Expression Analysis from Reads
The workflow Expression Analysis from Reads takes Reads as input and starts by annotating them with cell barcode and UMI, followed by trimming and mapping to create one or more Expression Matrices (- a single, multi-sample, normalized Expression Matrix (
 );
);
- a Dimensionality Reduction Plot (
 ) associated with the automated clusters, predicted cell types and additional cell annotations;
) associated with the automated clusters, predicted cell types and additional cell annotations;
- a Heat Map (
 ), a Dot Plot (
), a Dot Plot ( ), and a Violin Plot (
), and a Violin Plot ( ) with the predicted cell types as cell groups;
) with the predicted cell types as cell groups;
- a Cell Abundance Heat Map (
 ) with the automated clusters and predicted cell types as cell groups.
) with the automated clusters and predicted cell types as cell groups.
The workflow can be found in the toolbox here:
Workflows (![]() ) | From Reads (
) | From Reads (![]() ) | Expression Analysis from Reads (
) | Expression Analysis from Reads (![]() )
)
If you are connected to a CLC Server via your Workbench, you will be asked where you would like to run the analysis. We recommend that you run the analysis on a CLC Server when possible.
You can choose either one or more Sequence lists or Select files for import and select FASTQ files for importing.
The workflow offers a number of options described below. Note that not all parameters can be configured. Open parameters indicate places where customization may be necessary for different samples, but default settings are suitable in most cases.
The workflow can be run using Single Cell hg38 (Ensembl) or Single Cell Mouse (Ensembl) reference data sets (see The Reference Data Manager).
|
Note: Reference data elements cannot be configured during workflow execution. If other elements than those provided in the default reference data sets are needed a custom reference data set can be used, see
https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Custom_Sets.html. When creating custom reference data sets, the chosen gene track needs to match the gene annotations used for training the provided Cell Type Classifier ( |
The workflow allows the analysis of multiple samples and you can specify metadata during workflow execution for configuring which inputs belong to which sample. When there is only FASTQ file per sample, metadata is not necessary and "Use organization of input data" can be used, but metadata can still be useful, as it is converted to cell annotations and can be used for coloring the cells in the Dimensionality Reduction Plot. For more details on configuring workflow execution with metadata, see https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Batching_part_workflow.html. Make sure to inspect the batch overview to check that the analysis will be performed correctly.
Examples for how to use metadata for workflow execution can be found in Configuring the batch units.
It is important to select the proper read structure for annotating the reads with cell barcode and UMI. If the data has not been prepared using one of the predefined protocols, a custom read structure can be specified as detailed in Annotate Reads with Cell and UMI, where a list of many different single cell protocols is also linked. However, this requires editing the workflow, see https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Editing_existing_workflows.html for details.
Spike-in controls can be provided, if used during sample preparation. To learn how to import spike-in control files, see http://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Import_RNA_spike_in_controls.html.
The strand specificity and expected coverage bias must be specified. Strand specific "Forward" is most common, though 5' sequencing often requires strand specific "Reverse". For 5' sequencing, we recommend setting coverage bias to "Targeted". If an unsuitable strand specificity or coverage bias is chosen, warnings may be shown in the output RNA-seq report (for details see The Single Cell RNA-Seq Analysis report.)
An option to count intronic reads towards gene expression is also present. This is recommended when many transcripts are expected to be unprocessed, as is the case for single nucleus RNA sequencing.
For quality control a number of options exist. The option to remove empty droplets is not suitable for protocols that do not use droplets, and removing barcodes with low number of reads or expressed features might be more appropriate. Quality Control (QC) uses the number of reads mapped to the mitochondria, and for this the name of the mitochondria chromosome needs to be provided. The default value is often the correct name. After quality control, the matrices are collected and normalized jointly. Note that batch correction is not performed. Read more about QC and normalization in Cell preparation.
For clustering and creation of the Dimensionality Reduction Plot plot, it is possible to restrict analysis to highly variable genes. The data is then projected to a lower dimensional space using PCA. You can read about this feature in Feature selection and PCA.
The expression plots (Heat Map and Dot Plot) and Cell Abundance Heat Map group the cells based on the high confidence predicted cell types ("Cell type (high confidence)"). The Cell Abundance Heat Map additionally groups the cells based on the automated clusters obtained with resolution 1.0 ("Leiden (resolution=1.0)"). Any of these groups can be changed to:
- all predicted cell types ("Cell type (all)");
- automated clusters obtained with a different resolution
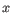 ("Leiden (resolution=
("Leiden (resolution=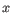 )"). All resolutions
)"). All resolutions
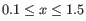 are produced, in steps of
are produced, in steps of 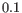 .
.
Subsections
