Find Resistance with Nucleotide DB
Identification of antimicrobial resistance genes is important for understanding the underlying mechanisms and the epidemiology of antimicrobial resistance. The Find Resistance with Nucleotide DB tool may be used for resistance typing of pre-assembled, complete or partial genomes simple contig sequences assembled using the de novo assembly algorithm of CLC Genomics Workbench (see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=De_novo_assembly.html).
Alternatively, use the Type a Known Species or Type among Multiple Species template workflows as described in Workflow templates.
The Find Resistance with Nucleotide DB tool is inspired by [Zankari et al., 2017] and uses BLAST for identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes within whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data. The tool's aim is to quantify the occurrence of entire resistance conferring genes, whether they break down (e.g. beta-lactamases) or expel (e.g. efflux-pumps) antibiotic compounds.
To perform resistance typing, go to:
Drug Resistance Analysis (![]() ) | Find Resistance with Nucleotide DB (
) | Find Resistance with Nucleotide DB (![]() )
)
Select the input genome or contigs (figure 15.4).
Figure 15.4: Pre-assembled and complete- or partial genomes simple contig sequences may be used as input for resistance typing.
You can then specify the settings for the tool (figure 15.5).
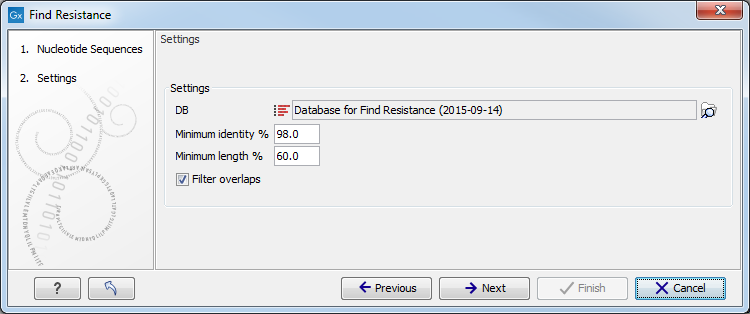
Figure 15.5: Select database and settings for resistance typing.
- DB Select the downloaded database for Find Resistance with Nucleotide DB (using the Download Resistance Database tool (see the Download Resistance Database section).
- Minimum Identity % is the threshold for the minimum percentage of nucleotides that are identical between the best matching resistance gene in the database and the corresponding sequence in the genome.
- Minimum Length % reflect the percentage of the total resistance gene length that a sequence must overlap a resistance gene to count as a hit for that gene. Here represented as a percentage of the total resistance gene length.
- Filter overlaps: will perform extra filtering of results per contig, where one hit is contained by the other with a preference for the hit with the higher number of aligned nucleotides (length * identity).
The output of the Find Resistance with Nucleotide DB tool is a table listing all the possible resistance genes and predicted phenotypes found in the input genome or contigs, as well as additional information such as degrees of similarity between the gene found in the genome and the reference (% identity and query /HSB values) and the location where the gene was found (contig name, and position in the contig). Depending on the type of database used, additional columns with link to resources may also be present in the table. To add the obtained resistance types to your Result Metadata Table, see the section Add to Result Metadata Table.
