.6). If the sample to be analyzed is split up into several files, the files need to be merged with the Create Sequence List tool before running the Taxonomic Profiling tool.
In the "Parameters" dialog, provide the reference database you will use to map the reads (figure 6.7). It is also possible to "Filter host reads". You must then specify the host genome (for example Homo sapiens GRCh38 in the case of human microbiota). The reference database can be obtained by using the Download Curated Microbial Reference Database tool (Download Curated Microbial Reference Database) or Download Custom Microbial Reference Database tool (Download Custom Microbial Reference Database). The host index and (if using the custom downloader) the microbial reference index are built with the Create Taxonomic Profiling Index tool (Create Taxonomic Profiling Index).
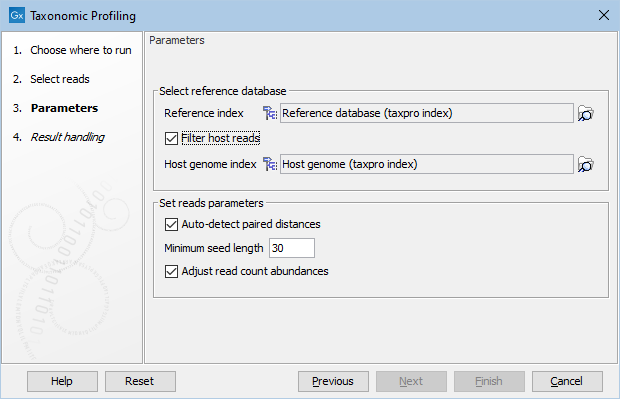
Figure 6.7: Set the parameters for taxonomic profiling.
The read mapping parameters used in the taxonomic profiler are the standard read mapping parameters (see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Mapping_parameters.html) except for the Minimum seed length, which may be specified explicitly here. The Minimum seed length defines the minimum seed (word) size, i.e., perfect match-length, for a position in the reference to be considered a valid candidate when matching the read. If no seed longer than this length can be found in the database, the read is considered "unmapped". Increasing the Minimum seed length will giver higher precision in the results, while lowering it will give a higher recall rate but with more possible false positives.
The option "Auto-detect paired distances" will generate an estimate of the paired distance range in an additional section of the report output by the tool and the estimated distances are used in the qualification phase, i.e. both reads of a read pair are required to map to the same reference sequence within the estimated distance to be assigned to the corresponding taxon.
When enabled, the option "Adjust read count abundances" will weight the reads assigned to a taxon by the number of nucleotides mapped to that taxon, otherwise raw read counts are reported. Specifically, the adjusted abundance is calculated as
Adjusted abundance = (abundance in nucleotides) / (average mapped read length),
where the denominator is the average length of all mapped reads. For data sets where all reads have similar length, the adjusted abundance is very similar to the read count assigned to a taxon. Note that occasionally, this weighting may lead to zero reads assigned to a qualified taxon if there are only few, shorter than average reads assigned to this taxon.
In the last dialog, choose from the different output options and Open or Save the results (figure 6.8).
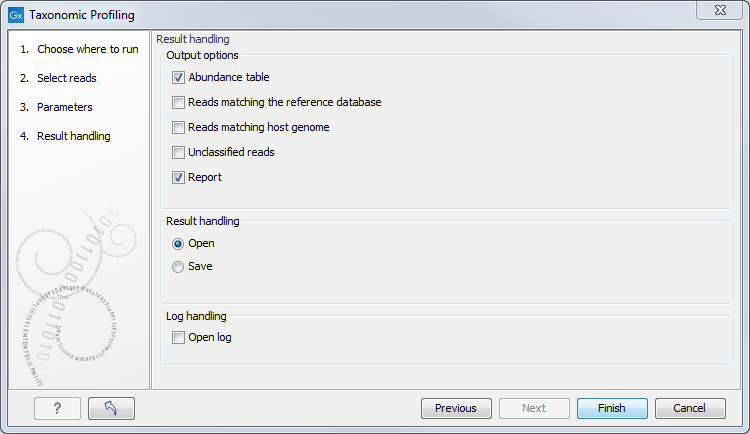
Figure 6.8: Tool output options.
The tool will generate by default an abundance table as well as a report with a list of the taxa and their abundances. You can choose to output additional files such as a sequence list of the reads matching the reference database and those matching the host, as well as the unclassified reads.
Subsections