Import PICRUSt2 Multiplication Table
The Import PICRUSt2 Multiplication Table (beta) tool can be used to import multiplication tables from PICRUSt2 [Douglas et al., 2020] in order to perform functional inference for OTU abundance tables using Infer Functional Profile (beta) or to normalize OTU abundance tables by rRNA copy numbers using Normalize OTU Table by Copy Number (beta).
Before running the tool it is necessary to download the relevant data files from the PICRUSt2 github repository (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/tree/master/picrust2/default_files), specifically three kinds of files are required:
- Files with 16S, 18S or ITS sequence alignments
- 16S alignments or prokaryotes (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/prokaryotic/pro_ref/pro_ref.fna)
- 18S alignments for fungi (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/fungi/fungi_18S/fungi_18S.fna.gz)
- ITS alignments for fungi (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/fungi/fungi_ITS/fungi_ITS.fna.gz)
- Files with rRNA copy numbers
- 16S rRNA copy numbers for prokaryotes (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/prokaryotic/16S.txt.gz)
- 18S rRNA copy numbers for fungi (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/fungi/18S_counts.txt.gz)
- ITS rRNA copy numbers for fungi (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/fungi/ITS_counts.txt.gz)
- Files with functional term counts associated with each type of rRNA
- EC terms associated with 16S regions in prokaryotes (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/prokaryotic/ec.txt.gz)
- Kegg orthology terms associated with 16S regions in prokaryotes (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/prokaryotic/ko.txt.gz)
- COG terms associated with 16S regions in prokaryotes (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/prokaryotic/cog.txt.gz)
- Pfam domains associated with 16S regions in prokaryotes (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/prokaryotic/pfam.txt.gz)
- TIGRFAM terms associated with 16S regions in prokaryotes (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/prokaryotic/tigrfam.txt.gz)
- EC terms associated with 18S regions in fungi (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/fungi/ec_18S_counts.txt.gz)
- EC terms associated with ITS regions in fungi (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2/blob/master/picrust2/default_files/fungi/ec_ITS_counts.txt.gz)
Only files corresponding to the same rRNA regions can be combined to obtain a valid PICRUSt2 Multiplication Table, e.g. 16S alignments for prokaryotes, 16S rRNA counts and COG terms associated with 16S regions in prokaryotes.
Note that the rRNA copy numbers for fungi 2 are not consistent for 18S and ITS regions, which may have implications for the normalization and thus also for the functional inference for fungal data.
The tool can import similarly prepared data if other data sources are available. The OTU sequences need not be aligned.
To run the tool, go to:
Databases (![]() ) | Functional Analysis (
) | Functional Analysis (![]() ) | Import PICRUSt2 Multiplication Table (beta) (
) | Import PICRUSt2 Multiplication Table (beta) (![]() )
)
In the tool dialog (figure 19.9), select which type of rRNA and which type of terms you would like to import, then select the corresponding three files downloaded above where
- File with aligned rRNA sequences: takes fasta files as input, e.g. one of the files listed under point 1.
- File with rRNA copy numbers: takes a tab separated text file with two columns as input, where the first column contains the name of an rRNA sequence from the fasta file and the second column the corresponding rRNA copy number, e.g. one of the files listed under point 2 or a fasta file with unaligned rRNA sequences. The file is expected to contain a header.
- File with functional counts: takes a tab separated text file as input. The first column contains the name of an rRNA sequence from the fasta file and the remaining columns contain the corresponding functional counts, where each column is identified with a functional term via the header line, e.g. one of the files listed under point 3.
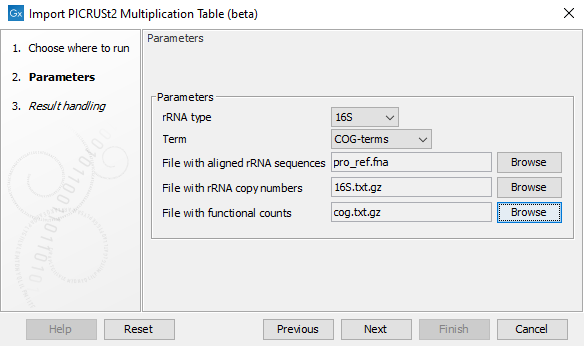
Figure 19.9: The Import PICRUSt2 Multiplication Table (beta) tool options.
After import the data in the multiplication table is displayed in a table (figure 19.10) where the name of the rRNA is given under the "Assembly" column, as these tables are typically derived from assemblies with known rRNA content, taxonomy and functional counts. The following four columns list the rRNA copy numbers registered for each type of rRNA, ITS regions will be listed as the selected rRNA type, e.g. 18S or 28S and the number of distinct funtional terms registered for that assembly in the column "Number of terms".
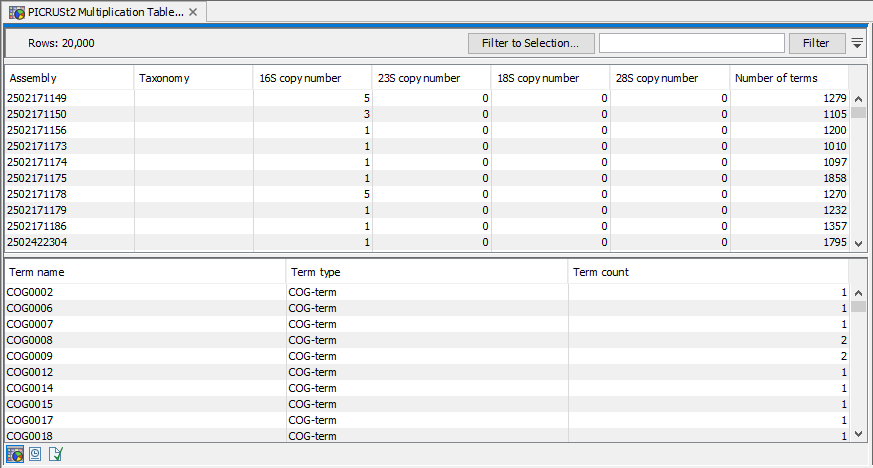
Figure 19.10: The PICRUSt2 Multiplication Table visualization.
When selecting one or several rows in the upper table, the lower table will show the combined functional counts for the selected row for each of the functional terms individually.
