Bin Pangenomes by Taxonomy
This tool assigns contigs and the reads they are composed of into bins with other contigs presumably of closely related taxonomy. For this we use a microbial reference (genome) sequence database, which comprises sequences with taxonomic information. Furthermore, in order to separate contigs that originate from plasmids from those of genomic origin, the Bin Pangenomes by Taxonomy tool additionally takes a plasmid database as input.
Binning occurs in 5 consecutive steps:
- Obtain taxonomic information for reads
- Obtain plasmid information for reads
- Map reads to contigs
- Assign taxonomic and plasmid labels to contigs
- Group and filter contigs according to labels (Contig purity)
To start the tool, go to:
Metagenomics (![]() ) | Taxonomic Analysis (
) | Taxonomic Analysis (![]() ) | Bin Pangenomes by Taxonomy (
) | Bin Pangenomes by Taxonomy (![]() )
)
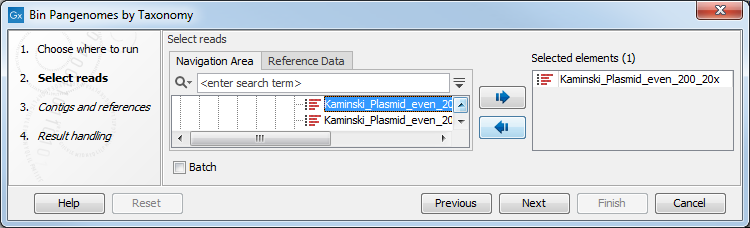
The Bin Pangenomes by Taxonomy takes one or several single or paired-end read files as input (figure 6.1).
The tool is designed to work on contigs assembled from the same set of reads used as input, previously assembled using the De Novo Assembly Metagenome tool (as in the workflow, see QC, Assemble and Bin Pangenomes). You can also specify here the minimum contig length desired (figure 6.2).
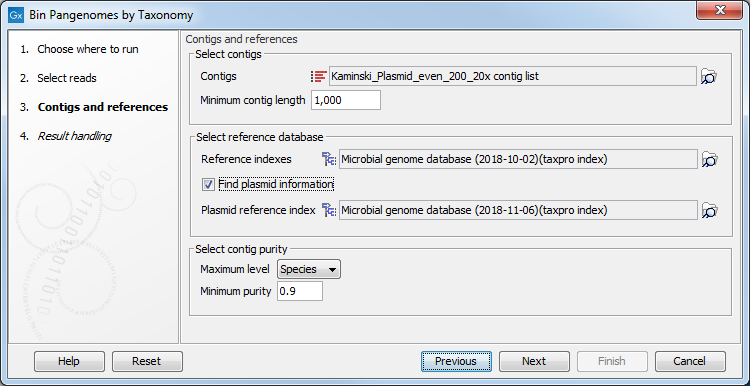
Figure 6.2: Select the references and specify the parameters needed for running the tool.
As reference databases, one or two Taxonomic Profiling index files can be provided:
- the file provided as "Reference indexes" is used to find taxonomic information for the reads
- the file provided as "Plasmid reference index" (once the "Find plasmid information option is checked) is used to distinguish genomic reads from plasmid reads.
Both references can be obtained by using the Download Curated Microbial Reference Database tool (Download Curated Microbial Reference Database) or Download Custom Microbial Reference Database tool (Download Custom Microbial Reference Database). If using the latter, the indexes can be built with the Create Taxonomic Profiling Index tool (Create Taxonomic Profiling Index).
Depending on the dataset, it may be necessary to adapt the contig purity settings, where "Maximum level" refers to a maximum level in the taxonomic tree and where a specific "Minimum purity" per contig needs to be reached in order for it to be considered a part of a bin. For example, if Maximum level = Genus and Minimum purity = 0.8 and 512 reads map to a given contig, at least 0.8 * 512 = 410 reads need to have the same Genus level taxonomy in order for the contig to become part of the respective bin. If more precise taxonomic information is available (e.g., on Species level) with the requested minimum purity, this information will be used instead.
The "Result handling" dialog allows you to specify the tool's outputs (figure 6.3):
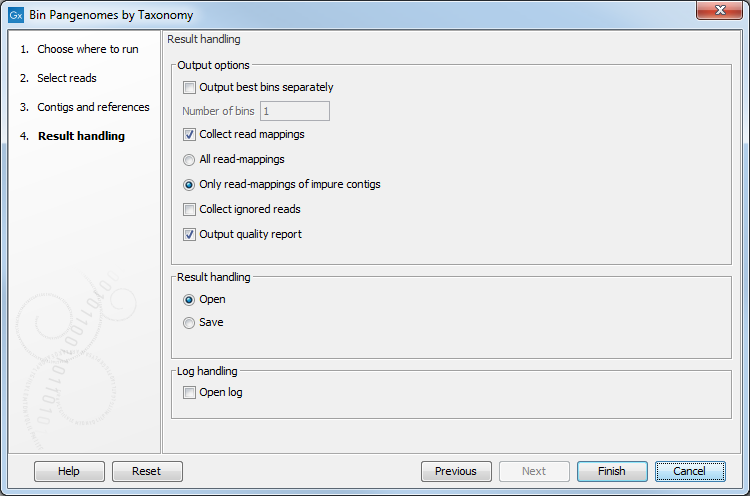
Figure 6.3: Specify the outputs needed.
- Choose to output a certain number of the best bins separately, which means that a chosen number of bins will be written to separate outputs. In this context, "best" is defined by completeness, estimated as the number of contig nucleotides in bin divided by the number of nucleotides in the assigned reference genome.
- Specify whether to collect the read mappings and which kind (all, only impure contigs)
- Collect ignored reads (i.e., reads not mapping to contigs)
- Output a quality report for the bins, where bins are ordered in order of completeness (see above).
The standard output of the Bin Pangenomes by Taxonomy tool consists of a list of (binned) contigs and one sequence list per input reads file (or two for paired reads) where each of the sequences is labeled according to its most probable origin and bin it ended up in (the bin annotation is stored as "Assembly ID" annotation in order for it to work seamlessly with other tools). Also, a column called "isPlasmid" provides a true/false label whether the contig/read was mapped respectively to a plasmid or a genome. The tool can also output a Taxonomy binning report.