Download Large MLST Scheme
To run the Download Large MLST Scheme tool choose:
Microbial Genomics Module (![]() ) | Databases (
) | Databases (![]() ) | Large MLST (
) | Large MLST (![]() ) | Download Large MLST Scheme (
) | Download Large MLST Scheme (![]() )
)
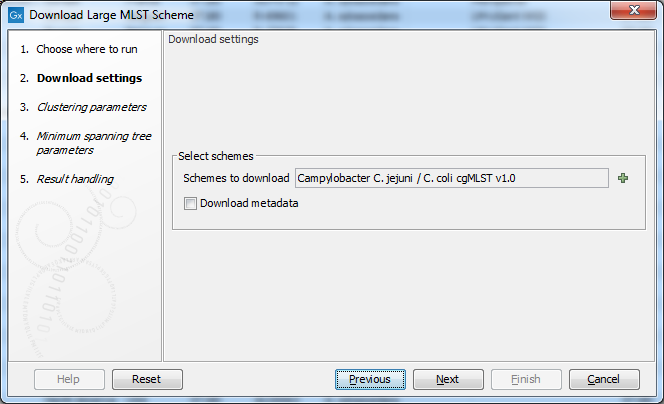
Figure 16.5: The Download Large MLST Scheme settings.
Use the Schemes to download selector (figure 16.6) to choose which schemes to download from PubMLST.
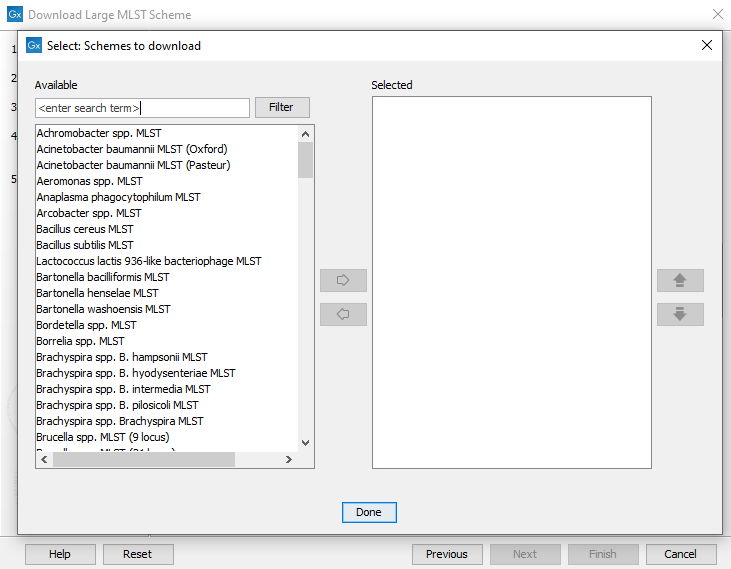
Figure 16.6: The schemes available for download.
Most of the schemes offered for download by PubMLST are classic (7-gene) schemes, but there are also core genome schemes available for several species, e.g.: Salmonella spp., N. gonorrhoeae, N. Meningitis, C. Jejuni / C. Coli, C. trachomatis, Vibrio cholerae, Listeria monocytogenes.
Some of the schemes offered by PubMLST may only contain allele and locus definitions and no sequence types.
The Download metadata option makes it possible to download and extract metadata for all of the isolates for a given species in PubMLST. Note that this is a potentially very slow operation.
The clustering parameters determine how the heatmap should be clustered (figure 16.7). The heatmap cellvalues are the observed frequencies of a given allele compared to the other alleles in the same locus.The possible cluster linkages are:
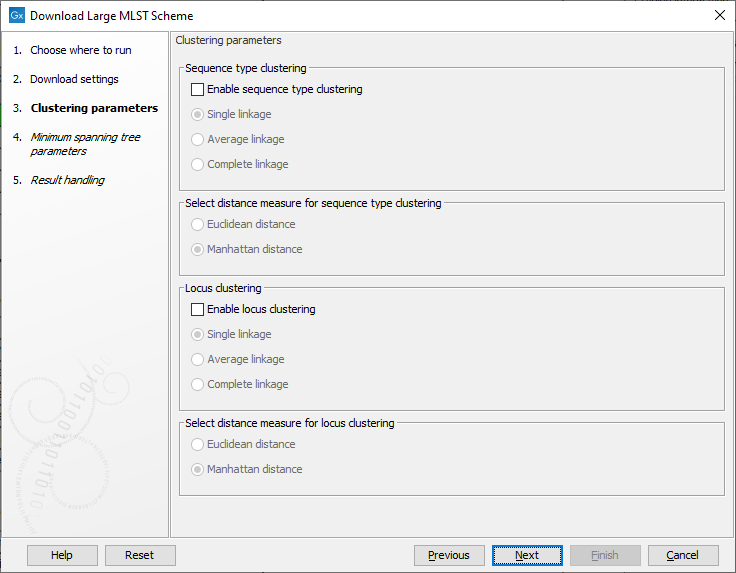
Figure 16.7: The clustering parameters.
- Single linkage: the distance between two clusters is computed as the distance between the two closest elements in the two clusters.
- Average linkage: The distance between two clusters is computed as the average distance between objects from the first cluster and objects from the second cluster.
- Complete linkage: The distance between two clusters is computed as the distance between the two farthest objects in the two clusters.
- Euclidean distance: the square-root of the sum-of-square differences between coordinates.
- Manhattan distance: the sum of absolute differences between coordinates.
The following options are available when creating a minimum spanning tree (figure 16.8):
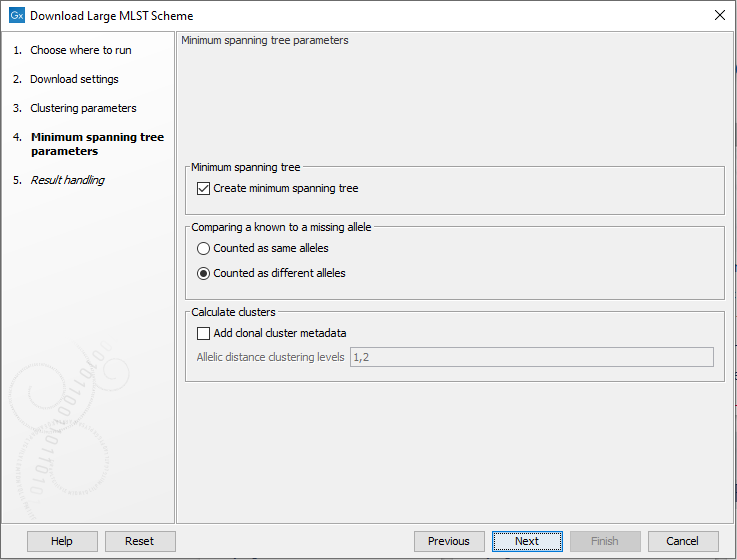
Figure 16.8: The minimum spanning tree parameters.
- Comparing a known to a missing allele: the minimum spanning tree is created using a distance matrix, where the distance is calculated between all pairs of sequence types. The distance is calculated as the number of loci where the allele assignment differs. But in some cases, a locus for a sequence type may not have an assigned allele (for instance, for the accessory genes in a wgMLST scheme). If this is the case, the behavior depends on this setting: if 'counted as same alleles' is selected, a locus where at least one allele is missing for the pair being compared will be ignored (it will not count as a difference). On the other hand, if 'Counted as different alleles' is selected, a missing allele being compared to a known allele will increase the distance between the sequence types being compared.
- Add clonal cluster metadata: it is possible to assign cluster information to the scheme which will show up as metadata. The clustering is based on the minimum spanning tree, and will be similar to the clustering obtained by using the 'collapse branches' slider in the minimum spanning tree view - that is, the clustering will be single-linkage clustering - i.e. all nodes in cluster are within the specified threshold to at least one other node in the cluster. Each cluster will get a name chosen from the sequence type in the cluster with most connections.
- Add clonal cluster metadata: specifies the level at which the clustering will be performed. It is possible to specify multiple, comma-separated values. E.g. '100,200' will assign clusters at allelic distances of 100 and 200 - this will create two new metadata columns, cc_100 and cc_200 with the new cluster information.
