Somatic variant detection
To call somatic variants, a number of steps are followed.
Firstly, positions of interest that may contain variation due to sequencing errors are identified. Two types of error are considered i) error that is due to the preceding sequenced nucleotides, and ii) error in homopolymer regions, which is typically dependent on how much the sample has been amplified. Empirical error distributions are made from both of these sequencing error types. For example, the probability of seeing a polyA homopolymer of length 18 given that the true length is 20 will be calculated.
Secondly, positions of interest that may contain variation not due to sequencing errors are identified. This identification is subject to user-controllable parameters (see the options under Variant detection and Variant detection general filters, LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants). Groups of adjacent positions of interest form a cluster. Often, such a cluster is just a single position, but it may be arbitrarily long.
For each of these clusters, all overlapping read fragments are reduced to their intersection with the sites of the cluster. These reduced fragments are then used in the further analysis of the cluster.
To identify which underlying haplotypes are present within a given cluster, the pairwise compatibility of the fragments is determined. Once this is known, the largest groups of such pairwise-compatible fragments are formed. Each nonconflicting group is then turned into a haplotype candidate by piecing together the information from the fragments within the group.
At this stage, homopolymer variants are filtered. The filtering is applied when a cluster contains variants that imply at least two homopolymer haplotypes, and where at least one of the homopolymers has length >=5. The filtering removes homopolymer variants that are likely to have arisen by error from the other homopolymers, as determined by the empirical homopolymer error model. If homopolymer variants with lengths
![]() , and counts
, and counts
![]() respectively are present in the sample, then the filtering proceeds as follows:
respectively are present in the sample, then the filtering proceeds as follows:
- Calculate the frequencies of the homopolymers that would maximize the likelihood given the observed counts under the homopolymer model. The likelihood is (up to a normalizing constant):
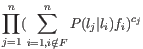
where
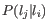 is the probability of observing a homopolymer of length
is the probability of observing a homopolymer of length 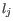 by error when the true length is
by error when the true length is 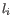 , and
, and 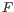 is the set of indexes of homopolymers that have been filtered. The maximum likelihood is found by expectation-maximization.
is the set of indexes of homopolymers that have been filtered. The maximum likelihood is found by expectation-maximization.
- Omit each homopolymer variant in turn, starting with the homopolymer with fewest counts and again calculate the frequencies of the remaining homopolymers that would maximize the likelihood.
- If the Bayesian Information Criterion improves by removing the homopolymer variant, then it is filtered away. The Bayesian Information Criterion embodies our preference for simple explanations of the data by applying a penalty to the maximum likelihood for each unfiltered variant.
Once a list of haplotypes believed to be present in a given region is constructed, each of them needs to be assigned a count. Counts are assigned per-position to the haplotypes. In doing so, the haplotype-based per position counts are compared to the fragment-based per position counts to make sure the cumulative difference for all positions is minimized. This ensures assigning the counts that best reconcile the observed fragments with the underlying haplotypes.
Notes
In contrast to the germline variant caller (Germline variant detection), the somatic variant caller makes no assumptions about the ploidy of a sample, and thus allows for sensitive detection of variant alleles at low frequencies.
A limit of maximum three alleles is enforced for each homopolymer locus and for alleles specifically marked with STR "Yes" that affect the same short tandem repeat. The alleles with the highest read counts are retained. See the description of the STR annotations and filter option under Variant filters in LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants for details about STR annotation.
Variant types
LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants reports SNVs, MNVs and InDels and replacements provided that the variants are contained within at least one paired end read and that their count and frequency satisfies the user-provided minimum requirements.
Variant annotations
Variants identified by LightSpeed Fastq to Somatic Variants are annotated with the following basic information: Chromosome, Region, Type, Reference, Allele, Reference allele, Length, Zygosity, Count, Coverage, Frequency, Forward read count, Reverse read count, Forward read coverage, Reverse read coverage, Forward/reverse balance and Genotype.
Read more about these general variant annotations here: https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcgenomicsworkbench/current/index.php?manual=Variant_tracks.html.
In addition, the following LightSpeed specific annotations are available:
- General annotations:
- Count The number of 'countable' reads supporting the allele. The 'countable' reads are those that are used by the variant detection tool when calling the variant. Which reads are 'countable' depends on the user settings when the variant calling is performed - if e.g. the user has chosen 'Ignore non-specific matches', reads belonging to non-specific read pairs are not 'countable'.
For paired-end sequencing data:
- Reads where R1 and R2 overlap only represent one fragment, and are counted only as one.
- Reads where R1 and R2 disagree do not contribute to the count.
For insertions, unaligned ends that are shorter than the full insertion, but match the insertion sequence, contribute to the count.
- Coverage The fragment coverage at this position. Both reads that support one of the called alleles (reads that are 'countable'), and reads that do not, are included.
For paired-end sequencing data:
- Reads where R1 and R2 overlap only represent one fragment, and are counted only as one when calculating the coverage.
- Reads where R1 and R2 disagree do not contribute to the coverage.
- Average quality The average base quality score of the bases supporting a variant. The average quality score is calculated by adding the Q scores of the nucleotides supporting the variant and dividing this sum by the number of nucleotides supporting the variant. For deletions, the average quality score reported is the lowest average quality of the two bases neighboring the deleted one. For insertions, the average quality is calculated for each of the inserted bases in the reads supporting the insertion, and the minimum of the average base qualities is reported. Average quality is only calculated for non-reference alleles, for reference alleles no average quality is reported.
- p-value - global error rate p-value from binomial test given count and coverage.
- p-value - global error rate (phred scaled) Log transformed p-value - global error rate.
- p-value - local error rate The minimum p-value from two individual tests: 1. A binomial test given forward count, forward coverage and a local error rate for forward reads estimated from the data. 2. A binomial test given reverse count, reverse coverage and a local error rate for reverse reads estimated from the data.
- Average mapping quality The average read mapping quality of specific proper read pairs supporting a variant. Mapping quality represents the confidence in how accurately each read is aligned to its genomic position based on alignment scores. A greater difference between the highest and second-best alignment scores corresponds to higher mapping quality, indicating reduced ambiguity in placement. Additional penalties are applied for reads where both ends are unaligned or where the read contains numerous mismatches to the reference sequence.
- Average mapping quality (incl. non-specific) Average mapping quality calculated from both specific and non-specific reads supporting a variant.
- STR Yes/No annotation. Yes, if the variant meets minimum repeat count, minimum repeat region length and maximum repeat element length specified in the wizard when calling variants. No, if one or more of the thresholds are not met.
- Repeat count The number of repeats excluding the variant. For example if a reference allele "AGAGAGAG" is called, and a low frequent stutter insertion allele is called "AGAGAGAGAG", the repeat unit is 2 and the repeat count is 4.
- Repeat unit length The length of a repeat unit. For example, for the dinucleotide repeat "AGAGAGAG", the repeat unit length is 2.
- Strand balance score 1 - (p-value from binomial test given forward count, count, and forward count/coverage).
- Inferred from unaligned ends Yes/no annotation indicating if the variant is a tandem duplication inferred from unaligned ends during detection of structural variants.
- Subtype Annotation indicating that an insertion is a tandem duplication. This annotation is added to tandem duplications inferred from unaligned ends during detection of structural variants, but also to insertions called by the standard variant caller that perfectly match a tandem duplication called during structural variant detection.
- Count The number of 'countable' reads supporting the allele. The 'countable' reads are those that are used by the variant detection tool when calling the variant. Which reads are 'countable' depends on the user settings when the variant calling is performed - if e.g. the user has chosen 'Ignore non-specific matches', reads belonging to non-specific read pairs are not 'countable'.
- Annotations added to variants that are called from UMI reads:
- Count (singleton UMI) The number of singleton UMI read pairs supporting the allele.
- Count (big UMI) The number of big UMI read pairs supporting the allele.
- Proportion (singleton UMIs) The fraction of singleton UMI read pairs relative to all UMI read pairs supporting the allele.
- Average size (UMIs) Average number of read pairs per UMI.
- Average size (simplex UMIs) Average number of read pairs per UMI for simplex UMI read pairs. The annotation is only added for duplex UMI protocols.
- Count (duplex UMIs) The number of duplex UMI read pairs supporting the allele. The annotation is only added for duplex UMI protocols.
- Average size (duplex UMIs) Average number of read pairs per UMI for duplex UMI read pairs. The annotation is only added for duplex UMI protocols.
Note that for insertions, counts from unaligned ends that are shorter than the full insertion, but matches the insertion sequence, are included in the variant annotations Count, Coverage, Frequency, Count (singleton UMI), Count (big UMI), and Proportion (singleton UMIs). Counts from unaligned ends are not included in Forward read count, Reverse read count, Forward coverage, reverse coverage and Forward/reverse balance.
